Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >What is a linux socket file?
What is a linux socket file?
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2023-04-20 17:25:543144browse
In Linux, a socket file is a special file type used for communication. It provides inter-process communication protected by file system access control. The socket is the basic operating unit that supports TCP/IP network communication. Linux implements the socket in the form of a file. The file corresponding to the socket belongs to the sockfs special file system. To create a socket is to create a special file in sockfs and Establish relevant data structures to implement socket functions.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is a socket file
A socket file is a special file type used for inter-process communication. Socket files can be read, written, and executed. In Linux systems, socket files are commonly used for network programming.
Use ls -l command to view, the first character is "s" (socket).
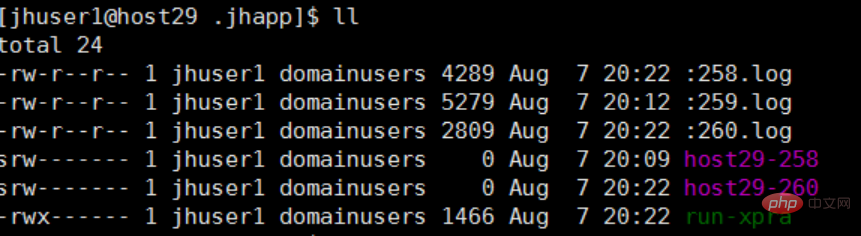
A socket is a special file type, similar to a TCP/IP socket, that provides inter-process communication protected by file system access control.
For example, when you use netcat to open a listening socket in one terminal:
nc -lU socket.sock
Then send data from another terminal via:
echo mytext | nc -U socket.sock
mytext appears on the first terminal.
By default, nc stops listening after the end-of-file character.
Socket Socket
In order to distinguish different application processes and connections, many computer operating systems provide a so-called # for applications to interact with the TCP/IP protocol. ##Socket interface.
Sockets can be said to be a very important concept in network programming. Linux implements sockets in the form of files. The files corresponding to the sockets belong to the sockfs special file system. Creating a socket is created in sockfs. A special file and establishes related data structures to implement socket functions. In other words, for each newly created BSD socket, the Linux kernel will create a new inode in the sockfs special file system.Introduction to Sockets
Sockets are the basic operating unit that supports TCP/IP network communication. They are the basis for our TCP/IP implementation. Communication interface. Linux implements sockets in the form of files. The files corresponding to the sockets belong to the sockfs special file system. To create a socket is to create a special file in sockfs and establish the correlation to realize the socket function. data structure. In other words, for each newly created socket, the Linux kernel will create a new inode in the sockfs special file system.Socket Socket is regarded as an endpoint for two-way communication between processes between different hosts. Simply put, it is an agreement between the two parties in the communication. Use the relevant functions in the socket to complete the communication process. The Socket is a bridge between the application and the network driver. The Socket is created in the application and establishes a relationship with the network driver through binding. After that, the data sent by the application to the socket is handed over by the socket to the network driver and sent to the network. After the computer receives the data related to the IP address and port number bound to the socket from the network, the network driver hands it to the Socket, and the application can extract the received data from the Socket. The network application is In this way, data is sent and received through Socket.
The operating system distinguishes network communication and connections between different application processes. There are three main parameters: the destination IP address of the communication, the transport layer protocol used (TCP or UDP) and the port number used.
The original meaning of Socket is "socket". By combining these three parameters and binding them to a "socket" Socket, the application layer can communicate with the transport layer through the socket interface to distinguish communications from different application processes or network connections, and implement concurrent services for data transmission.
