
We used different machine learning algorithms for sentiment analysis, and then compared the accuracy results of each algorithm to determine which algorithm is most suitable for this problem.
Sentiment analysis is an important content in natural language processing (NLP). Emotions are the feelings we have about an event, object, situation, or thing. Sentiment analysis is a research field that automatically extracts human emotions from text. It slowly started to develop in the early 90s.
This article will let you understand how to use machine learning (ML) for sentiment analysis and compare the results of different machine learning algorithms. The goal of this article is not to study how to improve algorithm performance.
Nowadays, we live in a fast-paced society, all goods can be purchased online, and everyone can post their own comments online. And negative online reviews of some products may damage the company's reputation, thereby affecting the company's sales. So it becomes very important for companies to use product reviews to understand what customers really want. However, there is too much comment data, and it is impossible to manually view all comments one by one. This is how sentiment analysis was born.
Now, let’s see how to use machine learning to develop a model to perform basic sentiment analysis.
Start now!
Getting data
The first step is to select a data set. You can choose from any public review, such as a tweet or a movie review. The dataset must contain at least two columns: labels and actual text segments.
The figure below shows some of the data sets we selected.

Figure 1: Data sample
Next, we import the required libraries:
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from nltk.stem.porter import PorterStemmer import re import string
As As you can see in the above code, we imported the NumPy and Pandas libraries to process the data. As for other libraries, we will explain them when they are used.
The data set is ready and the required libraries have been imported. Next, we need to use the Pandas library to read the data set into our project. We use the following code to read the data set into the Pandas data frame DataFrame
sentiment_dataframe = pd.read_csv(“/content/drive/MyDrive/Data/sentiments - sentiments.tsv”,sep = ‘t’)
Data processing
Now the data set has been imported into our project. We then process the data so that the algorithm can better understand the characteristics of the data set. We first name the columns in the dataset, which is done with the following code:
sentiment_dataframe.columns = [“label”,”body_text”]
Then, we numericize the label column: negative comments are replaced with 1, and positive comments are replaced with 0. The image below shows the values of sentiment_dataframe after a basic modification.

Figure 2: Data frame with basic modifications
Prepare the characteristic values and target values
Next step It is the preprocessing of data. This is a very important step, because machine learning algorithms can only understand/process numerical data, but not text. Therefore, feature extraction is required at this time to convert strings/text into numerical data. Additionally, redundant and useless data need to be removed as these data may contaminate our trained model. We remove noisy data, missing value data, and inconsistent data in this step.
对于情感分析,我们在数据帧中添加特征文本的长度和标点符号计数。我们还要进行词干提取,即将所有相似词(如 “give”、“giving” 等)转换为单一形式。完成后,我们将数据集分为两部分:特征值 X 和 目标值 Y。
上述内容是使用以下代码完成的。下图显示了执行这些步骤后的数据帧。
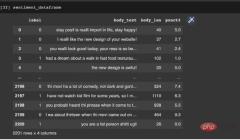
Figure 3: Data frame after the division of the data set
def count_punct(text): count = sum([1 for char in text if char in string.punctuation]) return round(count/(len(text) - text.count(“ “)),3)*100 tokenized_tweet = sentiment_dataframe[‘body_text’].apply(lambda x: x.split()) stemmer = PorterStemmer() tokenized_tweet = tokenized_tweet.apply(lambda x: [stemmer.stem(i) for i in x]) for i in range(len(tokenized_tweet)): tokenized_tweet[i] = ‘ ‘.join(tokenized_tweet[i]) sentiment_dataframe[‘body_text’] = tokenized_tweet sentiment_dataframe[‘body_len’] = sentiment_dataframe[‘body_text’].apply(lambda x:len(x) - x.count(“ “)) sentiment_dataframe[‘punct%’] = sentiment_dataframe[‘body_text’].apply(lambda x:count_punct(x)) X = sentiment_dataframe[‘body_text’] y = sentiment_dataframe[‘label’]
特征工程:文本特征处理
我们接下来进行文本特征抽取,对文本特征进行数值化。为此,我们使用计数向量器CountVectorizer,它返回词频矩阵。
在此之后,计算数据帧 X 中的文本长度和标点符号计数等特征。X 的示例如下图所示。
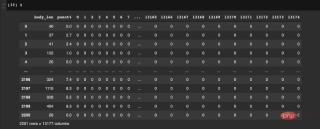
Figure 4: Sample of final features
使用的机器学习算法
现在数据已经可以训练了。下一步是确定使用哪些算法来训练模型。如前所述,我们将尝试多种机器学习算法,并确定最适合情感分析的算法。由于我们打算对文本进行二元分类,因此我们使用以下算法:
- K-近邻算法(KNN)
- 逻辑回归算法
- 支持向量机(SVMs)
- 随机梯度下降(SGD)
- 朴素贝叶斯算法
- 决策树算法
- 随机森林算法
划分数据集
首先,将数据集划分为训练集和测试集。使用 sklearn 库,详见以下代码:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y, test_size = 0.20, random_state = 99)
我们使用 20% 的数据进行测试,80% 的数据用于训练。划分数据的意义在于对一组新数据(即测试集)评估我们训练的模型是否有效。
K-近邻算法
现在,让我们开始训练第一个模型。首先,我们使用 KNN 算法。先训练模型,然后再评估模型的准确率(具体的代码都可以使用 Python 的 sklearn 库来完成)。详见以下代码,KNN 训练模型的准确率大约为 50%。
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3) model.fit(X_train, y_train) model.score (X_test,y_test) 0.5056689342403629
逻辑回归算法
逻辑回归模型的代码十分类似——首先从库中导入函数,拟合模型,然后对模型进行评估。下面的代码使用逻辑回归算法,准确率大约为 66%。
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression model = LogisticRegression() model.fit (X_train,y_train) model.score (X_test,y_test) 0.6621315192743764
支持向量机算法
以下代码使用 SVM,准确率大约为 67%。
from sklearn import svm model = svm.SVC(kernel=’linear’) model.fit(X_train, y_train) model.score(X_test,y_test) 0.6780045351473923
随机森林算法
以下的代码使用了随机森林算法,随机森林训练模型的准确率大约为 69%。
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier model = RandomForestClassifier() model.fit(X_train, y_train) model.score(X_test,y_test) 0.6938775510204082
决策树算法
接下来,我们使用决策树算法,其准确率约为 61%。
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier model = DecisionTreeClassifier() model = model.fit(X_train,y_train) model.score(X_test,y_test) 0.6190476190476191
随机梯度下降算法
以下的代码使用随机梯度下降算法,其准确率大约为 49%。
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier model = SGDClassifier() model = model.fit(X_train,y_train) model.score(X_test,y_test) 0.49206349206349204
朴素贝叶斯算法
以下的代码使用朴素贝叶斯算法,朴素贝叶斯训练模型的准确率大约为 60%。
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB model = GaussianNB() model.fit(X_train, y_train) model.score(X_test,y_test) 0.6009070294784581
情感分析的最佳算法
接下来,我们绘制所有算法的准确率图。如下图所示。

Figure 5: Accuracy performance of the different algorithms
可以看到,对于情感分析这一问题,随机森林算法有最佳的准确率。由此,我们可以得出结论,随机森林算法是所有机器算法中最适合情感分析的算法。我们可以通过处理得到更好的特征、尝试其他矢量化技术、或者使用更好的数据集或更好的分类算法,来进一步提高准确率。
既然,随机森林算法是解决情感分析问题的最佳算法,我将向你展示一个预处理数据的样本。在下图中,你可以看到模型会做出正确的预测!试试这个来改进你的项目吧!

Figure 6: Sample predictions made
The above is the detailed content of How to use machine learning to analyze sentiment. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
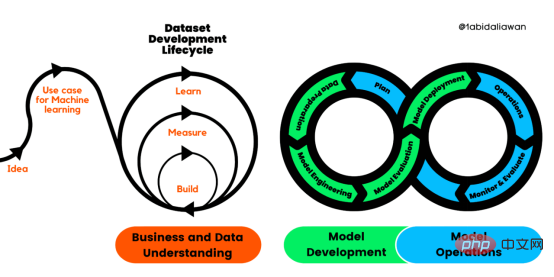 解读CRISP-ML(Q):机器学习生命周期流程Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:21 PM
解读CRISP-ML(Q):机器学习生命周期流程Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:21 PM译者 | 布加迪审校 | 孙淑娟目前,没有用于构建和管理机器学习(ML)应用程序的标准实践。机器学习项目组织得不好,缺乏可重复性,而且从长远来看容易彻底失败。因此,我们需要一套流程来帮助自己在整个机器学习生命周期中保持质量、可持续性、稳健性和成本管理。图1. 机器学习开发生命周期流程使用质量保证方法开发机器学习应用程序的跨行业标准流程(CRISP-ML(Q))是CRISP-DM的升级版,以确保机器学习产品的质量。CRISP-ML(Q)有六个单独的阶段:1. 业务和数据理解2. 数据准备3. 模型
 基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM
基于因果森林算法的决策定位应用Apr 08, 2023 am 11:21 AM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟在我之前的博客中,我们已经了解了如何使用因果树来评估政策的异质处理效应。如果你还没有阅读过,我建议你在阅读本文前先读一遍,因为我们在本文中认为你已经了解了此文中的部分与本文相关的内容。为什么是异质处理效应(HTE:heterogenous treatment effects)呢?首先,对异质处理效应的估计允许我们根据它们的预期结果(疾病、公司收入、客户满意度等)选择提供处理(药物、广告、产品等)的用户(患者、用户、客户等)。换句话说,估计HTE有助于我
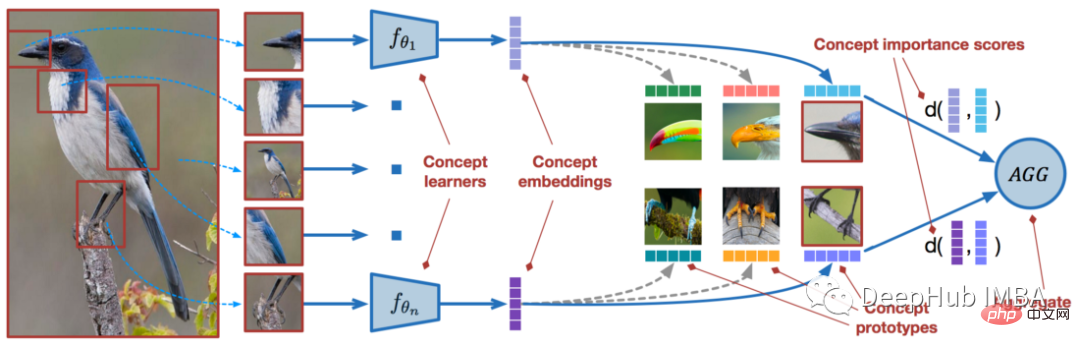
 2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:30 PM机器学习是一个不断发展的学科,一直在创造新的想法和技术。本文罗列了2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术。 本文罗列了2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术。2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术是一个教计算机从数据中学习的过程,无需明确的编程。机器学习是一个不断发展的学科,一直在创造新的想法和技术。为了保持领先,数据科学家应该关注其中一些网站,以跟上最新的发展。这将有助于了解机器学习中的技术如何在实践中使用,并为自己的业务或工作领域中的可能应用提供想法。2023年机器学习的十大概念和技术:1. 深度神经网
 使用PyTorch进行小样本学习的图像分类Apr 09, 2023 am 10:51 AM
使用PyTorch进行小样本学习的图像分类Apr 09, 2023 am 10:51 AM近年来,基于深度学习的模型在目标检测和图像识别等任务中表现出色。像ImageNet这样具有挑战性的图像分类数据集,包含1000种不同的对象分类,现在一些模型已经超过了人类水平上。但是这些模型依赖于监督训练流程,标记训练数据的可用性对它们有重大影响,并且模型能够检测到的类别也仅限于它们接受训练的类。由于在训练过程中没有足够的标记图像用于所有类,这些模型在现实环境中可能不太有用。并且我们希望的模型能够识别它在训练期间没有见到过的类,因为几乎不可能在所有潜在对象的图像上进行训练。我们将从几个样本中学习
 LazyPredict:为你选择最佳ML模型!Apr 06, 2023 pm 08:45 PM
LazyPredict:为你选择最佳ML模型!Apr 06, 2023 pm 08:45 PM本文讨论使用LazyPredict来创建简单的ML模型。LazyPredict创建机器学习模型的特点是不需要大量的代码,同时在不修改参数的情况下进行多模型拟合,从而在众多模型中选出性能最佳的一个。 摘要本文讨论使用LazyPredict来创建简单的ML模型。LazyPredict创建机器学习模型的特点是不需要大量的代码,同时在不修改参数的情况下进行多模型拟合,从而在众多模型中选出性能最佳的一个。本文包括的内容如下:简介LazyPredict模块的安装在分类模型中实施LazyPredict
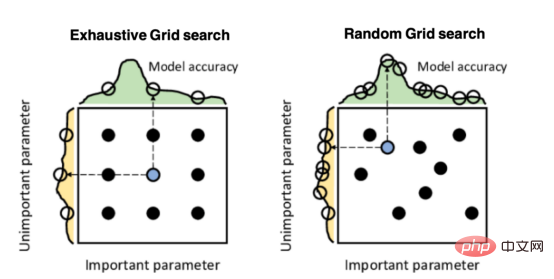 Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM
Mango:基于Python环境的贝叶斯优化新方法Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:44 PM译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟引言模型超参数(或模型设置)的优化可能是训练机器学习算法中最重要的一步,因为它可以找到最小化模型损失函数的最佳参数。这一步对于构建不易过拟合的泛化模型也是必不可少的。优化模型超参数的最著名技术是穷举网格搜索和随机网格搜索。在第一种方法中,搜索空间被定义为跨越每个模型超参数的域的网格。通过在网格的每个点上训练模型来获得最优超参数。尽管网格搜索非常容易实现,但它在计算上变得昂贵,尤其是当要优化的变量数量很大时。另一方面,随机网格搜索是一种更快的优化方法,可以提供更好的
 人工智能自动获取知识和技能,实现自我完善的过程是什么Aug 24, 2022 am 11:57 AM
人工智能自动获取知识和技能,实现自我完善的过程是什么Aug 24, 2022 am 11:57 AM实现自我完善的过程是“机器学习”。机器学习是人工智能核心,是使计算机具有智能的根本途径;它使计算机能模拟人的学习行为,自动地通过学习来获取知识和技能,不断改善性能,实现自我完善。机器学习主要研究三方面问题:1、学习机理,人类获取知识、技能和抽象概念的天赋能力;2、学习方法,对生物学习机理进行简化的基础上,用计算的方法进行再现;3、学习系统,能够在一定程度上实现机器学习的系统。
 超参数优化比较之网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯优化Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM
超参数优化比较之网格搜索、随机搜索和贝叶斯优化Apr 04, 2023 pm 12:05 PM本文将详细介绍用来提高机器学习效果的最常见的超参数优化方法。 译者 | 朱先忠审校 | 孙淑娟简介通常,在尝试改进机器学习模型时,人们首先想到的解决方案是添加更多的训练数据。额外的数据通常是有帮助(在某些情况下除外)的,但生成高质量的数据可能非常昂贵。通过使用现有数据获得最佳模型性能,超参数优化可以节省我们的时间和资源。顾名思义,超参数优化是为机器学习模型确定最佳超参数组合以满足优化函数(即,给定研究中的数据集,最大化模型的性能)的过程。换句话说,每个模型都会提供多个有关选项的调整“按钮


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







