 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Global IT giants are using AI to help data centers save energy and reduce emissions.
Global IT giants are using AI to help data centers save energy and reduce emissions.
Data centers power the applications, websites and services used by billions of people around the world every day, and they can be dangerous places for the workers who build and maintain them. Workers must sometimes service electrical equipment in the data center while its power is on. They may be exposed to chemicals such as chlorine, which is used as a disinfectant in water circulated through the liquid cooling systems of computers and servers. In June 2015, five people had to be taken to the hospital after a chlorine leak occurred at an Apple data center in Maiden, North Carolina.
Now, data centers are more secure than ever. But in search of forward-looking solutions, some tech giants say they are exploring how to apply artificial intelligence to prevent security issues. For example, Microsoft is developing an artificial intelligence system that can analyze data from various sources and generate alerts for data center construction and operations teams to "prevent or mitigate the impact of security incidents." A complementary but related system is also being developed in an attempt to detect and predict impacts on data center construction plans.
"These initiatives are in early testing and are expected to begin scaling to our production environments later this year," a Microsoft spokesperson told the outlet via email.
Meta also claims to be studying how artificial intelligence can predict how its data centers will operate under "extreme environmental conditions" that could lead to unsafe working conditions. The company said it has been developing physical models to simulate extreme conditions and feeding that data into AI models responsible for optimizing server power consumption, cooling and airflow.
Meta spokesperson told the media: "Our data centers hold a large amount of operational data, and in some areas there is a high frequency of sensors built into servers, racks and data halls." "Every server and network device Taking on different workloads will consume different power, generate different heat, and create different amounts of airflow in the data center. Our [infrastructure] team collects all the data from each server and then develops an AI model that can Allocate our servers and racks in data centers and send workloads to those servers to optimize [for] performance and efficiency."
Of course, besides security, businesses have other motivations to secure data The center is kept in top condition. Power outages are expensive—and increasingly frequent. One-third of data center owners and operators admitted to experiencing a major outage in the past 12 months, according to a 2020 survey by IT consulting firm IT Uptime Institute. One in six people claimed their outages cost more than $1 million, up from one in 10 in 2019.
Meta, which operates more than 20 data centers around the world, including new projects in Texas and Missouri, said it will build 50 to 100 new data centers per year for the foreseeable future.
AI also promises cost savings by finding energy-saving opportunities in data centers that are often unknown, another attractive aspect for businesses. In 2018, Google claimed that artificial intelligence systems developed by its DeepMind affiliate were able to save an average of 30% energy compared to the historical energy use of its data centers.
When contacted for comment, DeepMind said it had no updates to share beyond the initial announcement. IBM and Amazon did not respond to inquiries. But both Meta and Microsoft say they are now using AI to make similar power adjustments.
Microsoft launched an artificial intelligence "anomaly detection approach" in late 2021 that uses telemetry data from electrical and mechanical equipment to measure and mitigate abnormal power and water events within data centers. The company also uses AI-based methods to identify and fix issues with data center electrical meters and determine ideal locations to place servers to minimize wasted power, network and cooling capacity.
Meta says it has been using reinforcement learning to reduce the amount of air pumped into data centers for cooling purposes. At a high level, reinforcement learning is an artificial intelligence system that learns to solve problems through trial and error. Most data centers use outdoor air and evaporative cooling systems, so optimizing airflow is a top priority.
Reducing the environmental footprint is an added benefit of the energy regulating AI system. According to a report by the Environmental Investigation Agency, data centers consumed approximately 1% of global electricity demand and contributed 0.3% of all carbon dioxide emissions in 2020. A typical data center uses 3 million to 5 million gallons of water per day, equivalent to the water consumption of a city of 30,000 to 50,000 people.
Microsoft has previously said it plans to run all of its data centers on 100% renewable energy by 2025. Meta claims to have achieved this feat in 2020.
The above is the detailed content of Global IT giants are using AI to help data centers save energy and reduce emissions.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 未来数据中心的发展:人工智能与液体冷却的融合Sep 20, 2023 pm 12:21 PM
未来数据中心的发展:人工智能与液体冷却的融合Sep 20, 2023 pm 12:21 PM生成式人工智能(AI)的快速崛起凸显了企业采用人工智能的惊人速度。根据Accenture最近的一份报告,98%的企业领导人表示人工智能将在未来三到五年的战略中扮演重要角色。麦肯锡分析师发现,近65%的企业计划在未来三年内增加对人工智能的投资NVIDIA、AMD和Intel正在推出专为生成式人工智能和高性能计算(HPC)设计的新芯片,这种势头才刚刚开始。公共云提供商和新兴芯片企业也参与了竞争。IDC分析师预测,全球对人工智能软件、硬件和服务的支出将达到3000亿美元,超过今年预计的1540亿美元然
 浪潮信息与英特尔联合发布全球首个全液冷冷板服务器参考设计Jan 19, 2024 am 10:27 AM
浪潮信息与英特尔联合发布全球首个全液冷冷板服务器参考设计Jan 19, 2024 am 10:27 AM本站1月19日消息,据浪潮服务器官方消息,1月18日,浪潮信息与英特尔联合发布全球首个全液冷冷板服务器参考设计,并面向业界开放,推动全液冷冷板解决方案在全球数据中心的大规模部署应用。基于该参考设计,浪潮信息推出全液冷冷板服务器,号称实现服务器部件接近100%液冷散热,达到PUE值接近于1的水平。本站注:PUE是PowerUsageEffectiveness的缩写,计算公式为“数据中心总能耗/IT设备能耗”,其中数据中心总能耗包括IT设备能耗和制冷、配电等系统的能耗,PUE越接近1代表非IT设备耗
 PHP中的分布式数据中心May 23, 2023 pm 11:40 PM
PHP中的分布式数据中心May 23, 2023 pm 11:40 PM随着互联网的快速发展,网站的访问量也在不断增长。为了满足这一需求,我们需要构建高可用性的系统。分布式数据中心就是这样一个系统,它将各个数据中心的负载分散到不同的服务器上,增加系统的稳定性和可扩展性。在PHP开发中,我们也可以通过一些技术实现分布式数据中心。分布式缓存分布式缓存是互联网分布式应用中最常用的技术之一。它将数据缓存在多个节点上,提高数据的访问速度和
 AI和ML:数据中心的新前沿创新和优化Apr 20, 2023 pm 03:16 PM
AI和ML:数据中心的新前沿创新和优化Apr 20, 2023 pm 03:16 PM随着对数据处理和存储的需求持续激增,数据中心正在努力应对不断发展和扩展的挑战。平台、设备设计、拓扑结构、功率密度要求和冷却需求的不断变化都强调了对新结构设计的迫切需求。数据中心基础设施通常难以将当前和预计的IT负载与其关键基础设施保持一致,从而导致不匹配,威胁到它们满足不断升级的需求的能力。在此背景下,必须修改传统的数据中心方法。数据中心现在正在将人工智能(AI)和机器学习(ML)技术集成到其基础架构中,以保持竞争力。通过在传统数据中心架构中实施人工智能驱动层,企业可以创建自主数据中心,无需人工
 单租户人工智能工厂会成为最新的数据中心趋势吗?Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:25 PM
单租户人工智能工厂会成为最新的数据中心趋势吗?Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:25 PM托管数据中心通常设计用来容纳数十甚至数百个客户的不同应用程序。不过,英伟达提供了一种独特的数据中心模式,该数据中心专门为单一客户运行特定应用程序。“人工智能工厂”的出现这种新型的数据中心与传统数据中心不同,它专注于提供更高效、更灵活的基础设施服务。传统数据中心往往承载多个应用程序和多个租户,而新型数据中心更注重资源的动态分配和优化,以满足不同应用程序和租户的需求。这种新型数据中心的设计更加灵活和智能,能够根据需求实时调整资源分配,提高整体效率和性能。通过这种创新的设计理念,这些新的数据中心主要用
 数据中心idc机房建设的标准是什么Jan 23, 2024 am 10:50 AM
数据中心idc机房建设的标准是什么Jan 23, 2024 am 10:50 AM标准包括:1、基础设施标准;2、环境标准;3、设备标准;4、辅助区设置;5、防雷接地系统要求;6、动力环境监控系统要求;7、消防报警系统要求;8、防盗报警系统要求;9、安防系统要求;10、供配电系统要求等。详细介绍:1、基础设施标准:包括机房布局、强电、弱电、动力、空调、消防、安全等一系列的要素。需要制定严格的安全、可靠、高效的机房建设标准,以满足数据中心的高可用性和可维护性。
 警惕!ChatGPT爆火下的能耗危机,数据中心运营商挑战巨大Apr 11, 2023 pm 03:58 PM
警惕!ChatGPT爆火下的能耗危机,数据中心运营商挑战巨大Apr 11, 2023 pm 03:58 PM近期,美国OpenAI公司旗下智能聊天工具ChatGPT刷爆社交媒体,吸引超百亿美元投资,推动了资本市场布局人工智能应用的巨大热潮,风头一时无两。微软率先宣布砸100亿美金入股OpenAI,然后亚马逊和美版“今日头条”BuzzFeed宣布将在日常工作中启用ChatGPT,同时,百度也宣布于3月推出“中国版”的ChatGPT聊天机器人。在多家科技公司推波助澜后,ChatGPT瞬间引发全球关注。数据显示,亚马逊部署的机器人数量正在快速增加,每天增量达到1000个左右。此外,脸书母公司Meta也计划2
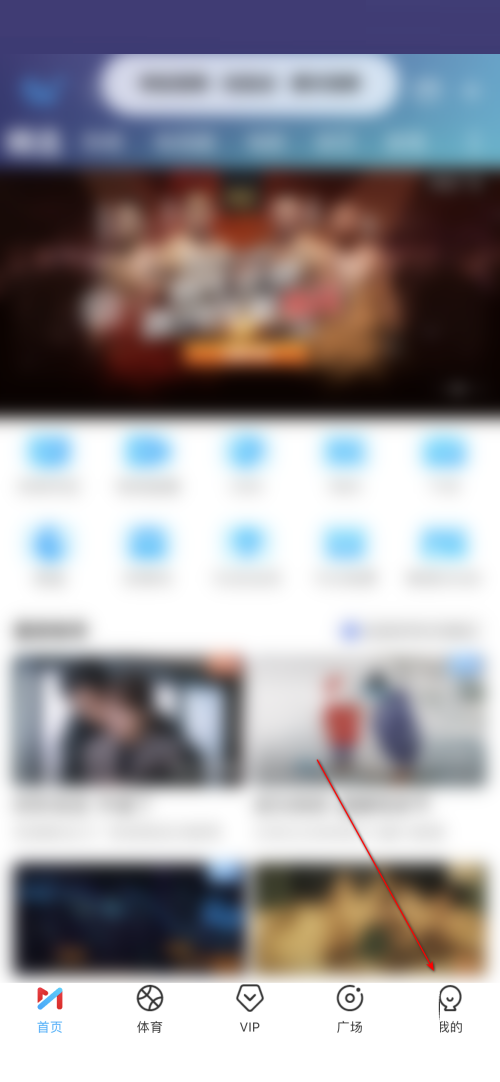 咪咕视频怎么进入数据中心-咪咕视频进入数据中心的方法Mar 18, 2024 am 11:49 AM
咪咕视频怎么进入数据中心-咪咕视频进入数据中心的方法Mar 18, 2024 am 11:49 AM近日有一些小伙伴咨询小编咪咕视频怎么进入数据中心?下面就为大家带来了咪咕视频进入数据中心的方法,有需要的小伙伴可以来了解了解哦。1、打开咪咕视频APP,在首页点击右下角我的(如图所示)。2、点击数据中心(如图所示)。3、即可查看到全部数据(如图所示)。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.




