 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Hot paper creates the prototype of 'Westworld': 25 AI agents grow freely in the virtual town
Hot paper creates the prototype of 'Westworld': 25 AI agents grow freely in the virtual townCan we create a world? In that world, robots can live, work, and socialize like humans, replicating all aspects of human society.
This kind of imagination has been perfectly restored in the setting of the film and television work "Westworld": many robots with pre-installed storylines were put into a theme park, They can behave like humans, remembering things they see, people they meet, and words they say. Each day, the bots are reset and returned to their core storyline.

Stills from "Westworld", the character on the left is a robot pre-installed with a storyline.
Expand your imagination: today, what would we do if we wanted to turn a large language model like ChatGPT into the master of Western World? ?
In a recent popular paper, researchers successfully built a "virtual town" in which 25 AI agents survive. Not only can they Engage in complex behaviors (such as hosting a Valentine's Day party) that are more realistic than human role-playing.
- Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.03442v1.pdf
- Demo address: https://reverie.herokuapp.com/arXiv_Demo/
From sandbox games like "The Sims" to cognitive models , virtual environments and other applications, for more than 40 years, researchers have been envisioning the creation of intelligent agents that can achieve trustworthy human behavior. In these scenarios, computationally driven agents behave consistently with their past experiences and respond believably to their environment. This simulation of human behavior can fill virtual spaces and communities with real social phenomena, train "people" to deal with rare but difficult interpersonal relationships, test social science theories, produce human processor models for theory and usability testing, and provide ubiquitous computing Application and social robot dynamics can also lay the foundation for NPC characters to navigate complex human relationships in the open world.
But the space of human behavior is huge and complex. Although large language models can simulate believable human behavior at a single point in time, to ensure long-term consistency, a general-purpose agent needs an architecture to manage growing memories as new interactions, conflicts, and events occur over time. and emerge and fade, while also dealing with the cascading social dynamics unfolding between multiple agents.
If a method can retrieve relevant events and interactions over a long period of time, reflect on these memories, and generalize and draw higher-level inferences, and apply this If we use this type of reasoning to create plans and responses that are meaningful to current and long-term agent behavior, then we are not far from realizing our dream.
This new paper introduces "Generative Agents" (generative agents), a type of agents that use generative models to simulate believable human behavior, and demonstrates that they can produce trustworthy human behaviors. Simulation of individual and emergent group behaviors:
- Ability to make broad inferences about oneself, other agents, and the environment;
- Ability to create daily plans that reflect one's own characteristics and experiences, execute these plans, react, and re-plan when appropriate; react when language commands them.
Behind "Generative Agents" is a new agent architecture that can store, synthesize and apply relevant memories using large languages Models generate believable behavior. 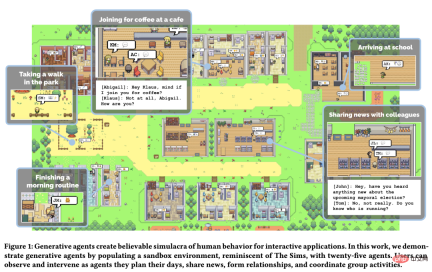
For example, "Generative Agents" will turn off the stove if they see their breakfast burning; if there is someone in the bathroom, they will wait outside; if they meet another agent they want to talk to, they will stop Come down and chat. A society full of "Generative Agents" is marked by emerging social dynamics, in which new relationships are formed, information is diffused, and coordination occurs among agents.
Specifically, the researcher announced several important details in this paper:
- Generative Agents are the A credible simulation of human behavior that dynamically adjusts based on the agent's changing experience and environment;
- A novel architecture that makes it possible for Generative Agents to remember, retrieve, Reflect, interact with other agents, and plan through dynamically evolving environments. The architecture leverages the powerful prompt capabilities of large language models and complements these capabilities to support long-term consistency of the agent, memory capabilities to manage dynamic evolution, and the recursive generation of additional generations;
- Two evaluations (control evaluation and end-to-end evaluation) to determine the cause-and-effect relationships of the importance of each component of the architecture, as well as to identify failures due to improper memory retrieval, etc.;
- The opportunities and ethical and social risks of Generative Agents in interactive systems are discussed. The researchers believe these agents should be tuned to mitigate the risk of users forming parasitic social relationships, documented to mitigate the risks posed by deepfakes and customized persuasion, and designed to complement rather than replace human interests. be applied in a different way.
Once the article was published, it aroused heated discussion across the Internet. Karpathy, who was already optimistic about the direction of "AutoGPT", praised repeatedly, thinking that "Generative Agents" is not a little bit better than "Open World", which he played with the concept before:

