Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >What is the command to view all files in a directory in Linux?
What is the command to view all files in a directory in Linux?
- 藏色散人Original
- 2023-04-17 09:46:4213586browse
The Linux command to view all files in a directory is "ls"; the ls command is the abbreviation of list and is the most common directory operation command. Its main function is to display the contents of the current directory. The basic format of this command is "[root@localhost ~]# ls [xuanxiang] muluming".

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.9.8 system, Dell G3 computer.
What is the Linux command to view all files in a directory?
ls command, the abbreviation of list, is the most common directory operation command. Its main function is to display the contents of the current directory. The basic format of this command is:
[root@localhost ~]# ls [选项] 目录名称
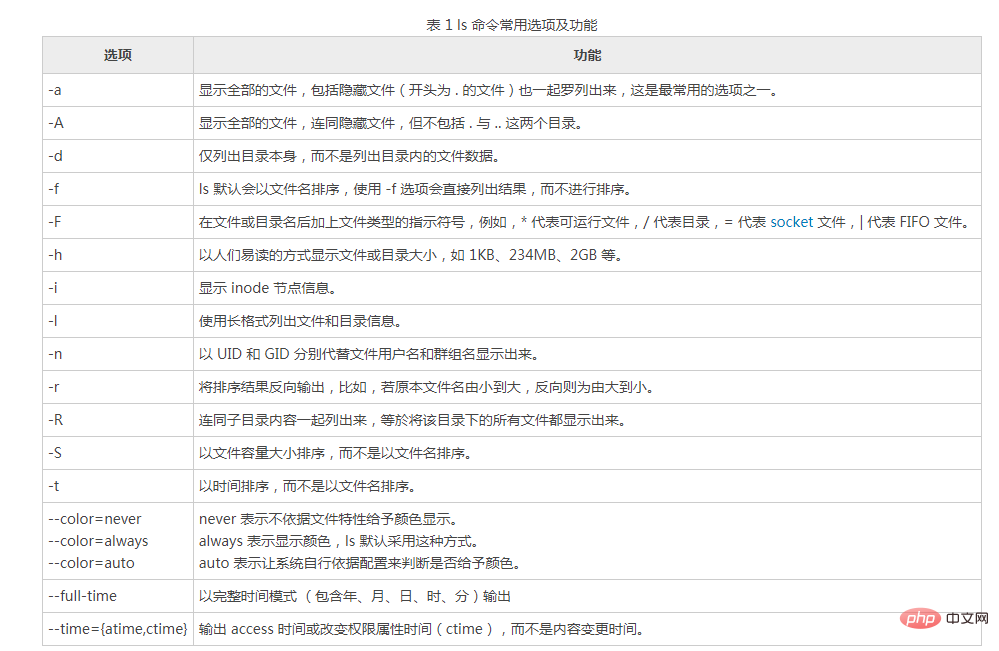
Note that when the ls command does not use any options, by default only the names of non-hidden files will be displayed and sorted by file names. , and at the same time, the file name will be colored according to the specific type of the file (blue shows directories, white shows general files). In addition, if you want to use the ls command to display more content, you need to use the corresponding options in Table 1.
Example:
[root@www ~]# ls -al ~ total 156 drwxr-x--- 4 root root 4096 Sep 24 00:07 . drwxr-xr-x 23 root root 4096 Sep 22 12:09 .. -rw------- 1 root root 1474 Sep 4 18:27 anaconda-ks.cfg -rw------- 1 root root 955 Sep 24 00:08 .bash_history -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 24 Jan 6 2007 .bash_logout -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 191 Jan 6 2007 .bash_profile -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 176 Jan 6 2007 .bashrc drwx------ 3 root root 4096 Sep 5 10:37 .gconf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 42304 Sep 4 18:26 install.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5661 Sep 4 18:25 install.log.syslog
By using -a, you will see several files starting with ., as well as directory files (.), (..), .gconf, etc., These are hidden directories and files. Among them, directory file names are displayed in blue, and general files are displayed in white.
Note that in the Linux system, hiding files is not to hide the files from other users, but to tell users that these files are important system files. Do not touch them unless necessary! Therefore, whether it is Linux or Windows, you can view hidden files very easily. However, in Windows, most viruses and Trojans will turn themselves into hidden files, giving users the illusion that the purpose of hiding files is to prevent User discovery.
Not only that, the ls command here also uses the -l option, so the detailed information of the file is displayed. The meanings of the 7 columns displayed by this option are:
First Column: Specifies the permissions that different users have on files. The meaning of specific permissions will be explained in subsequent chapters.
Second column: Reference count. The reference count of a file represents the number of hard links to the file, while the reference count of the directory represents how many first-level subdirectories the directory has.
The third column: owner, that is, which user this file belongs to. The default owner is the user who created the file.
The fourth column: the group to which the file belongs. The default group to which the file belongs is the effective group of the user who created the file. Generally, it is the group of the user who created the file.
The fifth column: size, the default unit is bytes.
The sixth column: File modification time, file status modification time or file data modification time will change this time. Note that this time is not the creation time of the file.
The seventh column: file name or directory name.
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What is the command to view all files in a directory in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

