 Backend Development
Backend Development Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial How to better understand recursive algorithms? Detailed explanation of Python examples
How to better understand recursive algorithms? Detailed explanation of Python examples
Recursion is indeed a relatively abstract mathematical logic, which can be simply understood as "the program calls its own algorithm."
Wikipedia’s explanation of recursion is:
Recursion (English: Recursion), also translated as recursion, in mathematics and computer science, refers to using the function itself in the definition of the function Methods. The term recursion is also more commonly used to describe the process of repeating things in a self-similar way.
For example, when two mirrors are approximately parallel to each other, the images nested in the mirrors appear in the form of infinite recursion. It can also be understood as the process of self-replication.
"Pass" means to pass, and "Return" means to return. First pass a method layer by layer, then pass it to the last layer and return the result back.

For example, I queued up for a nucleic acid test, and there were 100 people in front of me. I wanted to ask what time the medical staff would get off work, so I asked the brother in front of me, and he asked again. The people in front of him passed it on one by one, and finally passed it to the medical staff, who replied that they would get off work at 6 p.m. This sentence was passed back and finally reached me. I learned that the medical staff got off work at six o'clock.
This process is a recursive process. If "passing a message" itself is a method, then the entire process of transmitting a message is calling its own method, and finally obtains the result.
This is different from the cycle. The cycle is equivalent to putting headphones on everyone, and then an "intermediary" will ask you one by one if you know what time the medical staff will get off work. When you ask the medical staff, , got the answer, the "agent" told me to get off work at six o'clock.
In essence, recursion is to continuously dismantle a big problem, like peeling an onion, and finally dismantle it to the smallest level, and return the solution result.

Use Python to give the simplest example of a recursive function and talk about what recursive applications are.
We often see functions calling themselves to implement loop operations, such as functions for finding factorials.
The factorial of the integer n is n*(n-1)*(n-2)*...*3*2*1.
The following 5 lines of Python code can realize the calculation of factorial.
def fact(n): ''' n表示要求的数的阶乘 ''' if n==1: return n n = n*fact(n-1) return n print(factorial(5))
Many people may be confused about the calculation logic here, why the fact function calls itself and finally gets the result.
We can deduce according to mathematical logic:
The factorial of the integer n is: fact(n) = n*(n-1)*...*3*2*1.
The factorial of the integer n-1 is: fact(n-1) = (n-1)*(n-2)*...*3*2*1.
So it can be inferred that fact(n) = n*fact(n-1).
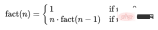
Is there a fact method that can be called for each number? When n=1 is finally called, the factorial of the result n is returned.

Look at the picture above, the recursive function will be called layer by layer, and finally when n=1, the result will be returned upward.
This is the whole process of recursion. If we give an accurate definition of recursion, it can be summarized as the following three points:
1. There is at least one clear end condition for recursion.
2. Give the solution when recursion terminates.
3. Each time you enter a deeper level of recursion, the problem size (calculation amount) should be reduced compared to the last recursion.
Take the above code as an example:
def factorial(n): ''' n表示要求的数的阶乘 ''' if n==1: # 1、明确递归终止条件; return n # 2、递归终止时的处理办法 n = n*factorial(n-1) # 递去 return n# 归来
In addition to common factorial cases, there are also Fibonacci sequences, which are also classic uses of recursion.
Fibonacci Sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89...
This sequence starts from the 3rd item, Each term is equal to the sum of the previous two terms.
It is defined recursively as follows: F(0)=0, F(1)=1, F(n)=F(n - 1) F(n - 2)(n ≥ 2, n∈ N*).
In Python, we can use recursive functions to implement the Fibonacci sequence:
# 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,试判断数列第12个数是哪个? def fab(n): ''' n为斐波那契数列 ''' if n <= 2: v = 1 return v v = fab(n-1)+fab(n-2) return v print(fab(12))
Use mathematical methods to derive:
- fab(0 ) = 0 (initial value).
- fab(1) = 1(initial value).
- For all integers n greater than 1: fab(n) = fab(n-1) fab(n-2) (recursive definition).
In fact, the above two recursive cases can be explained by mathematical induction, which is the knowledge of high school mathematics.
Generally, to prove a proposition P(n) related to a natural number n, there are the following steps:
(1) Prove that the proposition is true when n takes the first value n0. n0 takes the value 0 or 1 for general sequences, but there are also special cases.