套接字连接的过程如同(客户)打一个电话到一个大公司,接线员(服务器进程)接听电话并把它转接到你要找的部门,然后再从那里转到你要找的人(服务器套接字),然后接线员(服务器进程)再继续转接其它(客户)的电话。
套接字有本地套接字和网络套接字两种。本地套接字的名字是Linux文件系统中的文件名,一般放在/tmp或/usr/tmp目录中;网络套接字的名字是与客户连接的特定网络有关的服务标识符(端口号或访问点)。这个标识符允许Linux将进入的针对特定端口号的连接转到正确的服务器进程。
套接字类型
常用的TCP/IP协议的3种套接字类型如下所示。
流套接字(SOCK_STREAM):
流套接字用于提供面向连接、可靠的数据传输服务。看到这个我们想到了什么,是不是TCP
该服务将保证数据能够实现无差错、无重复发送,并按顺序接收。流套接字之所以能够实现可靠的数据服务,原因在于其使用了传输控制协议,即TCP(The Transmission Control Protocol)协议。
数据报套接字(SOCK_DGRAM)
数据报套接字提供了一种无连接的服务。该服务并不能保证数据传输的可靠性,数据有可能在传输过程中丢失或出现数据重复,且无法保证顺序地接收到数据。数据报套接字使用UDP(User Datagram Protocol)协议进行数据的传输。由于数据报套接字不能保证数据传输的可靠性,对于有可能出现的数据丢失情况,需要在程序中做相应的处理。
原始套接字(SOCK_RAW)
原始套接字(SOCKET_RAW)允许对较低层次的协议直接访问,比如IP、 ICMP协议,它常用于检验新的协议实现,或者访问现有服务中配置的新设备,因为RAW SOCKET可以自如地控制Windows下的多种协议,能够对网络底层的传输机制进行控制,所以可以应用原始套接字来操纵网络层和传输层应用。比如,我们可以通过RAW SOCKET来接收发向本机的ICMP、IGMP协议包,或者接收TCP/IP栈不能够处理的IP包,也可以用来发送一些自定包头或自定协议的IP包。网络监听技术很大程度上依赖于SOCKET_RAW
原始套接字与标准套接字(标准套接字指的是前面介绍的流套接字和数据报套接字)的区别在于:原始套接字可以读写内核没有处理的IP数据包,而流套接字只能读取TCP协议的数据,数据报套接字只能读取UDP协议的数据。因此,如果要访问其他协议发送数据必须使用原始套接字。
重要数据结构
下面是在网络编程中比较重要的几个数据结构
表示套接口的数据结构struct socket
用户使用socket系统调用编写应用程序时,通过一个数字来表示一个socket,所有的操作都在该数字上进行,这个数字称为套接字描述符。在系统调用 的实现函数里,这个数字就会被映射成一个表示socket的结构体,该结构体保存了该socket的所有属性和数据。
套接口是由socket数据结构代表的,形式如下
struct socket
{
socket_state state; /*指明套接口的连接状态,一个套接口的连接状态可以有以下几种
套接口是空闲的,还没有进行相应的端口及地址的绑定;还没有连接;正在连接中;已经连接;正在解除连接。*/unsignedlong flags;
structproto_ops ops; /*指明可对套接口进行的各种操作*/structinode inode; /*指向sockfs文件系统中的相应inode*/structfasync_struct *fasync_list; /* Asynchronous wake up list */structfile *file; /*指向sockfs文件系统中的相应文件 */structsock sk; /*任何协议族都有其特定的套接口特性,该域就指向特定协议族的套接口对
象。*/wait_queue_head_t wait;
short type;unsignedchar passcred;
};描述套接口通用地址的数据结构struct sockaddr
由于历史的缘故,在bind、connect等系统调用中,特定于协议的套接口地址结构指针都要强制转换成该通用的套接口地址结构指针。结构形式如下:
struct sockaddr {
sa_family_t sa_family; /* address family, AF_xxx, sa_family是地址家族,一般都是“AF_xxx”的形式。通常大多用的是都是AF_INET,代表TCP/IP协议族。*/
char sa_data[14]; /*14 bytes of protocol address, sa_data是14字节协议地址。*/
};此数据结构用做bind、connect、recvfrom、sendto等函数的参数,指明地址信息。但一般编程中并不直接针对此数据结构操作,而是使用另一个与sockaddr等价的数据结构
描述因特网地址结构的数据结构struct sockaddr_in
每个套接字域都有自己的地址格式。
AF_UNIX 域套接字格式:
#include <sys/un.h>
#define UNIX_PATH_MAX
108struct sockaddr_un {
sa_family_t sun_family; /
* AF_UNIX */
char sun_path[UNIX_PATH_MAX]; /* pathname */
};AF_INET 域套接字格式IPV4:
/* Internet address. */
struct in_addr {
uint32_t
s_addr; /* address in network byte order */
};IP地址是由4个字节组成的一个32位的值。
#include <netinet/in.h>
struct sockaddr_in
{ short sin_family;/* Addressfamily一般来说AF_INET(地址族)PF_INET(协议族) */
unsigned short sin_port;/* Portnumber(必须要采用网络数据格式,普通数字可以用htons()函数转换成网络数据格式的数字) */
struct in_addr sin_addr;/* Internetaddress存储IP地址 */
unsigned char sin_zero[sizeof(struct sockaddr) - __SOCKADDR_COMMON_SIZE - sizeof(in_port_t) - sizeof(struct in_addr)]; /* Samesizeasstructsockaddr没有实际意义,只是为了 跟SOCKADDR结构在内存中对齐*/
};AF_INET6 域套接字格式IPV6:
struct sockaddr_in6 {
sa_family_t sin6_family; /* AF_INET6 */
in_port_t sin6_port; /* port number */
uint32_t sin6_flowinfo; /* IPv6 flow information */
struct in6_addr sin6_addr; /* IPv6 address */
uint32_t sin6_scope_id; /* Scope ID (new in 2.4) */
};
struct in6_addr {
unsigned char s6_addr[16]; /* IPv6 address */
};对于应用程序来说,套接字就和文件描述符一样,并且通过一个唯一的整数值来区分。
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of What is a linux socket file?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

