
Life is short, novices learn Python!
I am a rookie brother. Today, we will share 6 magical built-in functions at once. In many computer books, they are also usually introduced as higher-order functions. And in my daily work, I often use them to make code faster and easier to understand.

Lambda function
The Lambda function is used to create anonymous functions, that is, functions without names. It is just an expression, and the function body is much simpler than def. Anonymous functions are used when we need to create a function that performs a single operation and can be written in one line.
lambda [arg1 [,arg2,.....argn]]:expression
The body of lambda is an expression, not a code block. Only limited logic can be encapsulated in lambda expressions. For example:
lambda x: x+2
If we also want to call the function defined by def at any time, we can assign the lambda function to such a function object.
add2 = lambda x: x+2 add2(10)
Output result:

Using the Lambda function, the code can be simplified a lot. Here is another example.
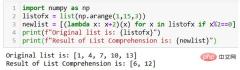
As shown in the figure above, the result list newlist is generated with one line of code using the lambda function.
Map function
The map() function maps a function to all elements of an input list.
map(function,iterable)
For example, we first create a function to return an uppercase input word, and then apply this function to all elements in the list colors.
def makeupper(word): return word.upper() colors=['red','yellow','green','black'] colors_uppercase=list(map(makeupper,colors)) colors_uppercase
Output result:

In addition, we can also use anonymous function lambda to cooperate with the map function, which can be more streamlined.
colors=['red','yellow','green','black'] colors_uppercase=list(map(lambda x: x.upper(),colors)) colors_uppercase
If we don’t use the Map function, we need to use a for loop.

#As shown in the figure above, in actual use, the Map function will be 1.5 times faster than the for loop method of sequentially listing elements.
Reduce function
Reduce() is a very useful function when you need to perform some calculations on a list and return the result. For example, when you need to calculate the product of all elements of a list of integers, you can use the reduce function. [1]
The biggest difference between it and the function is that the mapping function (function) in reduce() receives two parameters, while map receives one parameter.
reduce(function, iterable[, initializer])
Next we use an example to demonstrate the code execution process of reduce().
from functools import reduce def add(x, y) : # 两数相加 return x + y numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] sum1 = reduce(add, numbers) # 计算列表和
The result sum1 = 15 is obtained, and the code execution process is shown in the animation below.

▲Code execution process animation
Combined with the above figure, we will see that reduce applies an addition function add() to a list[1 ,2,3,4,5], the mapping function receives two parameters, and reduce() continues to accumulate the result with the next element of the list.
In addition, we can also use anonymous function lambda to cooperate with the reduce function, which can be more streamlined.
from functools import reduce numbers = [1,2,3,4,5] sum2 = reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, numbers)
The output sum2= 15 is obtained, which is consistent with the previous result.
Note: reduce() has been moved to the functools module since Python 3.x [2]. If we want to use it, we need to import it from functools import reduce.
enumerate function
The enumerate() function is used to combine a traversable data object (such as a list, tuple or string) into an index sequence, while listing the data and data subscripts. It is generally used in for loops. Its syntax is as follows:
enumerate(iterable, start=0)
Its two parameters, one is a sequence, iterator or other object that supports iteration; the other is the starting position of the subscript, which starts from 0 by default, and can also be used since Defines the starting number of the counter.
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'green', 'black'] result = enumerate(colors)
If we have a color list that stores colors, we will get an enumerate object after running it. It can be used directly in a for loop or converted to a list. The specific usage is as follows.
for count, element in result:
print(f"迭代编号:{count},对应元素:{element}")

Zip 函数
zip()函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表[3]。
我们还是用两个列表作为例子演示:
colors = ['red', 'yellow', 'green', 'black'] fruits = ['apple', 'pineapple', 'grapes', 'cherry'] for item in zip(colors,fruits): print(item)
输出结果:

当我们使用zip()函数时,如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同。
prices =[100,50,120] for item in zip(colors,fruits,prices): print(item)

Filter 函数
filter()函数用于过滤序列,过滤掉不符合条件的元素,返回由符合条件元素组成的新列表,其语法如下所示[4]。
filter(function, iterable)
比如举个例子,我们可以先创建一个函数来检查单词是否为大写,然后使用filter()函数过滤出列表中的所有奇数:
def is_odd(n): return n % 2 == 1 old_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] new_list = filter(is_odd, old_list) print(newlist)
输出结果:

今天分享的这6个内置函数,在使用 Python 进行数据分析或者其他复杂的自动化任务时非常方便。
The above is the detailed content of Six magical built-in functions in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of UseApr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of UseApr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 Python vs. C : Memory Management and ControlApr 19, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Python vs. C : Memory Management and ControlApr 19, 2025 am 12:17 AMPython and C have significant differences in memory management and control. 1. Python uses automatic memory management, based on reference counting and garbage collection, simplifying the work of programmers. 2.C requires manual management of memory, providing more control but increasing complexity and error risk. Which language to choose should be based on project requirements and team technology stack.
 Python for Scientific Computing: A Detailed LookApr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python for Scientific Computing: A Detailed LookApr 19, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython's applications in scientific computing include data analysis, machine learning, numerical simulation and visualization. 1.Numpy provides efficient multi-dimensional arrays and mathematical functions. 2. SciPy extends Numpy functionality and provides optimization and linear algebra tools. 3. Pandas is used for data processing and analysis. 4.Matplotlib is used to generate various graphs and visual results.
 Python and C : Finding the Right ToolApr 19, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Python and C : Finding the Right ToolApr 19, 2025 am 12:04 AMWhether to choose Python or C depends on project requirements: 1) Python is suitable for rapid development, data science, and scripting because of its concise syntax and rich libraries; 2) C is suitable for scenarios that require high performance and underlying control, such as system programming and game development, because of its compilation and manual memory management.
 Python for Data Science and Machine LearningApr 19, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python for Data Science and Machine LearningApr 19, 2025 am 12:02 AMPython is widely used in data science and machine learning, mainly relying on its simplicity and a powerful library ecosystem. 1) Pandas is used for data processing and analysis, 2) Numpy provides efficient numerical calculations, and 3) Scikit-learn is used for machine learning model construction and optimization, these libraries make Python an ideal tool for data science and machine learning.
 Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Learning Python: Is 2 Hours of Daily Study Sufficient?Apr 18, 2025 am 12:22 AMIs it enough to learn Python for two hours a day? It depends on your goals and learning methods. 1) Develop a clear learning plan, 2) Select appropriate learning resources and methods, 3) Practice and review and consolidate hands-on practice and review and consolidate, and you can gradually master the basic knowledge and advanced functions of Python during this period.
 Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python for Web Development: Key ApplicationsApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMKey applications of Python in web development include the use of Django and Flask frameworks, API development, data analysis and visualization, machine learning and AI, and performance optimization. 1. Django and Flask framework: Django is suitable for rapid development of complex applications, and Flask is suitable for small or highly customized projects. 2. API development: Use Flask or DjangoRESTFramework to build RESTfulAPI. 3. Data analysis and visualization: Use Python to process data and display it through the web interface. 4. Machine Learning and AI: Python is used to build intelligent web applications. 5. Performance optimization: optimized through asynchronous programming, caching and code
 Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Exploring Performance and EfficiencyApr 18, 2025 am 12:20 AMPython is better than C in development efficiency, but C is higher in execution performance. 1. Python's concise syntax and rich libraries improve development efficiency. 2.C's compilation-type characteristics and hardware control improve execution performance. When making a choice, you need to weigh the development speed and execution efficiency based on project needs.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool






