 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI The real hero behind ChatGPT: OpenAI chief scientist Ilya Sutskever's leap of faith
The real hero behind ChatGPT: OpenAI chief scientist Ilya Sutskever's leap of faithThe real hero behind ChatGPT: OpenAI chief scientist Ilya Sutskever's leap of faith
The emergence of ChatGPT has attracted much attention, but we should not forget the unknown genius behind it. Ilya Sutskever is the co-founder and chief scientist of OpenAI. It was under his leadership that OpenAI made significant progress in developing cutting-edge technologies and advancing the field of artificial intelligence.
In this article, we will explore how Sutskever went from a young researcher to one of the leading figures in the field of artificial intelligence in two decades. Whether you are an AI enthusiast, a researcher, or simply someone curious about the inner workings of this field, this article will provide valuable perspective and information.
This article follows the following timeline:
2003: Ilya Sutskever’s apprenticeship journey
2011: First introduction to AGI
2012: The revolution in image recognition
2013: Auction of DNNresearch to Google
2014: The revolution in language translation
2015: From Google to OpenAI: The new era of artificial intelligence Chapter
2018: GPT 1, 2 and 3
2021: Development of DALL-E 1
2022: Unveiling ChatGPT to the world
Ilya Sutskever
Co-founder and chief scientist of OpenAI, graduated from the University of Toronto in 2005 and received a CS degree in 2012 Ph.D. From 2012 to the present, he has worked at Stanford University, DNNResearch, and Google Brain, conducting research related to machine learning and deep learning. In 2015, he gave up his high-paying position at Google and co-founded OpenAI with Greg Brockman and others. Developed GPT-1, 2, 3 and DALLE series models. In 2022, he was elected as a fellow of the Royal Society of Science. He is a pioneer in the field of artificial intelligence who has been instrumental in shaping the current landscape of artificial intelligence and continues to push the boundaries of what is possible with machine learning. His passion for artificial intelligence has informed his groundbreaking research, which has shaped the development of the fields of deep learning and machine learning.
2003: First impression of Ilya Sutskever

Sutskever: I don’t understand. Hinton: Why don’t you understand? Sutskever: People train neural networks to solve problems. When people want to solve different problems, they have to start training again with another neural network. But I think people should have a neural network that can solve all problems.
When he was an undergraduate at the University of Toronto, Sutskever wanted to join Professor Geoffrey Hinton’s deep learning laboratory. So, he knocked on the door of Professor Hinton's office one day and asked if he could join the laboratory. The professor asked him to make an appointment in advance, but Sutskever didn't want to waste any more time, so he immediately asked: "How about now?"
Hinton realized that Sutskever was a keen student, so he gave He had two papers for him to read. A week later, Sutskever returned to the professor's office and told him he didn't understand.
"Why don't you understand?" the professor asked.
 ##“People train neural networks to solve problems, and when people want to solve a different problem, they have to start over with another neural network. But I think people should have a neural network that can solve all problems."
##“People train neural networks to solve problems, and when people want to solve a different problem, they have to start over with another neural network. But I think people should have a neural network that can solve all problems."
This passage demonstrates Sutskever's unique ability to draw conclusions, and this With abilities that would take even experienced researchers years to find, Hinton extended an invitation to join his lab.
######2011: First acquaintance with AGI############################# Sutskever: Me Don’t agree with this idea (AGI)#########When Sutskever was still at the University of Toronto, he flew to London to find a job at DeepMind. There he met Demis Hassabis and Shane Legg (co-founders of DeepMind), who were building AGI (Artificial General Intelligence). AGI is a general artificial intelligence that can think and reason like humans and complete various tasks related to human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, learning from experience, making decisions, and solving problems.
At the time, AGI was not something serious researchers would talk about. Sutskever also felt they had lost touch with reality, so he turned down the job, went back to college, and eventually joined Google in 2013.
2012: Image Recognition Revolution

Winning the ImageNet competition
Geoffrey Hinton has a unique vision and believed in deep learning when others did not. And he firmly believes that success in the ImageNet competition will settle this debate once and for all.
ImageNet Competition: The Stanford University Laboratory holds the ImageNet Competition every year. They provide contestants with a massive database of carefully labeled photos, and researchers from around the world come to compete to try to create a system that can recognize the most images.
Two of Hinton’s students, Ilya Sutskever and Alex Krizhevsky, participated in this competition. They broke the traditional manual design scheme, adopted a deep neural network, and broke through the 75% accuracy mark. So they won the ImageNet competition and their system was later named AlexNet.
Since then, the field of image recognition has taken on a completely new look.
Later, Sutskever, Krizhevsky, and Hinton published a paper on AlexNet, which became one of the most cited papers in computer science, cited by a total of other researchers More than 60,000 times.
2013: Auction of DNNresearch to Google

