Home >Java >javaTutorial >Java proxy pattern example code analysis
Java proxy pattern example code analysis
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2023-04-18 16:52:07869browse
1. Dynamic proxy mode
Characteristics of dynamic proxy:
When proxying an object, there is no need to implement the interface
-
The generation of proxy objects is to use the API of JDK to dynamically build proxy objects in memory (we need to specify the type of interface to create proxy objects/target objects)
Alias of dynamic proxy: JDK proxy, interface proxy
2, JDK dynamic proxy
Class diagram:
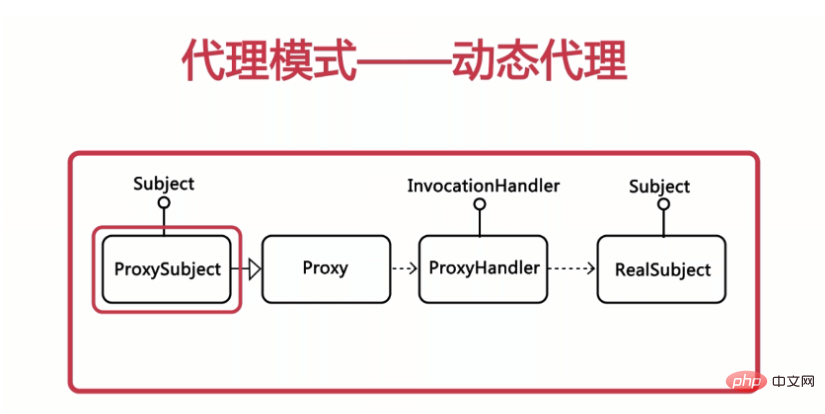
static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h):Returns an instance of the proxy class. The returned proxy class can be used as the proxy class (you can use the proxy class's Methods declared in the interface) Implementation steps of dynamic generation:
- Create a class that implements the interface InvocationHandler, which must implement the invoke method
- Create the proxied class and interface
- Call the static method of Proxy to create a proxy class:
newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class[]
- Call method through proxy
public interface Moveable {
void move();
}Now there is a car: //实现Moveable 接口,并随机暂停一段时间
import java.util.Random;
public class Car implements Moveable{
@Override
public void move() {
try{
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
System.out.println("汽车行驶中");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Time agent class: import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class TimeHandler implements InvocationHandler{
public TimeHandler(Object target){
super();
this.target = target;
}
private Object target;
/**
*
* @param proxy :被代理的对象
* @param method:被代理对象的方法
* @param args:方法的参数
* @return
* @throws Throwable
* 返回值:Object 方法的返回值
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("汽车开始行使");
method.invoke(target);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("汽车行驶结束,行驶的时间为:"+(endTime-startTime)+"毫秒");
return null;
}
}Test class: import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
InvocationHandler h = new TimeHandler(car);
Class<?> cls = car.getClass();
/**
* newProxyInstanced的参数
* 分别是:类加载器、实现的接口、实现的处理器
*/
Moveable m = (Moveable) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cls.getClassLoader(),
cls.getInterfaces(),h);
m.move();
}
}The output result is:
The car starts drivingNote: JDK proxy can only proxy classes that implement interfaces. Those that do not implement interfaces cannot proxy.The car is driving
The car ends driving, the driving time is: 137 milliseconds
//The following time is randomly generated and different every time
The above is the detailed content of Java proxy pattern example code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