Some researchers assert that the release of this research means that "large language models have achieved a new milestone":
"Generative Agents" behavior and interaction
To make “Generative Agents” more concrete, the study instantiates them as characters in a sandbox world.
Twenty-five agents live in a small town called Smallville, each represented by a simple avatar. All characters can:
- Communicate with others and the environment;
- Remember and recall what they have done and observed things;
- Reflect on these observations;
- Make a daily plan.
The researchers used natural language to describe the identity of each agent, including their occupation and relationship with other agents, And use this information as seed memory. For example, the agent John Lin has the following description (this article excerpts):
"John Lin is a drugstore owner who is willing to help others. He is always looking for ways to make customers more intelligent. Easy way to get drugs. John Lin's wife is university professor Mei Lin, and they live together with their son Eddy Lin, who studies music theory; John Lin loves his family very much; John Lin has known the old couple next door, Sam Moore and Jennifer Moore, for several years Years..."
After the identity is set, the next step is how the agent interacts with the world.
In each step of the sandbox, the agents output a natural language statement to describe their current actions, such as the statement "Isabella Rodriguez is writing a diary", "Isabella Rodriguez Checking mail" etc. These natural languages are then translated into concrete actions that affect the sandbox world. Actions are displayed on the sandbox interface as a set of emoticons that provide an abstract representation of the action.
To achieve this, the research employs a language model that converts actions into a set of emojis that appear in a dialog box above each agent avatar. For example, "Isabella Rodriguez is writing in her diary" appears as , and "Isabella Rodriguez is checking emails" appears as . Additionally, a full natural language description can be accessed by clicking on the agent avatar.
Agents communicate in natural language. If an agent realizes that there are other agents around it, they will think about whether to go over and chat. For example, Isabella Rodriguez and Tom Moreno had a conversation about the upcoming election:

In addition to this, users can also specify what role the agent plays, For example, if you designate one of the agents as a reporter, you can consult the agent for news content.
Interaction between the agent and the environment
Smallville town has many public scenes, including cafes, bars, parks, schools, dormitories, Houses and shops. In addition, each public scene also includes its own functions and objects, such as a kitchen in a house and a stove in the kitchen (Figure 2). There are also beds, tables, wardrobes, shelves, bathrooms and kitchens in the living space of the intelligent agent.
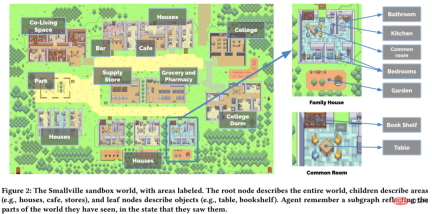
Agents can move around Smallville, enter or leave a building, navigate forward, and even approach another agent. The agent's movement is controlled by Generative Agents' architecture and sandbox game engine: when the model instructs the agent to move to a certain location, the study calculates its walking path to its destination in the Smallville environment, and the agent starts moving.
In addition, users and agents can also affect the status of other objects in the environment. For example, the bed is occupied when the agent is sleeping, and the refrigerator may be occupied when the agent has finished using the breakfast. is empty. End users can also rewrite the agent environment through natural language. For example, the user sets the shower status to leaking when Isabella enters the bathroom, and then Isabella will find tools from the living room and try to fix the leaking problem.
A day’s life of an agent
Starting from a description, the agent begins to plan a day’s life. As time passes in the sandbox world, the behavior of the agents gradually changes as they interact with each other, the world, and the memories they establish. The picture below shows a day in the life of drugstore owner John Lin.
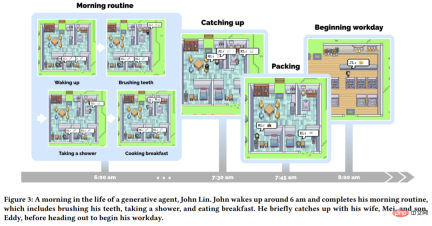
In this family, John Lin is the first to get up at seven in the morning, then brushes his teeth, takes a shower, gets dressed, eats breakfast, and then sits in the living room Browsing the news at the dinner table. At 8 a.m., John Lin's son Eddy also got up and got ready for class. Before he left, he had a conversation with John, the content of which was:

Not long after Eddy left, his mother Mei also woke up, and Mei asked Son, John recalled the conversation they just had, and then had the following conversation

