1. Introduction to the Object class
Object is a class provided by Java by default. Except for the Object class, all classes in Java have inheritance relationships. By default, it will inherit the Object parent class. That is, objects of all classes can be received using the reference of Object.
Example: Use Object to receive objects of all classes
class Person{}
class Student{}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
function(new Person());
function(new Student());
}
public static void function(Object obj) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
//执行结果:
Person@1b6d3586
Student@4554617cSo during development, the Object class is the highest unified type of parameters. But the Object class also has some well-defined methods. As follows:

Here are three of the methods: toString() method, equals() method, hashcode() method
2. Rewrite toString Method to print object
When we want to print the contents of the object, we can do it by overriding the toString method in the Object class!
The following explains why the toString() method should be overridden
The following code wants to print a Person object:
public class Person {
String name;
String gender;
int age;
public Person(String name, String gender, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("Jim","男", 18);
System.out.println(person);
}
}Look at the execution result and the printed content is not the specific content of the object.

Observe the println method source code here. In the source code, the valueOf method in the String class is called. When jumping to the source code at valueOf, you can find that the method body actually The toString method is called again,

Now let’s look at the specific implementation of toString,

getClass() .getName() returns the runtime class (Class) of this Object, and returns the name of the entity (class, interface, array class, basic type or void) represented by this Class object in the form of String
hashCode( ) method returns the "address"
Integer.toHexString(hashCode()) Gets the hash code value of this object (int type), and uses the wrapper class Integer class to get the hash code of this int type value, convert it to a hexadecimal unsigned integer, and represent the converted hexadecimal integer in the form of a string
So the output function println is implemented by calling toString at the bottom level. If you want To realize the specific content of the printing object, we only need to rewrite the toString method in the Object class according to our own ideas
public class Person {
String name;
String gender;
int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public Person(String name, String gender, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person("xin","男", 21);
System.out.println(person);
}
}Execution result:

3. Object comparison equals method
In Java, when == is compared:
If the left and right sides of == are basic type variables, what is compared is whether the value in the variable is Same
If the left and right sides of == are reference type variables, the comparison is whether the reference variable addresses are the same
If you want to compare the contents of the objects , the equals method in Object must be rewritten, because the equals method also compares according to the address by default. The following is the source code of the equals method:

Object comparison code example:
class Person{
private String name ;
private int age ;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.age = age ;
this.name = name ;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return false ;
}
if(this == obj) {
return true ;
}
//不是Person类对象
if (!(obj instanceof Person)) {
return false ;
}
Person person = (Person) obj ; // 向下转型,比较属性值
return this.name.equals(person.name) && this.age==person.age ;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("xin", 20);
Person p2 = new Person("xin", 20);
Person p3 = new Person("rong", 21);
System.out.println(p1.equals(p2));
System.out.println(p1.equals(p3));
}
}Execution result:
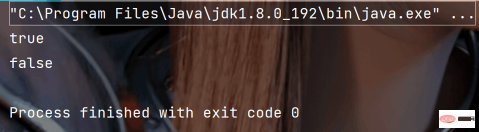
The function of hashCode() in the hash table is to obtain the hash code of the object and then determine the position of the object in the hash table. hashCode method source code:
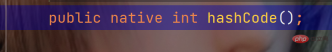
class Person {
public String name;
public int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
public class TestDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person per1 = new Person("xin", 21) ;
Person per2 = new Person("xin", 21) ;
System.out.println(per1.hashCode());
System.out.println(per2.hashCode());
}
}Execution result:

import java.util.Objects;
class Person {
public String name;
public int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(name, age);
}
}
public class TestDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person per1 = new Person("xin", 21) ;
Person per2 = new Person("xin", 21) ;
System.out.println(per1.hashCode());
System.out.println(per2.hashCode());
}
}Execution result:

The above is the detailed content of How to use methods in Java Object class. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to add complex borders to Excel cells using GrapeCity Documents for Java library in Java?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
How to add complex borders to Excel cells using GrapeCity Documents for Java library in Java?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:39 PMUsing POI library in Java to add borders to Excel files Many Java developers are using Apache...
 How to use CompletableFuture to ensure the order consistency of batch interface request results?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
How to use CompletableFuture to ensure the order consistency of batch interface request results?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:36 PMEfficient processing of batch interface requests: Using CompletableFuture to ensure that concurrent calls to third-party interfaces can significantly improve efficiency when processing large amounts of data. �...
 In JavaWeb applications, is it reasonable for Dao layer to cache all personnel entity classes?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:33 PM
In JavaWeb applications, is it reasonable for Dao layer to cache all personnel entity classes?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:33 PMIn JavaWeb applications, the feasibility of implementing entity-class caching in Dao layer When developing JavaWeb applications, performance optimization has always been the focus of developers. Either...
 Which motorcycle and motorcycle system is better? Comparison of advantages and disadvantages between open Android system and closed self-developed systemApr 19, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
Which motorcycle and motorcycle system is better? Comparison of advantages and disadvantages between open Android system and closed self-developed systemApr 19, 2025 pm 08:30 PMThe current status of motorcycle and motorcycle systems and ecological development of motorcycle systems, as an important bridge connecting knights and vehicles, has developed rapidly in recent years. Many car friends...
 How to get Java entity class attribute names elegantly to avoid hard-coded in MyBatis queries?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:27 PM
How to get Java entity class attribute names elegantly to avoid hard-coded in MyBatis queries?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:27 PMWhen using MyBatis-Plus or tk.mybatis...
 How to efficiently query personnel data in MySql and ElasticSearch through natural language processing?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
How to efficiently query personnel data in MySql and ElasticSearch through natural language processing?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:24 PMHow to query personnel data through natural language processing? In modern data processing, how to efficiently query personnel data is a common and important requirement. ...
 How to parse next-auth generated JWT token in Java and get information in it?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
How to parse next-auth generated JWT token in Java and get information in it?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:21 PMIn processing next-auth generated JWT...
 How to package in IntelliJ IDEA for specific Git versions to avoid including unfinished code?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to package in IntelliJ IDEA for specific Git versions to avoid including unfinished code?Apr 19, 2025 pm 08:18 PMIn IntelliJ...


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






