
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are valuable tools with a wide range of applications. As artificial intelligence becomes more advanced, it will increasingly become a core part of the security landscape. Artificial intelligence has both offensive and defensive applications, used to develop new types of attacks and defend against them.
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence in the Security Field
Artificial intelligence is already used in the security field, and its role will continue to grow over time. Some of the benefits of AI in security include:
Automation of repetitive tasks: Cybersecurity requires extensive data collection, analysis, systems management and other repetitive tasks that consume analysts’ time and resources. Artificial intelligence has the potential to automate these tasks, allowing security personnel to focus their efforts where they are needed most.
Improved threat detection and response: Artificial intelligence is ideal for collecting large amounts of data, analyzing it, and responding based on the extracted insights. These capabilities can enhance an organization's threat detection and response by accelerating and extending the detection and response to cyberattacks, thereby reducing the damage attackers can do to the organization.
Enhance situational awareness and decision-making: Often, security personnel experience data overload, with too much information to process and use effectively. Artificial intelligence excels at data collection and processing, providing insights that can improve security personnel’s situational awareness and ability to make data-driven decisions.
Challenges of Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Security
Artificial intelligence is a useful tool, but it is not perfect. Some of the challenges of implementing AI in security include:
Lack of transparency and explainability: AI systems are often “black boxes” that are trained by feeding them data and enabling them to build their own models. The resulting lack of transparency makes it difficult to extract information about how AI systems make decisions, so security personnel cannot easily learn from the model or correct it.
Bias and fairness issues: An AI system’s internal model is only as good as the data used to train it. If this data contains bias, then the AI system will be biased as well—a common concern.
Integrate with existing security systems: AI systems have the ability to enhance security operations, but are most effective when they become an integrated part of an organization’s security architecture. AI-driven solutions will have limited value to the organization if they don’t work well with the organization’s other tools.
Use cases of artificial intelligence in security
There are many potential applications of artificial intelligence in security. Some example use cases include:
Endpoint Security: Artificial intelligence solutions can analyze user and application behavior to identify indicators of compromised accounts or malware on protected systems.
Cybersecurity: Artificial intelligence systems can analyze packets or trends in network traffic that may indicate various types of attacks.
Cloud Security: Artificial Intelligence solutions can help solve common challenges in cloud security, such as ensuring cloud permissions, access controls, and security settings are properly configured.
Fraud Detection: Artificial intelligence systems can analyze users for unusual or malicious behavior that may indicate potential fraud.
Best Practices for Implementing Artificial Intelligence in Security
Artificial intelligence is a powerful tool, but it can also be a dangerous tool if used incorrectly. When designing and implementing AI-based security solutions, it is important to consider the following best practices.
Developing an Artificial Intelligence Strategy
Artificial intelligence is a promising security tool. It's ideally suited to address many of the key challenges security teams face, including large data volumes, limited resources, and the need to respond quickly to cyberattacks.
However, AI is not a panacea and must be strategically integrated into an organization’s security architecture to be effective. A key part of using AI for security is determining how to best deploy AI to solve the organization's security challenges and developing a strategy for integrating AI into the organization's security architecture and processes.
Ensuring Data Quality and Privacy
AI is only as good as the data used to train and operate on it. Organizations can enhance the effectiveness of AI systems by feeding them more, higher-quality data, providing a more comprehensive and complete view of the organization’s security posture.
However, AI’s use of data may raise concerns. If the data is corrupted or incorrect, then the AI system will make incorrect decisions. Sensitive data provided to AI systems may be at risk of exposure. When developing an AI strategy, organizations should consider how to ensure data quality and privacy when running AI systems.
Establishing an ethical framework for the use of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is a "black box" and the quality of the models it uses depends on the quality of the data used to train it. If the data is biased or unfair, so will the AI model.
Artificial intelligence systems can enhance security operations, but it is important to consider and address the ethical implications of their use. For example, if bias in an AI system could negatively impact an organization's employees, customers, suppliers, etc., then the AI system should not be relied upon as the final authority when making those decisions.
Test and update artificial intelligence models regularly
The quality of an artificial intelligence system model depends on the data used to train it. If the data is incomplete, biased, or out of date, then the AI system may not be able to make the best decisions.
Organizations using artificial intelligence systems should regularly test and update models to ensure they are current and correct. This is especially true when using AI for security, as the rapidly evolving security landscape means older AI models may not be able to detect new attacks.
The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Security
There is no doubt that the role of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity will only grow with time. Here are three predictions for how the role of artificial intelligence in security will evolve:
Advances in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning have received significant attention in recent years. , but the technology is still in its infancy. As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies improve and advance, their utility and potential security applications will only increase.
Integration with other emerging technologies
Artificial intelligence is emerging and developing simultaneously with other technologies such as 5G mobile networks and the Internet of Things. The integration of these emerging technologies has important implications for security, combining the data collection and remote management capabilities of IoT with the decision-making capabilities of artificial intelligence.
