 Java
Java javaTutorial
javaTutorial How does Java solve the maze, Tower of Hanoi and Eight Queens problems through recursive algorithms?
How does Java solve the maze, Tower of Hanoi and Eight Queens problems through recursive algorithms?How does Java solve the maze, Tower of Hanoi and Eight Queens problems through recursive algorithms?
1. Important rules of recursion
When executing a method, a new protected independent space (stack space) is created.
The local variables of the method are independent and will not affect each other.
If an application type variable (such as an array, object) is used in the method, the data of the reference type will be shared.
Recursion must approach the conditions for exiting the recursion, otherwise it will be infinite recursion.
When a method completes execution, or encounters return, it will return. The result will be returned to whoever calls it. At the same time, when the method completes execution or returns, the method will also return. The execution is completed.
2. Three cases of recursion
1. Mouse out of the maze

//一个7列8行的迷宫
//分析
//1.我们用一个二维数组来表示迷宫
//2.定义一个findWay方法来找路径,返回值为布尔类型,
//3.若找到路则返回true,否则返回false。
//4.我们用1来表示障碍物
//5.我们初始化老鼠当前坐标(1,1)
//6.用0表示能走,1表示不能走,2表示走过能走,3表示走过但走不通
//7.当map[6][5]=2时则说明找到了出迷宫的路,否则继续找路
//8.我们定义一个试探走的规则,我们假设 下->右->上->左
public class MiGong{
public static void main(String [] args){
//迷宫初始化
int [][] map = new int [8][7];
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
for(int j = 0 ; j < 8; j++){
map[j][0] = 1;
map[j][6] = 1;
}
map[3][1]= 1;
map[3][2]= 1;
for (int k = 0; k < map.length; k++) {
for(int m = 0; m < map[k].length; m++){
System.out.print(map[k][m] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
t way = new t();
way.findWay(map, 1, 1);
System.out.println("=====找到路径后的地图=====");
for (int k = 0 ;k < map.length; k++) {
for(int m = 0;m < map[k].length; m++){
System.out.print(map[k][m] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class t{
public boolean findWay(int [][] map ,int x , int y){
if(map[6][5]==2){//递归出口若终点处的值为2则表明能找到一条路
return true;
}else{
if(map[x][y]==0){//首先若当前位置为0,则表明可以走
map[x][y]=2;//我们假设选这条路可以走通,将当前位置赋为2
//然后按照我们的试探规则依次试探下->右->上->左
if(findWay(map, x+1, y))//递归调用findway函数如果下可以走则返回true
return true;
else if (findWay(map, x, y+1))//否则还继续看右边能不能走
return true;
else if(findWay(map, x-1, y))//上
return true;
else if(findWay(map, x, y-1))//左
return true;
else {
map[x][y]=3;
return false;
}
}else // map[x][y]=1,2,3
return false;
}
}
}2.Hanno Tower
It is said that in ancient Indian temples, there was a game called Hanoi Tower. The game is on a copper plate device with three rods (numbered A, B, C). On rod A, n gold disks are placed in order from bottom to top and from large to small. The goal of the game is to move all the gold disks on pole A to pole C and keep them stacked in the original order. Operating rules: Only one plate can be moved at a time, and during the movement, the large plate is always on the bottom and the small plate is on the top of the three rods. During the operation, the plate can be placed on any of the rods A, B, and C.
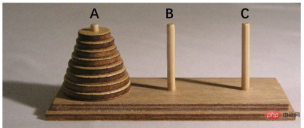
Analysis: For such a problem, it is impossible for anyone to directly write out every step of moving the plate, but we can use the following method to solve it. Suppose the number of moving plates is n. In order to move these n plates from pole A to pole C, the following three steps can be done:
(1) Using plate C as an intermediary, move 1 to n- from pole A Move plate No. 1 to pole B;
(2) Move the remaining nth plate in pole A to pole C;
(3) Use pole A as an intermediary; from pole B The rod moves disks 1 to n-1 to rod C.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HanoiTower{
public static void main(String []args ){
System.out.println("请输入你要移动的盘数:");
tower m = new tower();
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = input.nextInt();
m.moveWay(num,'A','B','C');
}
}
class tower{
//num表示要移动的盘的个数,a,b,c分别表示a塔,b塔,c塔
public void moveWay(int num,char a,char b,char c){
if(num == 1){//如果只有一个盘,直接将其从a移动到c
System.out.println(a + "->" + c);
}
else {//如果有多个盘将最后一个盘以上的盘看成一个整体,借助c,移动到b,然后将最后一个盘移到c
moveWay(num-1, a, c, b);
System.out.println(a + "->" + c);
//然后再将b的所有盘,借助a,移动到c
moveWay(num-1, b, a, c);
}
}
}3. Eight Queens
The problem is expressed as: Place 8 queens on an 8×8-square chess so that they cannot attack each other, that is, no two queens can be in How many ways are there on the same row, column or diagonal?

public class Queen8{
//第一个皇后先放在第一行第一列
//第二个放在第二行第一列,然后判断是否发生冲突
//如果冲突,则继续放第二列,第三列,依次直到找到不发生冲突的位置
//第三个皇后,还是按照第二个一样依次找直到第八个皇后也能放在一个不发生冲突的地方,就算找到一个可行解。
//当得到一个可行解时,回退到上一个栈开始回溯,既可以得到第一个皇后放在第一列的所有可行解
//然后回头继续第一个皇后放在第二列,重复前面的操作
//用一个一维数组来表示皇后放置的位置
//列如arry[1]=3,表示第二个皇后放在第二行第四列
int max = 8;
int [] arry = new int [max];
static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[]args){
Queen8 queen8 = new Queen8();
queen8.locate(0);
System.out.print("摆法一共有:"+ count +"种");
}
// 依次放入皇后,并判断是否冲突
public void locate(int n){
if(n == max){
display();
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < max; i++){
//先把皇后n放到第一列
arry[n] = i;
if(judge(n)){//不冲突则继续放置第n+1个皇后
locate(n+1);
}
//如果冲突则继续往后一列放置
}
}
public boolean judge(int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//arry[i]==arry[n]表示在同一列
//Math.abs(i-n)==Matn.abs(arry[i]-arry[n])表示在同一斜线
if(arry[i] == arry[n] || Math.abs(i - n) == Math.abs(arry[i] - arry[n])){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public void display(){
count++;
for(int i = 0; i < arry.length; i++){
System.out.print(arry[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}The above is the detailed content of How does Java solve the maze, Tower of Hanoi and Eight Queens problems through recursive algorithms?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PM
How do I use Maven or Gradle for advanced Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:46 PMThe article discusses using Maven and Gradle for Java project management, build automation, and dependency resolution, comparing their approaches and optimization strategies.
 How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How do I create and use custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:45 PMThe article discusses creating and using custom Java libraries (JAR files) with proper versioning and dependency management, using tools like Maven and Gradle.
 How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PM
How do I implement multi-level caching in Java applications using libraries like Caffeine or Guava Cache?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:44 PMThe article discusses implementing multi-level caching in Java using Caffeine and Guava Cache to enhance application performance. It covers setup, integration, and performance benefits, along with configuration and eviction policy management best pra
 How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PM
How can I use JPA (Java Persistence API) for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:43 PMThe article discusses using JPA for object-relational mapping with advanced features like caching and lazy loading. It covers setup, entity mapping, and best practices for optimizing performance while highlighting potential pitfalls.[159 characters]
 How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PM
How does Java's classloading mechanism work, including different classloaders and their delegation models?Mar 17, 2025 pm 05:35 PMJava's classloading involves loading, linking, and initializing classes using a hierarchical system with Bootstrap, Extension, and Application classloaders. The parent delegation model ensures core classes are loaded first, affecting custom class loa


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version





