In the TCP/IP protocol suite, the Domain Name System is one of the protocols that provides name resolution services for computer name to IP address mapping. However, sometimes it malfunctions, resulting in errors such as The requested control is not valid for this service NET HELPMSG 2191.
DNS clients and servers work together to provide computer name to IP address mapping name resolution services to computers and users.
After installing Windows, the client service is enabled by default for client and server versions of the operating system.
Once you specify the server's IP address in your TCP/IP network configuration, the DNS client queries the server to discover domain controllers and resolve computer names to IP addresses.
Only after the server responds to the client's query and provides the IP address of the domain controller, communication can occur between the client and the domain controller and the authentication process can begin.
Follow us as we show you how to enable DNS on Windows 11 and then jump to the list of solutions for the Requested Controls Not Working for this Service NET HELPMSG 2191 issue.
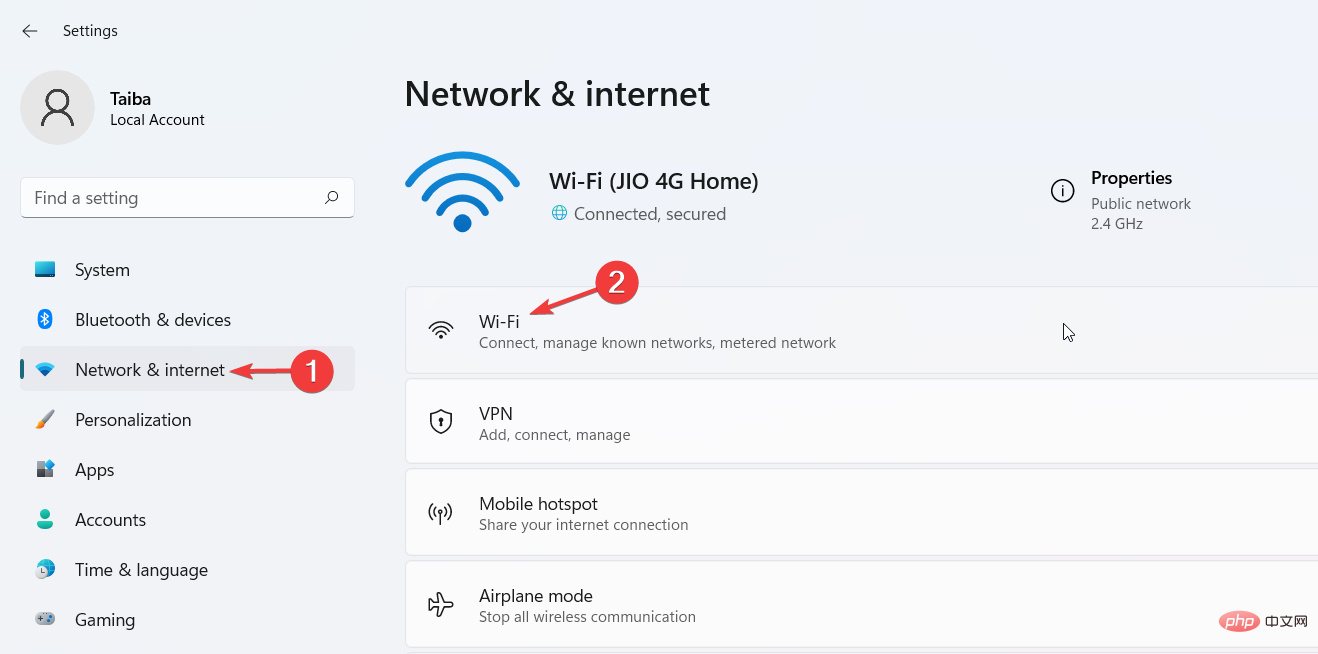
How to enable DNS on Windows 11?
- Open Control Panel and navigate to Network and Internet to find the settings we need to adjust.

- Go to the Network and Sharing Center.

- Click the Change Adapter Settings option to select the network to modify.

- Right-click the network where you want to enable DNS and select Properties.

- Navigate to the Network tab, select IPv4 and click Properties. IPv4 is the abbreviation for Internet Protocol version 4. It is the underlying technology that enables us to connect devices to the Internet and share information with them.

-
Select the radio button next to Use the following DNS server addresses and enter the preferred and backup servers. Any device connected to the Internet is assigned a unique numeric IP address, such as 99.48.

Some of the best third-party DNS servers are Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4), Cloudflare (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1), and OpenDNS (208.67.222.123 and 208.67.220.123). Each of these service providers has a primary and secondary DNS address that can be used for connections.
Because it's easy to remember, Google's public DNS is one of the most widely used addresses on the Internet.
The fact that Google logs IP addresses that access its servers for one to two days is important because it can be used for diagnostic and troubleshooting purposes.
There may also be some persistent logs, but Google claims it does not store any personally identifiable information in its logs. Therefore, if you value your privacy, you may want to consider using a different DNS address.
What should I do if I get a NET HELPMSG 2191 error?
1. Restart DNS
- Open the Windows search function and enter services. Click on the top result to open the service application.

- Here, scroll down until you encounter DNS Client, then right-click on it to select Properties.

- Click the Stop button and then click the Start button. However, if the button appears gray, go to the second solution.

You can use Microsoft Services (formerly NT Services, available on Windows platforms) to create long-running executable applications that run in their own sessions.
These services can start automatically when the computer starts, can be paused and restarted, and do not display any graphical user interface.
It's important to note that since clearing the DNS cache will delete all entries, it will also delete any invalid records, which will force your computer to repopulate these addresses the next time you try to access these websites.
These new addresses come from the DNS servers configured for your network.
2. Use the Registry Editor
- to open the Windows search function and enter regedit in the search bar. Select the top result to open the Registry Editor.

- Here, enter the following location and press Enter:
<strong>Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNSCache\Parameters</strong>
- Right click on a blank area and create a new DWORD or QWORD depending on your system. DWORD, short for Double Word, is a data type definition that is only available on Windows.

- Name it MaxCacheTtl and double-click it to set the value to Decimal and 86400.

- Repeat the same steps and create a new DWORD/QWORD named MaxNegativeCacheTtl. Set its value to 5. This way, the DNS cache will be reset every few hours.

In the Registry Editor, users can perform the following operations: create, manipulate, delete, and rename keys and subkeys in the registry, as well as modify and delete value data.
However, if you still can't complete the above solution or it doesn't work for you, check out What to do if you can't restart your DNS client.
Why use a third-party DNS server?
DNS servers are responsible for connecting domain names to their associated IP addresses. When you first enter a domain name into your browser, your computer contacts the DNS server currently in use and asks for the IP address associated with the domain name.
The IP address is then connected to your computer, which retrieves the page for you. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is most likely responsible for providing the server you use.
If you are behind a router, your computer may be using the router as its DNS server, but the router actually forwards requests to servers provided by your Internet service provider.

