
Artificial intelligence (AI) has huge potential to revolutionize business operations. In fact, one study found that 67% of enterprises expect AI and machine learning use cases to increase in the coming year. These technologies have advantages in improving business efficiency, generating insights, enhancing market competitiveness, and delivering personalized customer experiences.
However, in highly regulated industries, companies face special challenges related to AI explainability. Industries such as financial services, insurance and healthcare must use transparent, auditable decision-making platforms to adhere to strict regulations and compliance standards. Today, there are many artificial intelligence solutions that automate business processes and decisions, but few provide meaningful explanations. While full of potential, businesses must never lose sight of the why behind automated decisions and predictions.
Preparing for future regulations
Today, political organizations and society are calling for greater transparency in artificial intelligence. Additionally, governments and consumers want greater visibility into the algorithms behind their credit and loan approvals, marketing campaigns, and smart home technologies. Proposed legislation in the U.S.’s Algorithmic Accountability Act and global EU AI law seek to establish standards for safe, ethical and transparent AI outcomes. However, governments are only beginning to find ways to regulate AI as use cases are still evolving and emerging.
For example, the New York City Council passed a bill targeting artificial intelligence algorithms used in employment tools. The law, which takes effect in 2023, requires employers to hire independent auditors to conduct assessments, as well as artificial intelligence tools to evaluate job applicants and current employees. The law requires bias audits of artificial intelligence tools used to screen job applicants or promote employees. Fines of up to $1,500 will be imposed for biased AI algorithms or the use of such tools without prior notification to employees and candidates. In the short term, as regulations emerge and standards evolve, businesses should focus on ways to increase transparency and prepare for future regulations.
One challenge with leveraging machine learning is that, by definition, it is built on biases. Although not all bias is harmful, when it produces results that favor or disadvantage a protected class, such as gender, race, age, etc., and has a negative impact on a person, such as approval of clinical trials, health management, loans It becomes detrimental when qualifications or credit are approved.
The need to protect algorithms and prevent harmful bias is well known. But effectively combating harmful bias requires understanding the data behind every decision or prediction. To gain critical transparency, businesses must have visibility into the algorithms comprised of machine learning and business rules that drive decisions to provide a complete audit trail. For example, insurance companies using AI for claims approval must be able to clearly explain why each decision was made.
How the “black box” problem is burdening AI innovation
With artificial intelligence, many enterprises face a problem where their AI solutions provide predictions and enable automation, but cannot explain why It puts a business at risk of significant legal or reputational harm by making a certain decision and the factors that influence the outcome.
Businesses need to be able to clearly see the reasons behind results to ensure algorithmic decisions return the expected results. Turning the black box of AI into a transparent, explainable “glass box” is critical to preventing harm to customers and consumers and reducing risk to companies and brands.
Essentially, machine learning makes predictions based on historical data. “Fairness through awareness” refers to an approach that allows businesses to determine whether a model performs equally well for various groups with a shared characteristic through the use of metadata fields, even if that characteristic is not used directly in the model. This awareness helps businesses avoid, quantify and mitigate harmful biases before they lead to unfair or harmful decisions.
A clear vision for the future of enterprise artificial intelligence
As artificial intelligence is increasingly used across the enterprise, enterprises must seek transparency and auditability from artificial intelligence to ensure that the results are not subject to The impact of harmful biases. Only when we prioritize and implement explainable, transparent AI solutions can we reduce harmful biases, reduce risk and promote trust.
While skills-based hiring is growing in popularity, myths persist about the effectiveness and merits of the practice. Addressing these misconceptions is key to promoting the changes necessary to create a fairer, more sustainable workforce.
Life for Graduates
The U.S. labor market will continue to adjust in 2022. A survey of more than 2,300 executives found that 65% expect to add new permanent positions in the first half of the year. There are also 33% of people competing to fill job openings, and there are currently more than 10.8 million job openings in the United States. Traditional recruiting practices are not a viable means of meeting workforce needs. Companies must modernize their approach to remain competitive. This means embracing skills-based hiring.
Skills-based hiring emphasizes a candidate’s technical skills and core competencies, rather than degrees or certifications, as the most critical factors for job success. This practice requires the hiring team to define the required and preferred skills for a role and objectively assess these skills to minimize bias in the hiring process.
Leading companies are increasingly turning to skills-based hiring. Below we discuss some of the biggest myths about adopting a skills-based approach and how to address them to drive a cultural shift in your company.
1. Skill-based recruitment is unfair to college graduates.
Skills-based hiring is not about excluding college graduates from consideration or lowering barriers to entry. It's about articulating the specific skills that the degree represents. This allows both degree holders and job seekers who have gained skills through other means to be considered for the position. This helps democratize economic opportunity for all and expands the talent pool available to companies.
Positions that previously did not require academic qualifications now require a four-year degree, fueling the prestige economy and causing companies to pay more costs. Under this model, many once upwardly mobile jobs become out of reach for all, available only to those who can afford the rising costs of higher education. It also excludes talent from low-income communities, especially people of color. Skills-based hiring offers a practical way to address this inequality and restores candidacy to the 66% of Americans without a bachelor’s degree, including more than 75% of Black people and more than 80% of Hispanics .
2. Skills-based hiring leads to poor hiring and hurts the business.
Adopting a skills-based approach allows for more effective screening and recruitment of candidates. Skills-based hiring is five times more predictive of future performance than education-based hiring and 2.5 times more powerful than experience-based hiring. Additionally, many businesses report that employees without degrees are as productive as college graduates, and in some cases even more productive.
Other advantages of skills-based hiring include: reduced time to hire, increased employee engagement, and lower turnover.
3. Skill-based recruitment is not a realistic talent acquisition strategy.
Maybe not in the past. Historically, recruiting teams have taken a hyper-local perspective on recruiting efforts. With remote work on the rise, businesses can launch broader candidate searches to find people who match market skills needs.
From a macro perspective, this might look like forming partnerships with workforce development businesses in under-resourced areas to build a pipeline of candidates with diverse skills to fill remote roles. Through these partnerships, companies can drive business results and economic equity simultaneously.
While designing and launching skills-based hiring takes time and requires intentional learning and letting go, your company, employees, and community will ultimately benefit. Investing in skills-based hiring now will prepare businesses for the skills-driven jobs of the future and create an economy in which all Americans can meaningfully participate in the future.
The above is the detailed content of How to Prevent AI Bias in a Fair Way. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
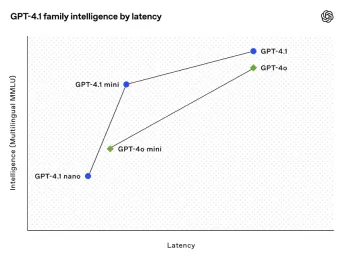 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function







