 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Detailed explanation of the three mountains of JS: scope and closure, prototype and prototype chain, asynchrony and single thread
Detailed explanation of the three mountains of JS: scope and closure, prototype and prototype chain, asynchrony and single threadjs serves as the backbone of the front-end. So, do you know what the three big mountains of javascript are?

1️⃣ Scope and closure
Scope refers to the current code Context controls the visibility and life cycle of variables and functions. The biggest function is to isolate variables, so variables with the same name in different scopes will not conflict.
Scope chain means that if the value is not found in the current scope, it will query the upper scope until the global scope, such a search process The chain formed is called a scope chain. [Recommended learning: javascript video tutorial]
Scopes can be stacked into a hierarchical structure, and child scopes can access the parent scope, but not vice versa.
Scope can be subdivided into four types: Global scope, Module scope,Function scope、Block-level scope
##Global scope: The code is in the program Can be accessed anywhere, such as the window object. However, global variables will pollute the global namespace and easily cause naming conflicts.
Module scope: There was no module definition in the early js syntax because the original script was small and simple. Later, as scripts became more and more complex, modular solutions emerged (AMD, CommonJS, UMD, ES6 modules, etc.). Usually a module is a file or a script, and this module has its own independent scope.
Function scope: As the name suggests, the scope created by the function. Closures are generated in this scope, which we will introduce separately later.
Block-level scope: Since js variable promotion has design flaws such as variable coverage and variable pollution, ES6 introduces the block-level scope keyword to solve these problems. Typical cases are the for loop of let and the for loop of var.
// var demo
for(var i=0; i<10; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
console.log(i); // 10
// let demo
for(let i=0; i<10; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
console.log(i); //ReferenceError:i is not definedAfter understanding the scope, let’s talk about itClosure: Function A contains function B, and function B uses the variables of function A, then function B A closure or closure is a function that can read the internal variables of function A.
closure is the non-release of the outer function variable by the inner function .
Characteristics of closure:
- There is a function in the function;
- Internal functions can access the scope of the outer function;
- Parameters and variables will not be GCed and always reside in memory;
- There are closures only where there is memory.
The application scenarios of closures are summarized below:
// demo1 输出 3 3 3
for(var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i);
}, 1000);
}
// demo2 输出 0 1 2
for(let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i);
}, 1000);
}
// demo3 输出 0 1 2
for(let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
(function(i){
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i);
}, 1000);
})(i)
}/* 模拟私有方法 */
// 模拟对象的get与set方法
var Counter = (function() {
var privateCounter = 0;
function changeBy(val) {
privateCounter += val;
}
return {
increment: function() {
changeBy(1);
},
decrement: function() {
changeBy(-1);
},
value: function() {
return privateCounter;
}
}
})();
console.log(Counter.value()); /* logs 0 */
Counter.increment();
Counter.increment();
console.log(Counter.value()); /* logs 2 */
Counter.decrement();
console.log(Counter.value()); /* logs 1 *//* setTimeout中使用 */
// setTimeout(fn, number): fn 是不能带参数的。使用闭包绑定一个上下文可以在闭包中获取这个上下文的数据。
function func(param){ return function(){ alert(param) }}
const f1 = func(1);setTimeout(f1,1000);/* 生产者/消费者模型 */
// 不使用闭包
// 生产者
function producer(){
const data = new(...)
return data
}
// 消费者
function consumer(data){
// do consume...
}
const data = producer()
// 使用闭包
function process(){
var data = new (...)
return function consumer(){
// do consume data ...
}
}
const processer = process()
processer()/* 实现继承 */
// 以下两种方式都可以实现继承,但是闭包方式每次构造器都会被调用且重新赋值一次所以,所以实现继承原型优于闭包
// 闭包
function MyObject(name, message) {
this.name = name.toString();
this.message = message.toString();
this.getName = function() {
return this.name;
};
this.getMessage = function() {
return this.message;
};
}
// 原型
function MyObject(name, message) {
this.name = name.toString();
this.message = message.toString();
}
MyObject.prototype.getName = function() {
return this.name;
};
MyObject.prototype.getMessage = function() {
return this.message;
};I seem to understand the concept of closures but seem to be missing something? The meaning is still not finished. I was also lost in closures, but after reading the life cycle of closures, I found myself again.

function test(a, b){
console.log(b);
return {
test: function(c) {
return test(c,a);
}
}
}
var a = test(100);a.test(101);a.test(102);
var b = test(200).test(201).test(202);
var c = test(300).test(301);c.test(302);
// undefined 100 100
// undefined 200 201
// undefined 300 301
2️⃣ Prototype and prototype chain
Where there are objects There isprototype. Each object will initialize a property inside it, which is prototype (prototype), and shared properties and methods are stored in the prototype. When we access the properties of an object, the js engine will first check whether the current object has this property. If not, it will check whether its prototype object has this property, and so on until the Object built-in object is retrieved. Such a search process formed the concept of prototype chain.
- __proto__属性在所有对象中都存在,指向其构造函数的prototype对象;prototype对象只存在(构造)函数中,用于存储共享属性和方法;constructor属性只存在于(构造)函数的prototype中,指向(构造)函数本身。
- 一个对象或者构造函数中的隐式原型__proto__的属性值指向其构造函数的显式原型 prototype 属性值,关系表示为:
instance.__proto__ === instance.constructor.prototype - 除了 Object,所有对象或构造函数的 prototype 均继承自 Object.prototype,原型链的顶层指向 null:
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null - Object.prototype 中也有 constructor:
Object.prototype.constructor === Object - 构造函数创建的对象(Object、Function、Array、普通对象等)都是 Function 的实例,它们的 __proto__ 均指向 Function.prototype。
看起来是不是有点乱??别慌!!一张图帮你整理它们之间的关系