Your computer stores DNS responses locally, which means you don't have to make a request every time you connect to a domain name you've already visited one or more times.
Once your computer determines the IP address associated with a domain name, it will retain that information for a period of time, allowing you to connect faster by skipping the request phase entirely.
As we established above, you are most likely using a server provided by your Internet Service Provider. However, you don't need to do this. Instead, you can use those operated by third-party companies.
In some cases, these DNS servers may be able to provide you with faster resolution, allowing you to connect to the domain name faster the first time you connect.
In practice, however, the actual speed difference you experience will depend on your distance from the third-party server and the speed of your Internet Service Provider's (ISPDNS) servers.
The above is the detailed content of The requested control is invalid NET HELPMSG 2191: 2 simple fixes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 win11 DNS服务器错误如何解决Jan 10, 2024 pm 09:02 PM
win11 DNS服务器错误如何解决Jan 10, 2024 pm 09:02 PM我们在连接网络时需要使用正确的dns才可以上网。同理,如果我们使用了错误的dns设置就会提示dns服务器错误了,这时候我们可以尝试在网络设置中选择自动获取dns来解决,下面就一起来看下具体解决方法吧。win11网络dns服务器错误怎么办方法一:重新设置DNS1、首先,点击任务栏中的开始进入,在其中找到并点开“设置”图标按钮。2、然后点击左侧栏中的“网络&Internet”选项命令。3、然后在右侧找到“以太网”选项,点击进入。4、之后,点击DNS服务器分配中的“编辑”,最后将DNS设置为“自动(D
 修复:Windows 11 更新错误 0x80072ee7Apr 14, 2023 pm 01:31 PM
修复:Windows 11 更新错误 0x80072ee7Apr 14, 2023 pm 01:31 PM某些 Windows 11 更新可能会导致问题和更大的版本,从而导致性能错误。例如,如果您不修复更新错误 0x80072ee7,它可能会使您的机器运行异常。它在不同的情况下触发,修复它取决于故障背后的原因。有时,用户报告在安装某些 Windows 更新时会出现此问题。浏览时不会随机出现安全通知和系统错误。如果发生这种情况,您的计算机可能存在不需要的程序或恶意软件。错误背后的原因各不相同,从防病毒问题到其他干扰 Windows 更新的软件。Windows 更新错误是如何发生的?如果浏览时出现 0x
 如何在 Windows 10 / 11 上的一张 LAN 卡中分配多个 IP 地址May 30, 2023 am 11:25 AM
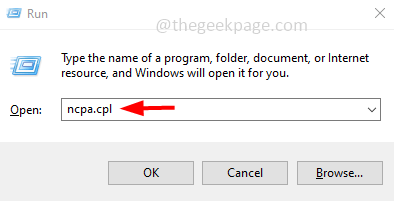
如何在 Windows 10 / 11 上的一张 LAN 卡中分配多个 IP 地址May 30, 2023 am 11:25 AM有时需要为单个LAN卡分配多个地址。例如,如果需要运行多个具有唯一IP地址的网站或将应用程序绑定到不同的IP地址等。如果您正在考虑如何为单个网络接口卡或LAN卡分配多个地址,那么本文将帮助您实现它。按照下面的步骤直到最后,它就会完成。那么让我们开始吧!在一张LAN卡中分配多个IP地址第1步:一起使用Windows+R键打开运行提示并键入ncpa.cpl,然后按回车键打开网络连接窗口。第2步:右键单击您的网络适配器以太网或WiFi选项,然后单击属性。第3步:从属性窗口
 如何修复 Xbox Series S/X 下载速度、降低 ping 和延迟Apr 16, 2023 pm 04:49 PM
如何修复 Xbox Series S/X 下载速度、降低 ping 和延迟Apr 16, 2023 pm 04:49 PM多年来,Xbox控制台得到了突飞猛进的改进。多年来,游戏不断发展,具有栩栩如生的功能,而游戏玩家似乎无法获得足够的体验。在Xbox上玩您最喜欢的游戏可能是一种完全引人入胜的体验。但是,有时使用这些高级功能,如果互联网速度不是那么好,我们最终会遇到延迟或ping问题。有时我们希望游戏下载速度更快。如今,像ForzaHorizon5和MortalKombat这样的游戏需要超过100GB的内存。如果我们没有正确的互联网设置来帮助我们,下载此类游戏可能需要很长时间。方法1:通过
 如何解决Steam错误代码105无法连接到服务器?Apr 22, 2023 pm 10:16 PM
如何解决Steam错误代码105无法连接到服务器?Apr 22, 2023 pm 10:16 PMSteam是一个流行的游戏库。它允许其用户玩游戏,并将游戏下载到他们的Steam帐户。由于它是一个基于云的库,它允许用户使用任何计算机,并允许他们在有限的计算机内存中存储许多游戏。这些功能使其在游戏玩家社区中非常受欢迎。但是,许多游戏玩家报告在他们的系统中看到以下错误代码。错误代码105-无法连接到服务器。服务器可能是离线错误这个错误主要是由于连接中的一些问题而出现的。当您在系统中看到此问题时,请尝试以下常规修复并检查问题是否得到解决。重启你的路由器。重新启动您的系统。还是看到问题了?不用担心
 如何在 Windows 11 上更改 DNS 设置May 01, 2023 pm 06:58 PM
如何在 Windows 11 上更改 DNS 设置May 01, 2023 pm 06:58 PM您的ISP配置在设置互联网连接时提供默认域名系统(DNS)。这会带来各种安全威胁并降低互联网速度,因此必须手动分配DNS服务器。浏览此详细指南,了解如何更改Windows11计算机上的DNS设置并保护您的在线状态。如何更改Windows11上的DNS设置?1.使用“设置”应用使用+快捷方式转到“设置”应用。WindowsI从左侧边栏中选择网络和互联网,然后从右侧选择Wi-Fi或以太网,具体取决于您的互联网连接。向下滚动并选择硬件属性。找到DNS服务器分配设置,然后单击它
 修复:DNS 服务器没有响应 Windows 11 中的问题Jun 01, 2023 pm 04:52 PM
修复:DNS 服务器没有响应 Windows 11 中的问题Jun 01, 2023 pm 04:52 PM当Windows用户无法在系统上的浏览器上浏览或加载网页时,他们碰巧想到了可能导致此问题的所有因素。尽管许多Windows用户在他们的系统上解决此问题时,它会抛出一条错误消息,指出“DNS服务器没有响应”,用户不知道如何解决此问题以使用稳定的互联网连接。我们在这篇文章中提出了一个解决方案,它肯定会解决这个问题。但是,请事先尝试这些解决方法——尝试重新启动路由器并检查这是否导致问题。更改浏览器应用程序。也就是说,如果您使用的是MicrosoftEdge浏览器,请将其关闭并打开Google
 解决“Windows 11 上的 DNS 服务器未响应”问题的 12 种方法Apr 15, 2023 pm 10:46 PM
解决“Windows 11 上的 DNS 服务器未响应”问题的 12 种方法Apr 15, 2023 pm 10:46 PM什么是DNS?DNS是域名系统的首字母缩写词,它是一个分散的命名系统,所有计算机、服务器和更多试图连接到互联网的设备都使用它。DNS有助于识别您的PC和发送到它的流量,系统会自动破译并显示必要的信息。为什么我在Windows11上收到“DNS服务器没有响应”?这个问题可能有很多原因。有时,Windows可能会将网络问题误认为是DNS问题,而有时它很可能是第三方应用程序干扰了您的网络。最近对AVG防病毒软件的更新似乎是导致此问题的主要原因,禁用该更新似乎可以解决大多数用户的此问题

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.




















