Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >Can linux get the hard disk size?
Can linux get the hard disk size?
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2023-04-13 16:41:401944browse
can be obtained. Obtaining method: 1. Use the df command to view the available and used disk space in the system, the syntax is "df -h"; 2. Use the du command to display the disk usage of files, folders, etc. in the default kilobyte size Situation; 3. Use the "ls -al" command to list the entire contents and size of a specific directory; 4. Use the stat command to display the size and other statistical information of files/directories or file systems; 5. Use " fdisk -l" command can display the disk size and disk partition information.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
Linux can get the hard disk size.
At work, we often encounter situations where the disk is full, especially after a server has been running for N years, it will be filled with various junk files, such as: intermediate files generated by compilation, Packaged image files, log files, etc.
Don’t ask me how I know, my last company’s server was like this. I need to delete some useless files every day to free up some space for work.
How to check the available space of Linux system disk? Below I will introduce to you 5 commands that I commonly use in my work.
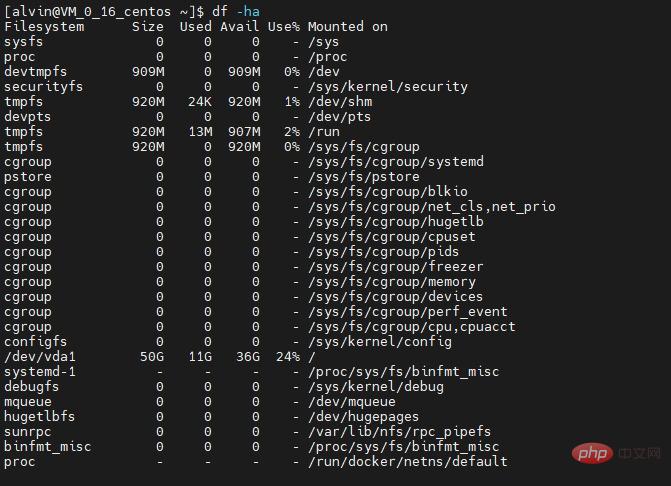
df command
#df command is the abbreviation of the English word disk-free, used to view the disk in the Linux system Available and used disk space. This command generally has the following common options:
-
df -h: Display disk space in human-readable format (otherwise the default display unit is bytes, which is not intuitive) -
df -a: Contains all file systems
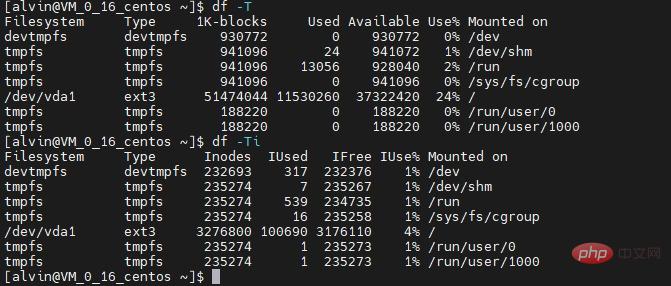
##df -T
: Displays disk usage and the file system type of each block (e.g., xfs, ext2, ext3, btrfs, etc.)- ##df -i
: Display used and free inodes
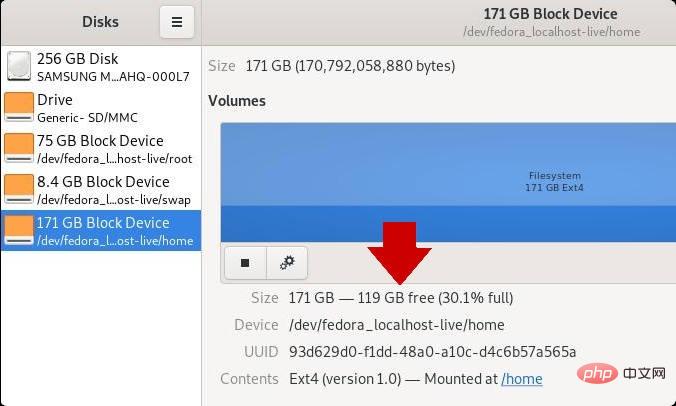
 #If you don’t like typing code and prefer to use a graphical interface, then in the GNOME desktop you can use a A software called
#If you don’t like typing code and prefer to use a graphical interface, then in the GNOME desktop you can use a A software called
(gnome-disk-utility) is used to obtain this information. Disks After booting you can view all the disks detected by your computer and click on a partition to see details about it, including used and remaining space.