相同的配方再来一刀
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; arr.__proto__ === Array.prototype; // true arr.__proto__.__proto__ === Object.prototype; // true Array.__proto__ === Function.prototype; // true
3️⃣ 异步和单线程
JavaScript 是 单线程 语言,意味着只有单独的一个调用栈,同一时间只能处理一个任务或一段代码。队列、堆、栈、事件循环构成了 js 的并发模型,事件循环 是 JavaScript 的执行机制。
为什么js是一门单线程语言呢?最初设计JS是用来在浏览器验证表单以及操控DOM元素,为了避免同一时间对同一个DOM元素进行操作从而导致不可预知的问题,JavaScript从一诞生就是单线程。
既然是单线程也就意味着不存在异步,只能自上而下执行,如果代码阻塞只能一直等下去,这样导致很差的用户体验,所以事件循环的出现让 js 拥有异步的能力。

更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程教学!!
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of the three mountains of JS: scope and closure, prototype and prototype chain, asynchrony and single thread. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 实战:vscode中开发一个支持vue文件跳转到定义的插件Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:43 PM
实战:vscode中开发一个支持vue文件跳转到定义的插件Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:43 PMvscode自身是支持vue文件组件跳转到定义的,但是支持的力度是非常弱的。我们在vue-cli的配置的下,可以写很多灵活的用法,这样可以提升我们的生产效率。但是正是这些灵活的写法,导致了vscode自身提供的功能无法支持跳转到文件定义。为了兼容这些灵活的写法,提高工作效率,所以写了一个vscode支持vue文件跳转到定义的插件。
 5个常见的JavaScript内存错误Aug 25, 2022 am 10:27 AM
5个常见的JavaScript内存错误Aug 25, 2022 am 10:27 AMJavaScript 不提供任何内存管理操作。相反,内存由 JavaScript VM 通过内存回收过程管理,该过程称为垃圾收集。
 Node.js 19正式发布,聊聊它的 6 大特性!Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node.js 19正式发布,聊聊它的 6 大特性!Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PMNode 19已正式发布,下面本篇文章就来带大家详解了解一下Node.js 19的 6 大特性,希望对大家有所帮助!
 聊聊如何选择一个最好的Node.js Docker镜像?Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
聊聊如何选择一个最好的Node.js Docker镜像?Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM选择一个Node的Docker镜像看起来像是一件小事,但是镜像的大小和潜在漏洞可能会对你的CI/CD流程和安全造成重大的影响。那我们如何选择一个最好Node.js Docker镜像呢?
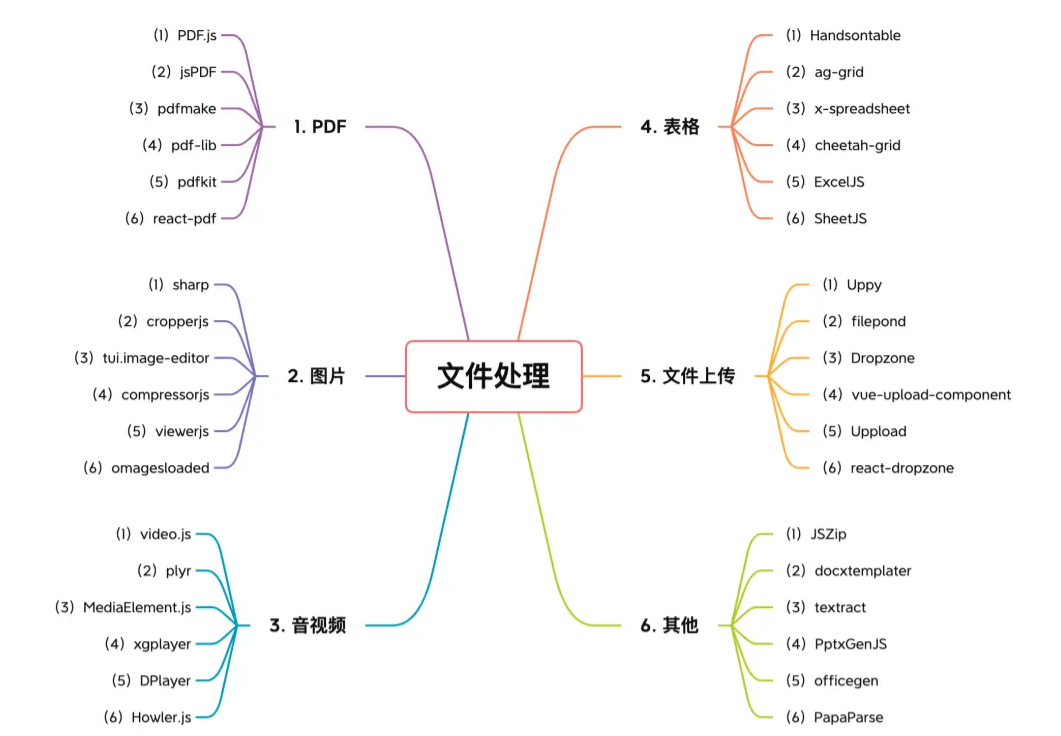 【6大类】实用的前端处理文件的工具库,快来收藏吧!Jul 15, 2022 pm 02:58 PM
【6大类】实用的前端处理文件的工具库,快来收藏吧!Jul 15, 2022 pm 02:58 PM本篇文章给大家整理和分享几个前端文件处理相关的实用工具库,共分成6大类一一介绍给大家,希望对大家有所帮助。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools









