Home >Java >javaTutorial >How to write a three-piece chess game in Java
How to write a three-piece chess game in Java
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-04-22 12:16:081585browse
The game operation is as shown in the figure:

Principle:
Mainly relies on the 3x3 two-dimensional array
Achievement:
1. Main–Main Program
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Player player=new Player();//玩家
Game game=new Game(player);
//一次循环代表一次游戏
while (true){
game.Init();//初始化
game.play();//开始游戏
game.destory();//释放
boolean q=player.queryContinue();
//一局游戏结束后,询问用户是否开始下一局游戏
if (!q){
System.out.println("欢迎下次继续游戏!");
break;
}
}
}
}2.AI–Computer
import java.util.Random;
//返回AI对象的落子位置
//用数组表示 第几行第几列 从0开始
//所以有效范围是[0,2]
public class AI {
private final Random random=new Random();
public int[] getPosition(){
int r=random.nextInt(3);//生成[0,2]的随机整数 0 1 2
int c=random.nextInt(3);
return new int[]{r,c};
}
}3.Player–Player
import java.util.Scanner;
//返回玩家落子位置
//用数组表示 第几行第几列 从0开始
//所以有效范围是[0,2]
public class Player {
private final Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
public int[] getPosition(){
System.out.println("请输入要落子的位置,行列有效取值范围为[0,2]");
System.out.print(">>>");
int r,c;
while (true){
System.out.print(">>>");
r=sc.nextInt();
c=sc.nextInt();
if (r>=0&&r<=2&&c>=0&&c<=2){
break;
}
System.out.println("行列有效范围为[0,2],请重新输入");
}
return new int[]{r,c};
}
//询问用户是否继续下一局
public boolean queryContinue(){
System.out.println("本局游戏结束,开始新游戏请输入true,否则输入false");
System.out.print(">>>");
return sc.nextBoolean();
}
}4. ChessBoard–Chessboard
import java.util.Arrays;
//棋盘 用来实例化对象
//棋盘对象
//功能 1、落子 2、判断棋盘状态
public class ChessBoard {
private static final int empty=0;//空白位置用0表示
private static final int circle=1;//落子为o的位置
private static final int cross=2;//落子为x的位置
private final int[][] array={
{empty,empty,empty},
{empty,empty,empty},
{empty,empty,empty}
};
public boolean moveCircleAt(int row,int column){//落一个o
if (array[row][column]!=empty){ //落子前需要先判断该位置是否为空白
return false;
}
array[row][column]=circle;
return true;
}
public boolean moveCrossAT(int row,int column){//某个位置落个x
if (array[row][column]!=empty){
return false;
}
array[row][column]=cross;
return true;
}
//棋盘的四种状态
public static final int CIRCLE_WIN=0;//执o者赢 //三横三竖两对角成直线
public static final int CROSS_WIN=1;//执x者赢
public static final int DRAW=2;//平局 //没有成直线 但无落子位置了
public static final int CONTINUE=3;//继续
public int getState(){//得到棋盘的状态
//判断行
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
if(array[i][0]==array[i][1]&&array[i][1]==array[i][2]){
if (array[i][0]==circle){
System.out.println("恭喜你赢了!");
return CIRCLE_WIN;
}
else if (array[i][0]==cross){
System.out.println("很遗憾你输了!");
return CROSS_WIN;
}
}
}
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
if (array[0][i]==array[1][i]&&array[1][i]==array[2][i]){