Social ability
In addition, "Generative Agents" also show the emergence of social behaviors. By interacting with each other, "Generative Agents" exchange information and form new relationships in the Smallville environment. These social behaviors are natural and not predetermined. For example, when an agent notices the presence of the other party, a conversation may occur, and conversation information can be spread between agents.
Let’s look at a few examples:
Information dissemination. When agents notice each other, they may engage in conversation. When doing this, information can be propagated from one agent to another. For example, in a conversation between Sam and Tom at the grocery store, Sam tells Tom about his candidacy in the local election:


Later that day, after Sam leaves, Tom and John, who heard from another source, discuss Sam's chances of winning the election:

Gradually, Sam's candidacy became the talk of the town, with some supporting him and others hesitant.
Relationship memory. Over time, the agents in the town form new relationships and remember their interactions with other agents. For example, Sam didn't know Latoya Williams at first. While walking in Johnson Park, Sam met Latoya and introduced themselves to each other. Latoya mentioned that he was working on a photography project: "I am here to take photos for a project that I am working on." In the subsequent interaction, Sam and Latoya The interaction showed memory of this event, with Sam asking: "Latoya, how is your project going?" Latoya replied: "It's going great!"
Coordination ability. Isabella Rodriguez, who owns Hobbs Cafe, is hosting a Valentine's Day party on Feb. 14 from 5 to 7 p.m. From this seed, Isabella Rodriguez would extend invitations when she met friends and customers at Hobbs Cafe or elsewhere. On the afternoon of the 13th, Isabella began decorating the café. Maria, a regular customer and close friend of Isabella's, comes to the café. Isabella asks Maria to help decorate the party, and Maria agrees. Maria's character description is that she likes Klaus. That night, Maria invites her crush, Klaus, to a party with her, and Klaus happily accepts.
On Valentine’s Day, five agents, including Klaus and Maria, showed up at Hobbs Café at 5 pm to enjoy the festivities (Figure 4). In this scenario, the end-user only sets Isabella’s initial intention of hosting a party and Maria’s infatuation with Klaus: the social behaviors of spreading information, decorating, asking each other out, arriving at the party, and interacting at the party are initiated by the agent architecture.

Architecture
Generative Agents need a framework to guide their behavior in the open world, designed to allow Generative Agents to interact with Other agents interact and react to changes in the environment.
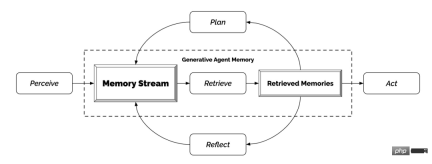
Generative Agents take their current environment and past experience as input and generate behavior as output. The architecture of Generative Agents combines large language models with mechanisms to synthesize and retrieve relevant information to regulate the output of the language model.
Without synthesis and retrieval mechanisms, large language models can output behaviors, but Generative Agents may not respond based on the agent’s past experience, making it impossible to make important inferences , and may not be able to maintain long-term coherence. Even with current best-performing models (e.g. GPT-4), challenges with long-term planning and coherence remain.
Because Generative Agents generate large amounts of events and memory streams that must be retained, a core challenge in their architecture is to ensure that the most relevant items in the agent's memory are retrieved and synthesized when needed. part.

The architectural center of Generative Agents is the memory stream - a database that comprehensively records the agent's experience. The agent retrieves relevant records from the memory stream to plan the agent's action behavior and respond appropriately to the environment, and each behavior is recorded to recursively synthesize higher-level behavioral guidance. Everything in the Generative Agents architecture is recorded and reasoned in the form of natural language descriptions, allowing agents to take advantage of the reasoning capabilities of large language models.
Currently, this research implements the gpt3.5-turbo version using ChatGPT. The research team anticipates that the architectural foundations of Generative Agents—memory, planning, and reflection—are likely to remain unchanged. Newer language models (such as GPT-4) have better expressiveness and performance, which will further expand Generative Agents.
Memory and retrieval
The architecture of Generative Agents implements a retrieval function that combines the current situation as input and returns a subset of the memory stream to pass to the language model. There are many possible implementations of the retrieval function, depending on what factors are important to the agent in deciding how to act.
Reflection
The study also introduced a second type of memory called "reflection." Reflections are higher-level, more abstract thoughts generated by an agent. Reflection is generated periodically. In this study, the agent will only start to reflect when the sum of its importance scores for recent events exceeds a certain threshold.
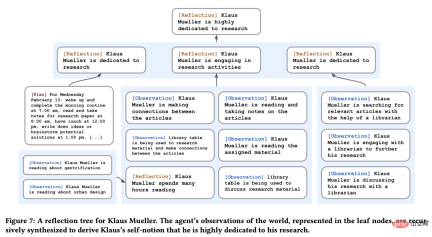
In fact, the Generative Agents proposed in the study reflected about two to three times a day. The first step in reflection is for the agent to determine what to reflect on by identifying questions that can be asked based on the agent's recent experiences.
Planning and Reaction
Planning is used to describe the sequence of future actions of an agent and to help the agent maintain its behavior over time consistent. The plan should include location, start time and duration.
To create a reasonable plan, Generative Agents will recursively generate more details from top to bottom. The first step is to create a plan that roughly outlines your "schedule" for the day. To create an initial plan, the study prompts the language model with a general description of the agent (e.g., name, characteristics, summary of their recent experiences, etc.).
In the process of executing planning, Generative Agents sense the surrounding environment, and the perceived observations are stored in their memory streams. The study uses these observations to prompt language models to decide whether agents should continue with their current plans or react differently.
Experimentation and Evaluation
The study conducted two evaluations of Generative Agents: one was a controlled evaluation to test whether the agents could independently generate credible individual behavior; the other is an end-to-end evaluation, in which multiple Generative Agents interact openly over two days of game time, in order to understand the stability and emergent social behavior of the agent.
For example, Isabella plans to host a Valentine’s Day party. She spreads the information, and by the end of the simulation, 12 characters know about it. Seven of them were "undecided" - three had other plans, and four had not expressed their thoughts, just like how humans get along.

#At the technical evaluation level, this research uses natural language to "interview" the agent to evaluate the agent's maintenance of "personality", memory, and planning. , ability to react and reflect accurately, and conducted ablation experiments. Experimental results show that each of these components is critical for the agent to perform well on the task.
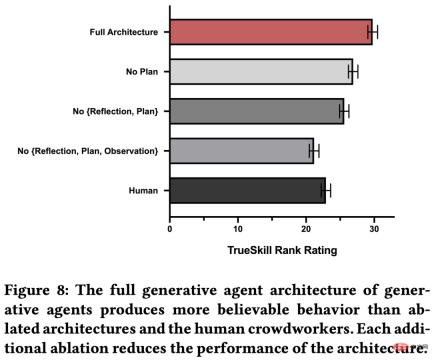
In experimental evaluations, the most common errors made by agents include:
- It fails to retrieve relevant memories;
- Fabricate and modify the memory of the agent;
- "Inherit" overly formal speech or behavior from the language model.
Interested readers can read the original text of the paper to learn more about the research details.
The above is the detailed content of Hot paper creates the prototype of 'Westworld': 25 AI agents grow freely in the virtual town. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Steam 未检测到 Windows 11/10 中已安装的游戏,如何修复Jun 27, 2023 pm 11:47 PM
Steam 未检测到 Windows 11/10 中已安装的游戏,如何修复Jun 27, 2023 pm 11:47 PMSteam客户端无法识别您计算机上的任何游戏吗?当您从计算机上卸载Steam客户端时,会发生这种情况。但是,当您重新安装Steam应用程序时,它会自动识别已安装文件夹中的游戏。但是,别担心。不,您不必重新下载计算机上的所有游戏。有一些基本和一些高级解决方案可用。修复1–尝试在同一位置安装游戏这是解决这个问题的最简单方法。只需打开Steam应用程序并尝试在同一位置安装游戏即可。步骤1–在您的系统上打开Steam客户端。步骤2–直接进入“库”以查找您拥有的所有游戏。第3步–选择游戏。它将列在“未分类
 欢乐追逃游戏即将开始!亚瑟和安琪拉520限定皮肤震撼登场!May 19, 2023 pm 08:23 PM
欢乐追逃游戏即将开始!亚瑟和安琪拉520限定皮肤震撼登场!May 19, 2023 pm 08:23 PM5月18日消息,为了庆祝即将到来的520节日,《王者荣耀》推出了令人期待的活动和全新限定皮肤。这次的活动将带来一场名为"追逃游戏"的欢乐庆典,而亚瑟和安琪拉将成为主角,以传说品质的520限定皮肤惊艳登场。据ITBEAR科技资讯了解,亚瑟和安琪拉是《王者荣耀》中备受喜爱的英雄角色,他们以各自独特的魅力和技能征服了众多玩家。而这次的520限定皮肤让他们焕发出全新的魅力,给玩家们带来不一样的游戏体验。安琪拉520限定皮肤以马戏团为主题,她身穿充满节日氛围的撞色裙子,伴随着皮皮精灵的
 用Python写游戏脚本原来这么简单Apr 13, 2023 am 10:04 AM
用Python写游戏脚本原来这么简单Apr 13, 2023 am 10:04 AM前言最近在玩儿公主连结,之前也玩儿过阴阳师这样的游戏,这样的游戏都会有个初始号这样的东西,或者说是可以肝的东西。当然,作为一名程序员,肝这种东西完全可以用写代码的方式帮我们自动完成。游戏脚本其实并不高深,最简单的体验方法就是下载一个Airtest了,直接截几个图片,写几层代码,就可以按照自己的逻辑玩儿游戏了。当然,本篇文章不是要讲Airtest这个怎么用,而是用原始的python+opencv来实现上面的操作。这两天我写了一个公主连结刷初始号的程序,也不能算写游戏脚本的老手,这篇文章主要是分享一
 电脑游戏下载到d盘还是c盘Mar 16, 2023 pm 03:02 PM
电脑游戏下载到d盘还是c盘Mar 16, 2023 pm 03:02 PM电脑游戏下载到d盘。C盘是系统盘,是专门为安装系统而设置的磁盘空间,里面安装的东西越少越好;C盘安装的东西多,电脑就会很卡。C盘系统运行会产生很多缓存与磁盘碎片,这些都会影响系统的运行及速度;如果再安装游戏或者软件,会更加加速缓存与碎片产生的数量与速度。
 Win11玩游戏卡顿怎么解决Jun 29, 2023 pm 01:20 PM
Win11玩游戏卡顿怎么解决Jun 29, 2023 pm 01:20 PMWin11玩游戏卡顿怎么解决?近期有用户给自己的电脑升级了Win11系统,但是在后续在使用电脑玩游戏时,游戏却出现了卡顿掉帧的情况,这是这怎么回事呢?出现这一情况的原因有很多,下面小编为大家带来了几种方法解决,我们一起来看看吧。 Win11玩游戏卡顿掉帧的解决方法 一、散热 1、有些设备在温度过高时,会通过降频的方法来降低温度。 2、这时候可以先打开系统设置,在左上角搜索电源,点击显示所有结果。 3、然后在下拉列表中打开选择电源计划。 4、再勾选开启高性能模式即可。 5、如果高
 win7玩游戏怎么优化可以让游戏更加流畅Jul 02, 2023 pm 01:53 PM
win7玩游戏怎么优化可以让游戏更加流畅Jul 02, 2023 pm 01:53 PMwin7玩游戏怎么优化可以让游戏更加流畅?如果你喜欢使用电脑来玩一些比较大型的游戏,那么就可以对你的电脑进行系统的优化。优化之后可以更好的发挥出电脑硬件的性能,获得更高的流畅性,玩游戏时获得更好的游戏体验。win7玩游戏优化可以让游戏更加流畅方法 1、在桌面上找到计算机,右键选中它并点击属性。 2、在系统属性面板中找到高级系统设置。 3、找到性能设置。 4、勾选让windows选择计算机的数值设置。以上就是【win7玩游戏怎么优化可以让游戏更加流畅-win7玩游戏优化可以让游戏更加流
 Win7游戏帧数优化方法Jul 15, 2023 am 08:05 AM
Win7游戏帧数优化方法Jul 15, 2023 am 08:05 AM针对游戏游戏玩家来讲,游戏的帧率针对游戏的流畅性、可操作性感受全是十分核心的。客户不仅仅可以根据更新配备来提升游戏帧数,变更显卡设置还可以保证相同的实际效果。下边咱们就一起来看看详细的方式吧。游戏帧数优化技术:1、鼠标右键桌面上空白,开启“NVIDIA操作面板”。2、挑选“配备Surround、PhysX”。3、启用图例部位,随后将下边滚轮拉到特性部位。4、还能够点一下“管理方法3D设定”5、将垂直同步关掉,如下图所示。6、再将三重缓冲关掉。7、通过以上的提升,大家就可以在玩游戏时得到更高的帧率
 win10电脑玩一会游戏卡死画面定格怎么办Jul 09, 2023 pm 05:17 PM
win10电脑玩一会游戏卡死画面定格怎么办Jul 09, 2023 pm 05:17 PM在操作电脑系统的过程中,我们经常会遇到各种各样的一些问题,比如说电脑用着用着就死机等情况时有发生。最近就有网友说自己的win10电脑玩一会游戏卡死画面定格怎么办?别急,下面小编就教下大家win10电脑玩游戏卡死画面定格的解决方法。具体的解决方法如下:1、同时按下快捷键Ctrl+Alt+Delete,调出任务管理器。2、切换到进程选项中,点击windows资源管理器,再点击右下角的重新启动。3、如果系统桌面上的图标都消失的情况下,我们点击文件,找到并单击运行新任务选项。4、在输入框里输入explo


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