##Sutskever&Krizhevsky : You deserve a greater percentage of your dividends. Hinton: You're sharing too much of my money. Sutskever&Krizhevsky: But we have already decided to give you the lion’s share. Hinton: It speaks to their character.
Hinton, together with Sutskever and Krizhevsky, formed a new company called DNNresearch. They don't have any products and have no plans to build any in the future.
Hinton asked the lawyer how to maximize the value of his new company, even though it currently only has three employees, no products, and no foundation. One of the options the lawyer gave him was to set up an auction. Four companies were involved in the acquisition: Baidu, Google, Microsoft and DeepMind (then a young startup based in London). The first to exit was DeepMind, followed by Microsoft, and finally only Baidu and Google were left competing.
By close to midnight one night, the auction price was as high as $44 million, and Hinton paused the bidding and went to sleep. The next day, he announced that the auction was over and sold his company to Google for $44 million, deciding that finding the right home for his research was more important. At this point, Hinton, like his students, puts their ideas ahead of financial gain.
When it came time to split the proceeds, Sutskever and Krizhevsky insisted that Hinton should get a larger share (40%), even though Hinton suggested that they might as well get some sleep. The next day, they still insisted on this distribution method. Hinton later commented: "It reflects who they are as people, not me."
After that, Sutskever became a research scientist at Google Brain. His ideas changed even more and began to gradually align with those of the founder of DeepMind. He began to believe that AGI's future was right in front of him. Of course, Sutskever himself has never been afraid to change his mind in the face of new information or experience. After all, believing in AGI requires a leap of faith, As Sergey Levine (Sutskever’s colleague at Google) commented on Sutskever: "He is a man who is not afraid to 'believe.'"
2014: The Revolution in Language Translation

Sutskever: The correct conclusion is that if you have a very large data set and a very large neural network, then success is inevitable. (The best performing translator)
After acquiring DNNResearch, Google hired Sutskever as a research scientist at Google Brain.
While working at Google, Sutskever invented a variant of a neural network that could translate English into French. He proposed "Sequence to Sequence Learning", which captures the sequence structure of the input (such as an English sentence) and maps it to an output that also has a sequence structure (such as a French sentence).
He said the researchers didn't believe neural networks could translate, so it was a big surprise when they actually did. His invention beats the best-performing translators and provides a major upgrade to Google Translate. Language translation will never be the same again.
2015: From Google to OpenAI: A new chapter in artificial intelligence

Sam Altman and Greg Brockman brought Sutskever and nine other researchers together to see if it was still possible to form a research lab with the best minds in the field. When discussions began about the lab that would become OpenAI, Sutskever realized he had found a group of like-minded people who shared his beliefs and aspirations.
Brockman extended invitations to the 10 researchers to join his lab and gave them three weeks to decide. When Google found out about this, they offered Sutskever a substantial amount of money to join them. After being rejected, Google increased their salary to nearly $2 million in the first year, which was two or three times what OpenAI was paying him.
But Sutskever happily passed up a multimillion-dollar job offer at Google to eventually become a co-founder of the nonprofit OpenAI.
OpenAI’s goal is to use artificial intelligence to benefit all mankind and advance artificial intelligence in a responsible manner.
2018: Development of GPT 1, 2 & 3

Led by Sutskever OpenAI invented GPT-1, which was subsequently developed into GPT-2, GPT-3 and ChatGPT.
GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) model is a series of language models based on neural networks. Every update of the GPT model is a breakthrough in the field of natural language processing.
- GPT-1 (2018) : This is the first model in the series, trained on a large-scale Internet text dataset. One of its key innovations is the use of unsupervised pre-training, where the model learns to predict words in a sentence based on the context of preceding words. This enables the model to learn language structures and generate human-like text.
- GPT-2 (2019) : In GPT- 1, it was trained on a larger data set, resulting in a more powerful model. One of the major advancements of GPT-2 is its ability to generate coherent and fluent text passages on a wide range of topics, making it a key player in unsupervised language understanding and generation tasks.
- ##GPT-3 (2020):GPT-3 is a substantial leap forward in both scale and performance. It was trained on a massive dataset using 175 billion parameters, much larger than previous models. GPT-3 achieves state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of language tasks, such as question answering, machine translation, and summarization, with near-human capabilities. It also shows the ability to perform simple coding tasks, write coherent news articles, and even generate poetry.
- GPT-4: Expected to appear soon, expected to be 2023.
2021: Development of DALL-E 1

Many of today's major image generators - DALL-E 2, MidJourney - owe their roots to DALL-E 1, as they are based on the same transformer architecture and work on similar Training is performed on image datasets and related text descriptions. In addition, both DALL-E 2 and MidJourney are based on the fine-tuning process of DALL-E 1.
2022: Unveiling ChatGPT to the world

ChatGPT works by pre-training a deep neural network on a large text dataset and then fine-tuning it on a specific task, such as answering questions or generating text. It is a conversational artificial intelligence system based on the GPT-3 language model.
Understanding the context of a conversation and generating appropriate responses is one of ChatGPT’s primary features. The bot remembers your conversation threads and makes follow-up responses based on previous questions and answers. Unlike other chatbots, which are often limited to pre-programmed reactions, ChatGPT can generate reactions within the app, allowing it to have more dynamic and diverse conversations.
Elon Musk is one of the founders of OpenAI. He said:
"ChatGPT is terrifyingly good. We are not far away from dangerously powerful artificial intelligence. ". Endnotes
Ilya Sutskever’s passion for artificial intelligence drove his groundbreaking research that changed the course of the field. His work in deep learning and machine learning has been instrumental in advancing the state of the art and shaping the future direction of the field.We have also witnessed firsthand the impact of Sutskever’s work in the field of artificial intelligence. He has changed the course of the field and will continue to work in this direction. Despite facing material temptations many times, Sutskever chose to pursue his passion and focus on his research; his dedication to his work is exemplary for any researcher. 
Now we have witnessed the impact Sutskever has had on our world. Obviously, this is just the beginning.
The above is the detailed content of The real hero behind ChatGPT: OpenAI chief scientist Ilya Sutskever's leap of faith. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Personal Hacking Will Be A Pretty Fierce BearMay 11, 2025 am 11:09 AMCyberattacks are evolving. Gone are the days of generic phishing emails. The future of cybercrime is hyper-personalized, leveraging readily available online data and AI to craft highly targeted attacks. Imagine a scammer who knows your job, your f
 Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AM
Pope Leo XIV Reveals How AI Influenced His Name ChoiceMay 11, 2025 am 11:07 AMIn his inaugural address to the College of Cardinals, Chicago-born Robert Francis Prevost, the newly elected Pope Leo XIV, discussed the influence of his namesake, Pope Leo XIII, whose papacy (1878-1903) coincided with the dawn of the automobile and
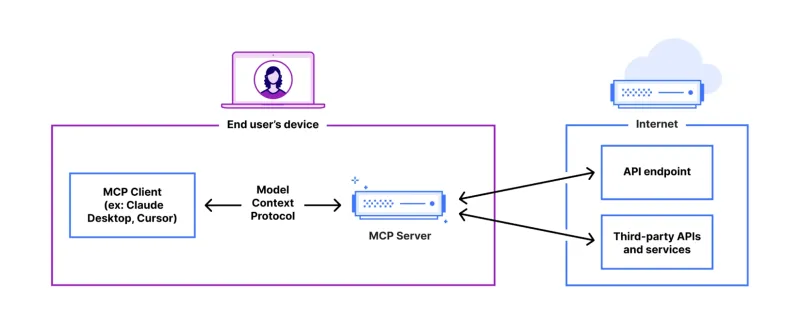 FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AM
FastAPI-MCP Tutorial for Beginners and Experts - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:56 AMThis tutorial demonstrates how to integrate your Large Language Model (LLM) with external tools using the Model Context Protocol (MCP) and FastAPI. We'll build a simple web application using FastAPI and convert it into an MCP server, enabling your L
 Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AM
Dia-1.6B TTS : Best Text-to-Dialogue Generation Model - Analytics VidhyaMay 11, 2025 am 10:27 AMExplore Dia-1.6B: A groundbreaking text-to-speech model developed by two undergraduates with zero funding! This 1.6 billion parameter model generates remarkably realistic speech, including nonverbal cues like laughter and sneezes. This article guide
 3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AM
3 Ways AI Can Make Mentorship More Meaningful Than EverMay 10, 2025 am 11:17 AMI wholeheartedly agree. My success is inextricably linked to the guidance of my mentors. Their insights, particularly regarding business management, formed the bedrock of my beliefs and practices. This experience underscores my commitment to mentor
 AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AM
AI Unearths New Potential In The Mining IndustryMay 10, 2025 am 11:16 AMAI Enhanced Mining Equipment The mining operation environment is harsh and dangerous. Artificial intelligence systems help improve overall efficiency and security by removing humans from the most dangerous environments and enhancing human capabilities. Artificial intelligence is increasingly used to power autonomous trucks, drills and loaders used in mining operations. These AI-powered vehicles can operate accurately in hazardous environments, thereby increasing safety and productivity. Some companies have developed autonomous mining vehicles for large-scale mining operations. Equipment operating in challenging environments requires ongoing maintenance. However, maintenance can keep critical devices offline and consume resources. More precise maintenance means increased uptime for expensive and necessary equipment and significant cost savings. AI-driven
 Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Why AI Agents Will Trigger The Biggest Workplace Revolution In 25 YearsMay 10, 2025 am 11:15 AMMarc Benioff, Salesforce CEO, predicts a monumental workplace revolution driven by AI agents, a transformation already underway within Salesforce and its client base. He envisions a shift from traditional markets to a vastly larger market focused on
 AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AM
AI HR Is Going To Rock Our Worlds As AI Adoption SoarsMay 10, 2025 am 11:14 AMThe Rise of AI in HR: Navigating a Workforce with Robot Colleagues The integration of AI into human resources (HR) is no longer a futuristic concept; it's rapidly becoming the new reality. This shift impacts both HR professionals and employees, dem


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)