(2) Assume that the proposition is true when n=k (k≥n0, k is a natural number), and prove that the proposition is also true when n=k 1.
Based on (1) (2), for all natural numbers n (≥n0), the proposition P(n) is true.
In addition to mathematical explanations, I have also seen someone give a more vivid explanation of recursion before:
1、我们已经完成了吗?如果完成了,返回结果。如果没有这样的终止条件,递归将会永远地继续下去。
2、如果没有,则简化问题,解决较容易的问题,并将结果组装成原始问题的解决办法。然后返回该解决办法。
哈哈,到这里大家是不是对递归有了一个更加深刻的认识。
如果还不清楚,没关系,这里还有更多的递归案例,用Python来实现,可以说非常简洁。
「最大公因数:」
def gcd(m, n): if n == 0: return m else: return gcd(n, m%n)
「从 1 到 n 的数字之和:」
def sumnums(n): if n == 1: return 1 return n + sumnums(n - 1) print(sumnums(3))
「字符串倒序:」
def reverse(string): if len(string) == 0: return string else: return reverse(string[1:]) + string[0] reverseme = '我是帅哥' print(reverse(reverseme))
「汉诺塔问题:」
def towerOfHanoi(numrings, from_pole, to_pole, aux_pole):
if numrings == 1:
print('Move ring 1 from', from_pole, 'pole to', to_pole, 'pole')
return
towerOfHanoi(numrings - 1, from_pole, aux_pole, to_pole)
print('Move ring', numrings, 'from', from_pole, 'pole to', to_pole, 'pole')
towerOfHanoi(numrings - 1, aux_pole, to_pole, from_pole)
numrings = 2
towerOfHanoi(numrings, 'Left', 'Right', 'Middle')
「二分法找有序列表指定值:」
data = [1,3,6,13,56,123,345,1024,3223,6688]
def dichotomy(min,max,d,n):
'''
min表示有序列表头部索引
max表示有序列表尾部索引
d表示有序列表
n表示需要寻找的元素
'''
mid = (min+max)//2
if mid==0:
return 'None'
elif d[mid]<n:
print('向右侧找!')
return dichotomy(mid,max,d,n)
elif d[mid]>n:
print('向左侧找!')
return dichotomy(min,mid,d,n)
else:
print('找到了%s'%d[mid])
return
res = dichotomy(0,len(data),data,222)
print(res)
有位大佬说过:To Iterate is Human, to Recurse, Divine。
中文译为:人理解迭代,神理解递归。
可见递归是非常神奇的算法,它的神奇之处在于它允许用户用有限的语句描述无限的对象。
当然人无完人,递归也是有缺点的,它一般效率较低,且会导致调用栈溢出。
因为递归不断调用自身函数,且产生大量变量,而栈空间的容量是有限的,循环太多就会效率低下,甚至导致调用栈溢出。
The above is the detailed content of How to better understand recursive algorithms? Detailed explanation of Python examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM
特斯拉自动驾驶算法和模型解读Apr 11, 2023 pm 12:04 PM特斯拉是一个典型的AI公司,过去一年训练了75000个神经网络,意味着每8分钟就要出一个新的模型,共有281个模型用到了特斯拉的车上。接下来我们分几个方面来解读特斯拉FSD的算法和模型进展。01 感知 Occupancy Network特斯拉今年在感知方面的一个重点技术是Occupancy Network (占据网络)。研究机器人技术的同学肯定对occupancy grid不会陌生,occupancy表示空间中每个3D体素(voxel)是否被占据,可以是0/1二元表示,也可以是[0, 1]之间的