Impact on the security industry and job market
Like many other industries, artificial intelligence will have an impact on the security industry and the job market. As AI is used to perform repetitive tasks and enhance safety operations, human operator roles will increasingly focus on working with these systems to deliver enhanced safety at scale.
The above is the detailed content of What is AI cybersecurity?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Tool Calling in LLMsApr 14, 2025 am 11:28 AM
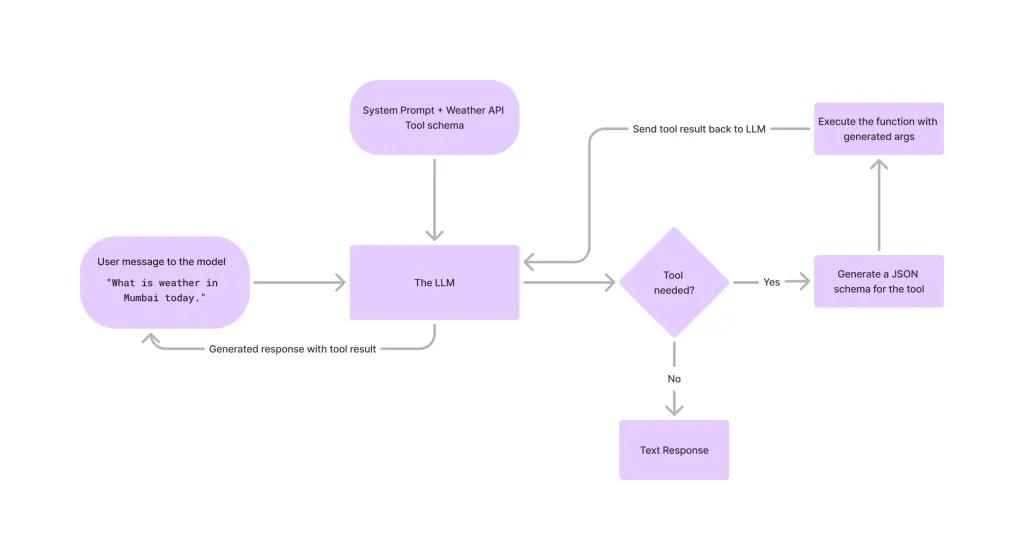
Tool Calling in LLMsApr 14, 2025 am 11:28 AMLarge language models (LLMs) have surged in popularity, with the tool-calling feature dramatically expanding their capabilities beyond simple text generation. Now, LLMs can handle complex automation tasks such as dynamic UI creation and autonomous a
 How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global HealthApr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global HealthApr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AMCan a video game ease anxiety, build focus, or support a child with ADHD? As healthcare challenges surge globally — especially among youth — innovators are turning to an unlikely tool: video games. Now one of the world’s largest entertainment indus
 UN Input On AI: Winners, Losers, And OpportunitiesApr 14, 2025 am 11:25 AM
UN Input On AI: Winners, Losers, And OpportunitiesApr 14, 2025 am 11:25 AM“History has shown that while technological progress drives economic growth, it does not on its own ensure equitable income distribution or promote inclusive human development,” writes Rebeca Grynspan, Secretary-General of UNCTAD, in the preamble.
 Learning Negotiation Skills Via Generative AIApr 14, 2025 am 11:23 AM
Learning Negotiation Skills Via Generative AIApr 14, 2025 am 11:23 AMEasy-peasy, use generative AI as your negotiation tutor and sparring partner. Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining
 TED Reveals From OpenAI, Google, Meta Heads To Court, Selfie With MyselfApr 14, 2025 am 11:22 AM
TED Reveals From OpenAI, Google, Meta Heads To Court, Selfie With MyselfApr 14, 2025 am 11:22 AMThe TED2025 Conference, held in Vancouver, wrapped its 36th edition yesterday, April 11. It featured 80 speakers from more than 60 countries, including Sam Altman, Eric Schmidt, and Palmer Luckey. TED’s theme, “humanity reimagined,” was tailor made
 Joseph Stiglitz Warns Of The Looming Inequality Amid AI Monopoly PowerApr 14, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Joseph Stiglitz Warns Of The Looming Inequality Amid AI Monopoly PowerApr 14, 2025 am 11:21 AMJoseph Stiglitz is renowned economist and recipient of the Nobel Prize in Economics in 2001. Stiglitz posits that AI can worsen existing inequalities and consolidated power in the hands of a few dominant corporations, ultimately undermining economic
 What is Graph Database?Apr 14, 2025 am 11:19 AM
What is Graph Database?Apr 14, 2025 am 11:19 AMGraph Databases: Revolutionizing Data Management Through Relationships As data expands and its characteristics evolve across various fields, graph databases are emerging as transformative solutions for managing interconnected data. Unlike traditional
 LLM Routing: Strategies, Techniques, and Python ImplementationApr 14, 2025 am 11:14 AM
LLM Routing: Strategies, Techniques, and Python ImplementationApr 14, 2025 am 11:14 AMLarge Language Model (LLM) Routing: Optimizing Performance Through Intelligent Task Distribution The rapidly evolving landscape of LLMs presents a diverse range of models, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Some excel at creative content gen


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