if (array[0][i]==circle){
System.out.println("恭喜你赢了!");
return CIRCLE_WIN;
}
else if(array[0][i]==cross){
System.out.println("很遗憾你输了!");
return CROSS_WIN;
}
}
}
//正负对角线
//正负对角线
if ((array[0][0]==array[1][1]&&array[1][1]==array[2][2])
||(array[0][2]==array[1][1]&&array[1][1]==array[2][0])){
if (array[1][1]==circle){
System.out.println("恭喜你赢了!");
return CIRCLE_WIN;
}
else if (array[1][1]==cross){
System.out.println("很遗憾你输了!");
return CROSS_WIN;
}
}
//无获胜
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
for (int j=0;j<3;j++){
if (array[i][j]==empty){
return CONTINUE;
}
}
}
return DRAW;//无获胜也无空白 平局
}
private static String show(int i){ //显示
switch (i){
case empty:
return " ";
case circle:
return "o";
case cross:
return "x";
default:
return "1";
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String s="---------\n";
for (int i=0;i<2;i++){ //前两行
s+=String.format("|%s|%s|%s|\n",show(array[i][0]),show(array[i][1]),show(array[i][2]));
s+="---------\n";
}
//最后一行
s+=String.format("|%s|%s|%s|\n",show(array[2][0]),show(array[2][1]),show(array[2][2]));
s+="---------";
return s;
}
public void reset() {
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
Arrays.fill(array[i],empty);//所有位置再次设置为空白
}
}
}5. Game–Game
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Game {
private final ChessBoard chessboard;
private final Player player;
private final AI ai;
public Game(Player player){
this.chessboard=new ChessBoard();
this.player=player;
this.ai=new AI();
}
//初始化
public void Init(){
System.out.println("欢迎进入三子棋游戏");
System.out.println(chessboard);
}
//回合制游戏,游戏主流程
public void play(){
while (true){ //一次循环=player回合+AI回合
if (playerTurn()){//玩家回合
break;
}
if (aiTurn()){//ai回合
break;
}
}
}
private boolean aiTurn() {
System.out.println("AI回合:");
while (true) {
int[] rc=ai.getPosition();
int row=rc[0];
int column=rc[1];
if(chessboard.moveCrossAT(row, column)){
break;
}
}
System.out.println(chessboard);
return chessboard.getState()!=ChessBoard.CONTINUE;
}
private boolean playerTurn() {
System.out.println("玩家回合:");
while (true) {
int[] rc=player.getPosition();
int row=rc[0];
int column=rc[1];
if(chessboard.moveCircleAt(row, column)){
break;
}
System.out.println("该位置已经有棋子,请重新选择位置");
}
System.out.println(chessboard);
return chessboard.getState()!=ChessBoard.CONTINUE;
}
//新一局游戏开始时 游戏的界面需要重置 否则会是上一局游戏的结局界面
public void destory(){
chessboard.reset();
}
}Running results:
1. Test the legality of the position
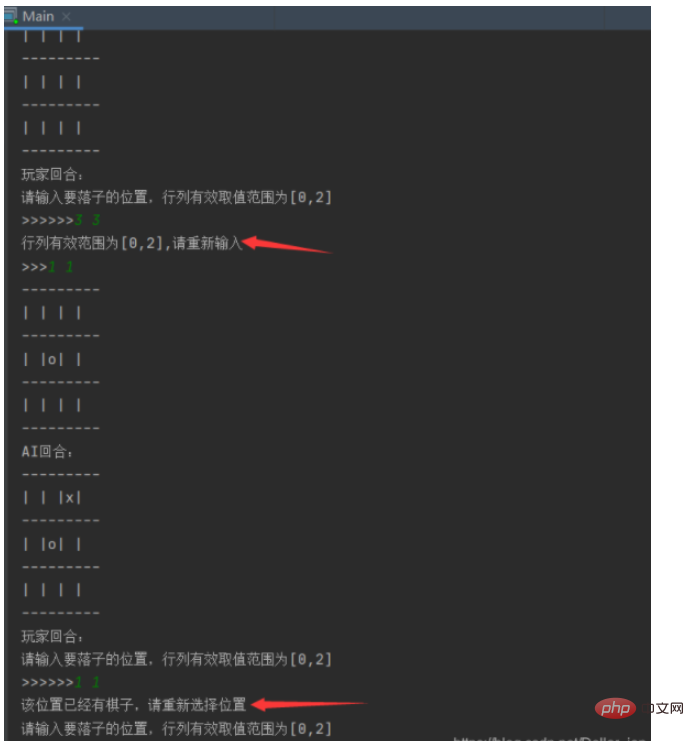
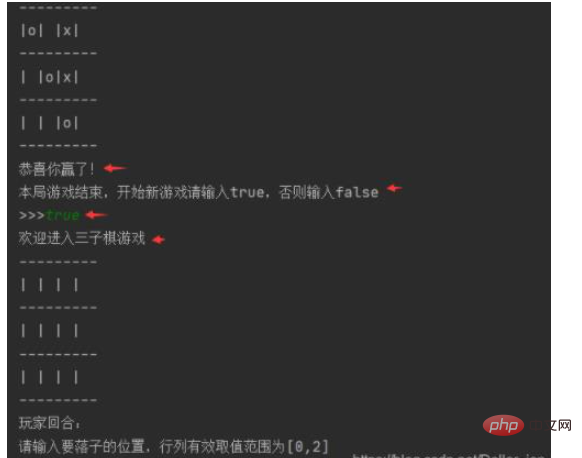
2. Test the board status/win or loss
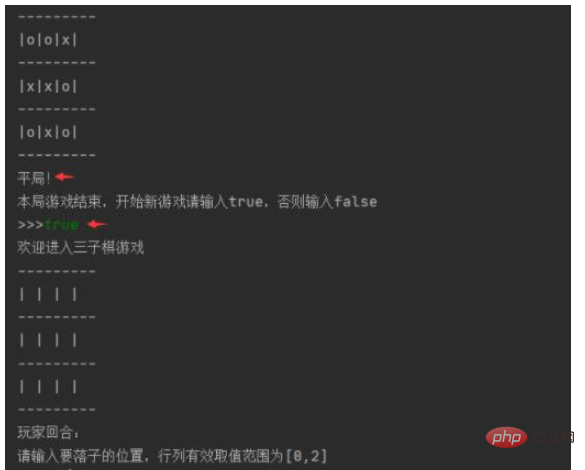
3. Test draw
The above is the detailed content of How to write a three-piece chess game in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:yisu.com. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete