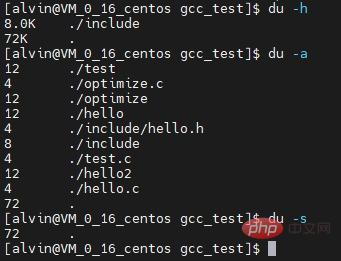
du
command is the abbreviation of the English word disk useage , which displays disk usage of files, folders, etc. in default kilobyte size. Commonly used options include the following:
- du -h
: Display the disk usage of all directories and subdirectories in human-readable format
- du -a
: Display the disk usage of all files
- du -s
: Display only the total, only List the final total value
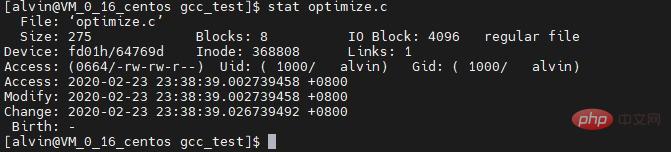
 Similarly, in the GNOME desktop, there is also a software called
Similarly, in the GNOME desktop, there is also a software called
, You can check the disk usage very intuitively. In the KDE desktop, the corresponding software is Filelight software. In both software, disk usage is mapped to a series of concentric circles, with the base folder in the middle (usually your
directory, but you can set it yourself ), each outer ring represents a deeper directory level. Hover your mouse anywhere to get detailed information about the space occupied by this part of the disk.
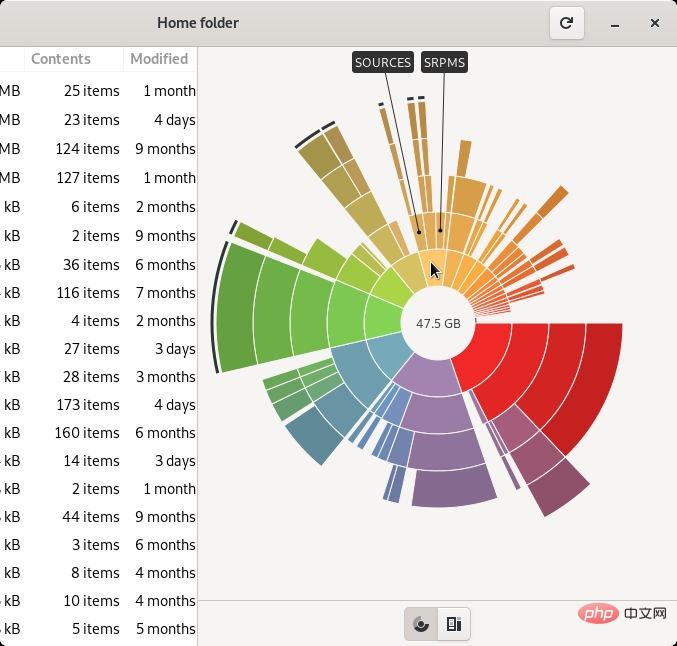
ls
The command is familiar to everyone, use ls The -al command lists the entire contents of a specific directory and its size.
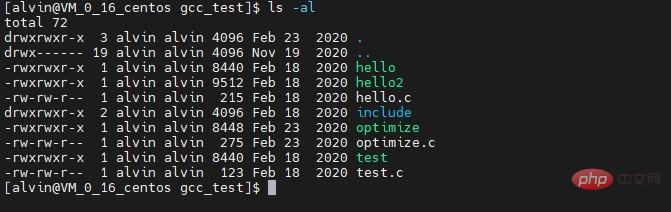
stat
The command can be directly followed by a file or directory to display the file / Directory or file system size and other statistics.
fdisk -l
can display the disk size and disk partition information.
The above commands are very commonly used when I check the available disk space, and they are all built-in commands in the Linux system and do not require additional installation. There are also some third-party tools with similar functions, such as Disks, Ncdu and other tools, which can visually display disk space utilization.
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of Can linux get the hard disk size?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