 基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟在我之前的博客中,我们已经了解了如何使用因果树来评估政策的异质处理效应。如果你还没有阅读过,我建议你在阅读本文前先读一遍,因为我们在本文中认为你已经了解了此文中的部分与本文相关的内容。为什么是异质处理效应(HTE:heterogenous treatment effects)呢?首先,对异质处理效应的估计允许我们根据它们的预期结果(疾病、公司收入、客户满意度等)选择提供处理(药物、广告、产品等)的用户(患者、用户、客户等)。换句话说,估计HTE有助于我
 Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM
Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟引言模型超参数(或模型设置)的优化可能是训练机器学习算法中最重要的一步,因为它可以找到最小化模型损失函数的最佳参数。这一步对于构建不易过拟合的泛化模型也是必不可少的。优化模型超参数的最著名技术是穷举网格搜索和随机网格搜索。在第一种方法中,搜索空间被定义为跨越每个模型超参数的域的网格。通过在网格的每个点上训练模型来获得最优超参数。尽管网格搜索非常容易实现,但它在计算上变得昂贵,尤其是当要优化的变量数量很大时。另一方面,随机网格搜索是一种更快的优化方法,可以提供更好的
 因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM
因果推断主要技术思想与方法总结Apr 12, 2023 am 08:10 AM导读:因果推断是数据科学的一个重要分支,在互联网和工业界的产品迭代、算法和激励策略的评估中都扮演者重要的角色,结合数据、实验或者统计计量模型来计算新的改变带来的收益,是决策制定的基础。然而,因果推断并不是一件简单的事情。首先,在日常生活中,人们常常把相关和因果混为一谈。相关往往代表着两个变量具有同时增长或者降低的趋势,但是因果意味着我们想要知道对一个变量施加改变的时候会发生什么样的结果,或者说我们期望得到反事实的结果,如果过去做了不一样的动作,未来是否会发生改变?然而难点在于,反事实的数据往往是
 使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PM
使用Pytorch实现对比学习SimCLR 进行自监督预训练Apr 10, 2023 pm 02:11 PMSimCLR(Simple Framework for Contrastive Learning of Representations)是一种学习图像表示的自监督技术。 与传统的监督学习方法不同,SimCLR 不依赖标记数据来学习有用的表示。 它利用对比学习框架来学习一组有用的特征,这些特征可以从未标记的图像中捕获高级语义信息。SimCLR 已被证明在各种图像分类基准上优于最先进的无监督学习方法。 并且它学习到的表示可以很容易地转移到下游任务,例如对象检测、语义分割和小样本学习,只需在较小的标记
 盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM
盒马供应链算法实战Apr 10, 2023 pm 09:11 PM一、盒马供应链介绍1、盒马商业模式盒马是一个技术创新的公司,更是一个消费驱动的公司,回归消费者价值:买的到、买的好、买的方便、买的放心、买的开心。盒马包含盒马鲜生、X 会员店、盒马超云、盒马邻里等多种业务模式,其中最核心的商业模式是线上线下一体化,最快 30 分钟到家的 O2O(即盒马鲜生)模式。2、盒马经营品类介绍盒马精选全球品质商品,追求极致新鲜;结合品类特点和消费者购物体验预期,为不同品类选择最为高效的经营模式。盒马生鲜的销售占比达 60%~70%,是最核心的品类,该品类的特点是用户预期时
 人类反超 AI:DeepMind 用 AI 打破矩阵乘法计算速度 50 年记录一周后,数学家再次刷新Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:16 PM
人类反超 AI:DeepMind 用 AI 打破矩阵乘法计算速度 50 年记录一周后,数学家再次刷新Apr 11, 2023 pm 01:16 PM10 月 5 日,AlphaTensor 横空出世,DeepMind 宣布其解决了数学领域 50 年来一个悬而未决的数学算法问题,即矩阵乘法。AlphaTensor 成为首个用于为矩阵乘法等数学问题发现新颖、高效且可证明正确的算法的 AI 系统。论文《Discovering faster matrix multiplication algorithms with reinforcement learning》也登上了 Nature 封面。然而,AlphaTensor 的记录仅保持了一周,便被人类
 研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM
研究表明强化学习模型容易受到成员推理攻击Apr 09, 2023 pm 08:01 PM译者 | 李睿 审校 | 孙淑娟随着机器学习成为人们每天都在使用的很多应用程序的一部分,人们越来越关注如何识别和解决机器学习模型的安全和隐私方面的威胁。 然而,不同机器学习范式面临的安全威胁各不相同,机器学习安全的某些领域仍未得到充分研究。尤其是强化学习算法的安全性近年来并未受到太多关注。 加拿大的麦吉尔大学、机器学习实验室(MILA)和滑铁卢大学的研究人员开展了一项新研究,主要侧重于深度强化学习算法的隐私威胁。研究人员提出了一个框架,用于测试强化学习模型对成员推理攻击的脆弱性。 研究


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor






