 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI DetectGPT: Zero-shot machine-generated text detection using probabilistic curvature
DetectGPT: Zero-shot machine-generated text detection using probabilistic curvatureThe purpose of DetectGPT is to determine whether a piece of text was generated by a specific llm, such as GPT-3. To classify paragraph x, DetectGPT first generates a small perturbation on paragraph ~xi using a common pre-trained model (e.g., T5). DetectGPT then compares the log probability of the original sample x with each perturbed sample ~xi. If the average log ratio is high, the sample is likely from the source model.

ChatGPT is a hot topic. There is ongoing discussion about whether it is possible to detect that an article was generated by a large language model (LLM). DetectGPT defines a new curvature-based criterion for judging whether to generate from a given LLM. DetectGPT does not require training a separate classifier, collecting a dataset of real or generated passages, or explicitly watermarking the generated text. It uses only log probabilities computed by the model of interest and article random perturbations from another general-purpose pretrained language model (e.g., T5).
1. DetectGPT: Random permutations and assumptions
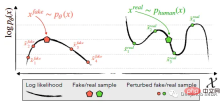
Identifies and utilizes the machine-generated channel x~pθ (left) located in the negative of logp (x) Trend in regions of curvature where nearby samples have lower model log probability on average. In contrast, human-written text x~preal(.) (right) tends not to occupy regions with significant negative log-probability curvature.
DetectGPT is based on the assumption that samples from the source model pθ usually lie in the negative curvature region of the pθ logarithmic probability function, which is different from human text. If we apply a small perturbation to a piece of text x~pθ, yielding ~x, the number of machine-generated samples log pθ(x) - log pθ(~x) should be relatively large compared to human-written text. Using this assumption, first consider a perturbation function q(.|x), which gives a distribution over ~x, a slightly modified version of x with similar meaning (usually consider a rough paragraph-length text x). For example, q(.|x) might be the result of simply asking a human to rewrite one of the sentences for x while preserving the meaning of x. Using the concept of perturbation function, the perturbation difference d (x; pθ, q) can be defined:




Sampling in semantic space ensures that all samples stay close to the data manifold, since the log probability is expected to always decrease if perturbation markers are added randomly. So the goal can be interpreted as approximately constraining the curvature on the data manifold.
4. Results display
Zero-sample machine-generated text detection

Each experiment uses 150 to 500 examples for evaluation. Machine-generated text is generated by prompting the first 30 tokens of real text. Use AUROC) to evaluate performance.
It can be seen that DetectGPT maximizes the average detection accuracy of XSum stories (AUROC increased by 0.1) and SQuAD Wikipedia context (AUROC increased by 0.05).
For 14 of the 15 dataset and model combinations, DetectGPT provides the most accurate detection performance, with an average improvement in AUROC of 0.06.
Comparison with supervised detectors
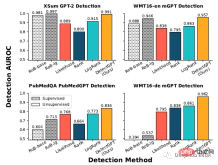
# Supervised machine-generated text detection models trained on large datasets of real and generated text are The performance on text within the distribution (top row) is as good as DetectGPT, or even better. The zero-shot method is applied to new domains (bottom row) such as PubMed medical text and German news data in WMT16.
Evaluated on 200 samples from each dataset, the supervised detector performs similarly to DetectGPT on in-distribution data such as English news, but in the case of English scientific writing, its performance is significantly worse than zero sample approach, which completely fails in German writing.
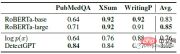
DetectGPT’s average AUROC for GPT-3 is comparable to supervised models trained specifically for machine-generated text detection.
150 examples were extracted from PubMedQA, XSum and writingprompt data sets. Two pre-trained roberta-based detector models are compared with DetectGPT and the probabilistic threshold baseline. DetectGPT can provide detections that compete with more powerful supervised models.
Variation of machine-generated text detection
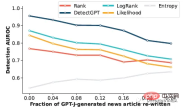
This part is to see if the detector can detect human-edited machine-generated text. Manual revision was simulated by replacing 5 word spans of the text with samples from T5–3B until r% of the text was replaced. DetectGPT maintains detection AUROC above 0.8 even though nearly a quarter of the text in the model sample has been replaced. DetectGPT shows the strongest detection performance across all revision levels.
The above is the detailed content of DetectGPT: Zero-shot machine-generated text detection using probabilistic curvature. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
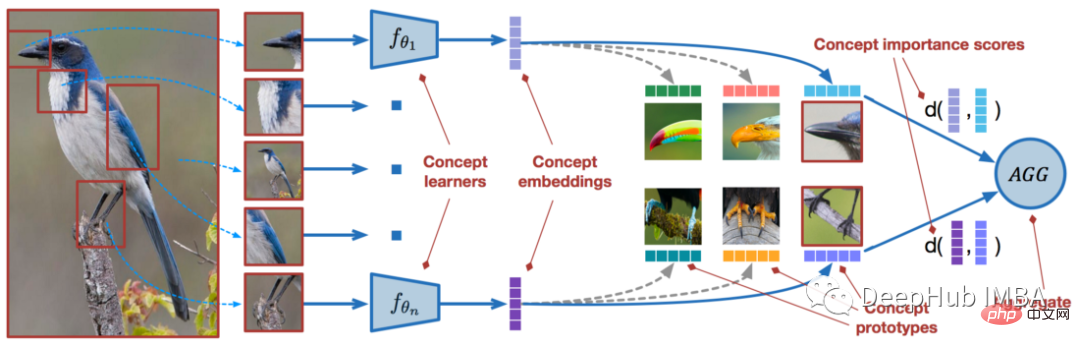 使用PyTorch进行小样本学习的图像分类Apr 09, 2023 am 10:51 AM
使用PyTorch进行小样本学习的图像分类Apr 09, 2023 am 10:51 AM近年来,基于深度学习的模型在目标检测和图像识别等任务中表现出色。像ImageNet这样具有挑战性的图像分类数据集,包含1000种不同的对象分类,现在一些模型已经超过了人类水平上。但是这些模型依赖于监督训练流程,标记训练数据的可用性对它们有重大影响,并且模型能够检测到的类别也仅限于它们接受训练的类。由于在训练过程中没有足够的标记图像用于所有类,这些模型在现实环境中可能不太有用。并且我们希望的模型能够识别它在训练期间没有见到过的类,因为几乎不可能在所有潜在对象的图像上进行训练。我们将从几个样本中学习
 为大模型提供全新科学复杂问答基准与测评体系,UNSW、阿贡、芝加哥大学等多家机构联合推出SciQAG框架Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
为大模型提供全新科学复杂问答基准与测评体系,UNSW、阿贡、芝加哥大学等多家机构联合推出SciQAG框架Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM编辑|ScienceAI问答(QA)数据集在推动自然语言处理(NLP)研究发挥着至关重要的作用。高质量QA数据集不仅可以用于微调模型,也可以有效评估大语言模型(LLM)的能力,尤其是针对科学知识的理解和推理能力。尽管当前已有许多科学QA数据集,涵盖了医学、化学、生物等领域,但这些数据集仍存在一些不足。其一,数据形式较为单一,大多数为多项选择题(multiple-choicequestions),它们易于进行评估,但限制了模型的答案选择范围,无法充分测试模型的科学问题解答能力。相比之下,开放式问答
 在自定义数据集上实现OpenAI CLIPSep 14, 2023 am 11:57 AM
在自定义数据集上实现OpenAI CLIPSep 14, 2023 am 11:57 AM在2021年1月,OpenAI宣布了两个新模型:DALL-E和CLIP。这两个模型都是多模态模型,以某种方式连接文本和图像。CLIP的全称是对比语言-图像预训练(ContrastiveLanguage-ImagePre-training),它是一种基于对比文本-图像对的预训练方法。为什么要介绍CLIP呢?因为目前火热的StableDiffusion并不是单一模型,而是由多个模型组成。其中一个关键组成部分是文本编码器,用于对用户的文本输入进行编码,而这个文本编码器就是CLIP模型中的文本编码器CL
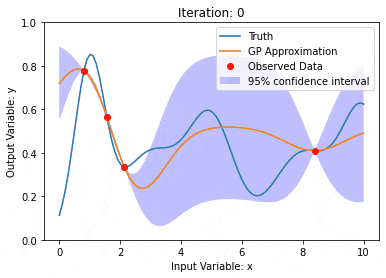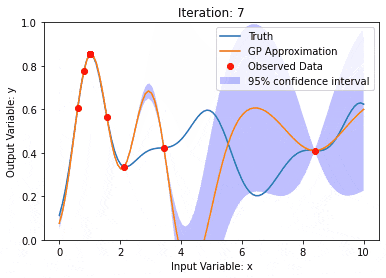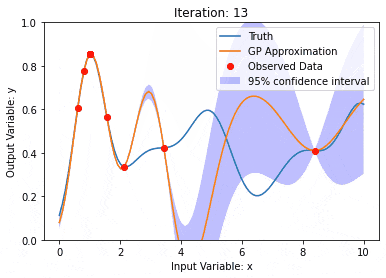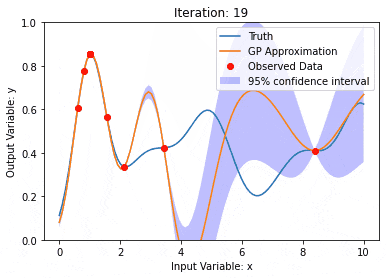 利用核模型高斯过程(KMGPs)进行数据建模Jan 30, 2024 am 11:15 AM
利用核模型高斯过程(KMGPs)进行数据建模Jan 30, 2024 am 11:15 AM核模型高斯过程(KMGPs)是一种复杂的工具,用于处理各种数据集的复杂性。它通过核函数扩展了传统高斯过程的概念。本文将详细讨论KMGPs的理论基础、实际应用和面临的挑战。核模型高斯过程是对传统高斯过程的一种扩展,用于机器学习和统计学。了解kmgp前,需掌握高斯过程基础知识,再理解核模型的作用。高斯过程(GPs)高斯过程是随机变量集合,有限个变量联合高斯分布,用于定义函数概率分布。高斯过程在机器学习中常用于回归和分类任务,可用于拟合数据的概率分布。高斯过程的一个重要特征是能够提供不确定性估计和预测
 模块化MoE将成为视觉多任务学习基础模型Apr 13, 2023 pm 12:40 PM
模块化MoE将成为视觉多任务学习基础模型Apr 13, 2023 pm 12:40 PM多任务学习(MTL)存在很多挑战,因为不同任务之间的梯度可能矛盾。为了利用任务之间的关联,作者引入了 Mod-Squad 模型,它是多个专家组成的模块化模型。模型可以灵活优化任务和专家的匹配,针对任务选择部分专家。模型让每一个专家只对应部分任务,每一个任务只对应部分专家,以此最大化利用任务之间的正向联系。Mod-Squad 整合了 Mixture of Expert (MoE) 层到 Vision Transformer 模型中,并引入了新的损失函数鼓励专家和任务之间的稀疏但强烈的依赖关系。此外
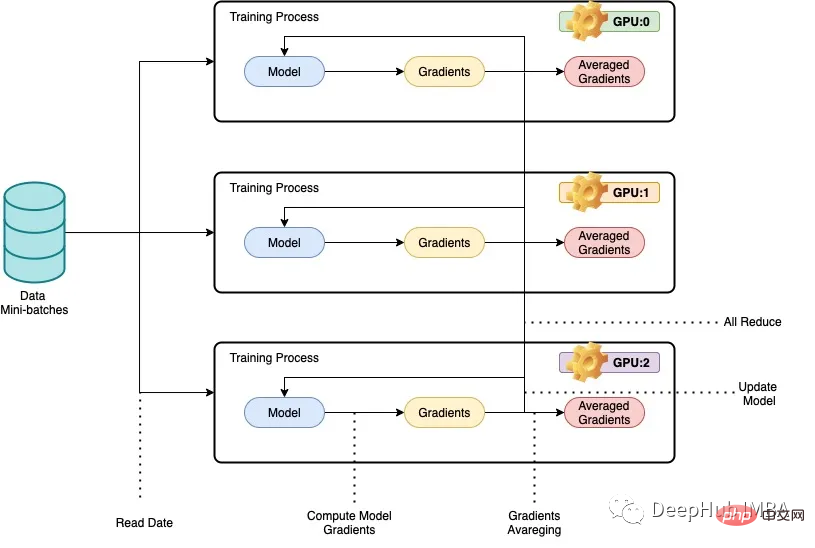 PyTorch 并行训练 DistributedDataParallel 完整代码示例Apr 10, 2023 pm 08:51 PM
PyTorch 并行训练 DistributedDataParallel 完整代码示例Apr 10, 2023 pm 08:51 PM使用大型数据集训练大型深度神经网络 (DNN) 的问题是深度学习领域的主要挑战。 随着 DNN 和数据集规模的增加,训练这些模型的计算和内存需求也会增加。 这使得在计算资源有限的单台机器上训练这些模型变得困难甚至不可能。 使用大型数据集训练大型 DNN 的一些主要挑战包括:训练时间长:训练过程可能需要数周甚至数月才能完成,具体取决于模型的复杂性和数据集的大小。内存限制:大型 DNN 可能需要大量内存来存储训练期间的所有模型参数、梯度和中间激活。 这可能会导致内存不足错误并限制可在单台机器上训练的
 计算人工智能的碳成本Apr 12, 2023 am 08:52 AM
计算人工智能的碳成本Apr 12, 2023 am 08:52 AM如果您正在寻找有趣的话题,那么人工智能 (AI) 不会让您失望。人工智能包含一组强大的令人费解的统计算法,可以下棋、破译潦草的笔迹、理解语音、分类卫星图像等等。用于训练机器学习模型的巨型数据集的可用性一直是人工智能成功的关键因素之一。但所有这些计算工作都不是免费的。一些人工智能专家越来越关注与构建新算法相关的环境影响,这场辩论引发了关于如何让机器更有效地学习以减少人工智能碳足迹的新想法。回到地球要深入了解细节,我们首先需要考虑数以千计的数据中心(遍布世界各地),它们24小时全天候处理我们的计算请
 2022年深度学习在时间序列预测和分类中的研究进展综述Apr 13, 2023 pm 12:25 PM
2022年深度学习在时间序列预测和分类中的研究进展综述Apr 13, 2023 pm 12:25 PM时间序列预测的transformers的衰落和时间序列嵌入方法的兴起,还有异常检测、分类也取得了进步2022年整个领域在几个不同的方面取得了进展,本文将尝试介绍一些在过去一年左右的时间里出现的更有前景和关键的论文,以及Flow Forecast [FF]预测框架。时间序列预测1、Are Transformers Really Effective for Time Series Forecasting?https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.13504.pdfTransfor


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool






