With the increasing popularity of artificial intelligence (AI) in society, it has also entered the field of network security. Artificial intelligence can help improve cybersecurity in a variety of ways, including automatically detecting and responding to threats, improving network efficiency, and helping to identify vulnerabilities. In this article, we’ll discuss some of the ways artificial intelligence is changing cybersecurity and how it can help businesses stay secure.

Artificial intelligence is changing the landscape of cybersecurity. The strengths of this paper demonstrate that by implementing artificial intelligence systems, organizations will be able to increase detection and response speed and more proactively anticipate and deal with emerging threats.
What is artificial intelligence (AI)?
Artificial intelligence is an intelligence displayed by machines, rather than the natural intelligence displayed by humans and other animals. AI applications can analyze data and make decisions on their own, without human intervention.
Artificial intelligence is achieved by evaluating the processes of the human brain and studying the patterns of the human brain. These threat investigations lead to the creation of intelligent software, systems or artificial intelligence solutions.
The foundation of artificial intelligence is based on the so-called Turing test of artificial intelligence. The Turing test in artificial intelligence is a method of determining whether a machine can exhibit behavior that is indistinguishable from humans. If the answer to this question is yes, then the machine has passed the Turing test and is considered intelligent.
The three main components of artificial intelligence are:
- Artificial intelligence learning is the acquisition of new knowledge or skills from experience process.
- Reasoning is the ability to draw logical conclusions from a set of premises.
- Self-correction is the ability to recognize and correct errors.
What is the role of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity?
The role of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity is to help organizations reduce the risk of intrusions and improve their overall security posture. Artificial intelligence plays a role in cybersecurity by learning from past data to identify patterns and trends. This information is then used to predict future attacks. AI-driven systems can also be configured to automatically respond to threats and combat cyber threats in a faster timeframe.
As the enterprise attack surface continues to grow and evolve, analyzing and enhancing cyber threats and cyber attacks is no longer a human challenge. Depending on the size of the organization, up to hundreds of billions of time-varying signals must be processed to correctly calculate risk.
In response to this unprecedented challenge, artificial intelligence tools and methods such as neural networks continue to evolve to help information security teams protect sensitive products with more effective and efficient threat detection and threat elimination capabilities. information, reduce the risk of intrusion, and improve security posture.
Applications of Machine Learning in Cyberspace
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that uses algorithms to automatically learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
It is mainly used for network security and has two purposes:
- Anomaly detection: Machine learning can be used to automatically detect anomalies, such as abnormal user behavior or unexpected network activities, which Anomalies may indicate a security threat. For example, crowdstrike, darktrace and many other products use this technology.
- Classification: Machine learning can be used to automatically classify data, such as emails or files, into categories (such as spam or malware) for more efficient processing.
AI/Cybersecurity Dilemma - Potential Disadvantages
We are all in favor of using artificial intelligence to solve security problems.
Cybercriminals can train artificial intelligence systems or feed incorrect data into the data sets used by artificial intelligence. This will allow them to create more realistic and sophisticated attacks. Additionally, artificial intelligence can be used to automate attacks, allowing a single actor to conduct large-scale attacks.
AI systems are also susceptible to being fooled by so-called “adversarial examples” — inputs specifically designed to trick the system into misclassifying them. For example, an image of a stop sign that is slightly altered so that it is no longer recognized as a stop sign could be fooled by a self-driving car into thinking it is something else, such as a yield sign. This can have disastrous consequences.
As artificial intelligence becomes more widely used in cybersecurity, it is important to consider potential risks and how to mitigate them. One way to do this is to ensure that AI systems are “explainable” – that is, they can provide reasons for their decisions. This will help ensure that decisions are transparent and accountable, while also helping to prevent adversarial examples from being used to trick the system.
In conclusion, AI-based cybersecurity systems show great potential in helping organizations. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and take steps to mitigate them.
How is artificial intelligence used in security?
Artificial intelligence has several good application cases in the field of network security. Starting with researchers or think tanks, here’s a great example of Gartner’s prism for cybersecurity use cases. Hyperautomation has become a topic of much concern since Gartner’s predictions – meaning that another level of automation will be launched based on the next generation of general artificial intelligence systems. This involves combining AI/ML with automated quality assurance to simplify the management of alert and incident response efforts. Essentially, it will help enterprises enhance no-code or low-code security at scale and improve business agility and DevOps strategies.
The following is a list of applicable examples for Security Services and Cloud Security:
- Transaction Fraud Detection
- File-based Malware Detection
- Process Behavioral Analysis
- Abnormal System Behavior Detection
- Network, Domain and Reputation Assessment
- Asset Inventory and Dependency Mapping Optimization
- Account acquisition identification
- Adaptive runtime access and authorization
- Identification proofing
- The difference between machines and humans
- Text-based malicious intent Detection
- Same person identification
- Web content visual analysis
- Security operation task automation
- Business data risk classification
- Strategy recommendation engine
- Event Correlation
- Hazard Intelligence
- Security Posture and Risk Score
Here’s How Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity Is How Examples of reducing the time to identify, detect, and respond to cybersecurity threats:
(1) Automated malware detection and prevention
Artificial Intelligence (AI) compared to traditional software-driven or manual methods ) and machine learning can help combat cybercriminals, automatically detect threats and respond more effectively. Machine learning techniques improve malware detection by combining large amounts of data from anti-malware components on the host, network and cloud.
Previously unknown samples may be new files in malware and ransomware attack detection, contributing to endpoint protection mechanisms. Its hidden properties may or may not be malicious. Likewise, malware that is able to evade detection is not guaranteed to be caught every time.
This does not mean that all malware attacks can be stopped with artificial intelligence. The model is a collection of mathematically structured rules that support data attributes.
(2) Phishing and Spam Detection
Deep learning uses large amounts of data to train deep neural networks, which then learn over time how to classify images or complete other tasks.
Deep learning models can achieve good accuracy even for attack operations with relatively loose features. It is used to detect insecure jobs and other images as well as spam and phishing attacks.
Google uses deep learning to detect hard-to-detect image-based emails, emails with hidden content, and communications from newly formed domains. This helps detect sophisticated phishing attacks, including Internet traffic patterns associated with spam.
(3) Faster and more accurate anomaly detection - SIEM and SOAR platform
Artificial intelligence can identify malicious and benign anomalies in network traffic data in near real-time . By applying machine learning algorithms to network traffic data, previously unknown attacks can be detected, as well as known attacks that have been modified to evade detection.
SIEM and SOAR systems add to an organization’s security infrastructure. Advanced analytics and machine learning are used to identify alerts, but this requires fine-tuning due to the occurrence of false positives.
SOAR is the engine that handles remediation and response to SIEM alerts. It is designed to help security teams automate the response process by collecting alerts, managing cases, and responding to SIEM's never-ending notifications.
Threat intelligence capabilities are one of its solutions, giving security teams a deeper understanding of not only computer systems but also other threats, understanding of IoT devices and other integrations.
(4) Looking for zero-day vulnerabilities
In a "zero-day attack", criminals exploit a software flaw that has not been patched by the manufacturer to infect computers with malware. However, current discussions and developments in artificial intelligence may help.
Deep learning architectures can be used to discover hidden or latent patterns and become more context-sensitive over time, which can help identify zero-day vulnerabilities or activities. Natural language processing can scan source code for dangerous files and flag them. Generative adversarial networks can learn to mimic any data distribution and can also be useful in identifying complex defects.
(5) Improve detection and response speed
The first step in protecting an enterprise network is to detect threats. It would be ideal if unreliable data could be quickly detected. It will protect the network from permanent damage.
Combining artificial intelligence with cybersecurity is the best way to detect and respond to threats in real time. Artificial intelligence checks the entire system for risks. Unlike human intelligence, artificial intelligence in the cyber domain can detect risks early, resulting in faster and more accurate security alerts, making cybersecurity experts work more efficiently.
(6) Detect new threats
Predictive analytics for identifying anomalous behavior or activity patterns is one of the primary applications of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity. Cybercriminals are always looking for new ways to exploit systems. Artificial intelligence can help identify these new threats before they cause any damage.
(7) Reduce the number of false positives
When there are too many false positives, it will take up time that could have been used to solve actual problems. But using artificial intelligence to identify security incidents can reduce the number of false positives and get teams back to work quickly.
With the help of data science, artificial intelligence can quickly analyze large amounts of events and identify a wide range of security risks, from malware to risky behaviors that may lead to phishing or malicious code downloads. Threat identification. These systems improve over time, leveraging previous attacks to identify current and new attacks. Behavioral history helps AI identify and respond to behavior that deviates from established norms by creating profiles of users, assets, and networks.
Artificial intelligence systems are being trained to detect malware, perform pattern recognition, and use advanced algorithms to detect even the smallest malware or ransomware attacks before they enter the system. feature.
Through natural language processing, AI can provide greater predictive intelligence by scraping articles, news, and research about cyber dangers and curating the material itself. AI-based security solutions that can provide the latest knowledge about global and industry-specific threats, making smarter prioritization decisions based on what is most likely to be used to attack a system, rather than what is likely to be used to attack a system .
(8) Detecting Bots
Bots now make up a large portion of Internet traffic, but they can be deadly. From account takeovers using stolen passwords to fraudulent account creation and data fraud, bots can be a serious threat. Manual responses are ineffective against automated threats. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can help analyze website traffic and differentiate between good bots, bad bots and humans.
By analyzing user behavior patterns, businesses can understand what a typical user experience looks like, as well as what uncommon high-risk experiences look like. From here we can decipher the purpose of their network communications, putting us one step ahead of the evil robots.
(9) Intrusion risk prediction
Artificial intelligence system helps determine the IT asset inventory, which is a complete and accurate list of the threats to various systems All devices, users and applications with different access permissions. Now, given asset inventory and threat exposure (as mentioned above), AI-based systems can predict how and where they are most likely to be hacked, thus planning to direct resources to the weakest locations.
This intrusion risk prediction will help organizations stay prepared to limit the impact and break the attack chain. Additionally, leveraging risk data, policies and procedures can be developed and modified through AI-based analysis to enhance cyber resilience.
Summary
It is obvious that artificial intelligence can be a powerful tool in the fight against cybercrime. By automating tasks currently performed by human security analysts, the number of false positives can be reduced and the process of detection and response can be accelerated.
More importantly, be aware of the potential risks associated with using artificial intelligence and take steps to mitigate them.
The above is the detailed content of The role of artificial intelligence in cybersecurity. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
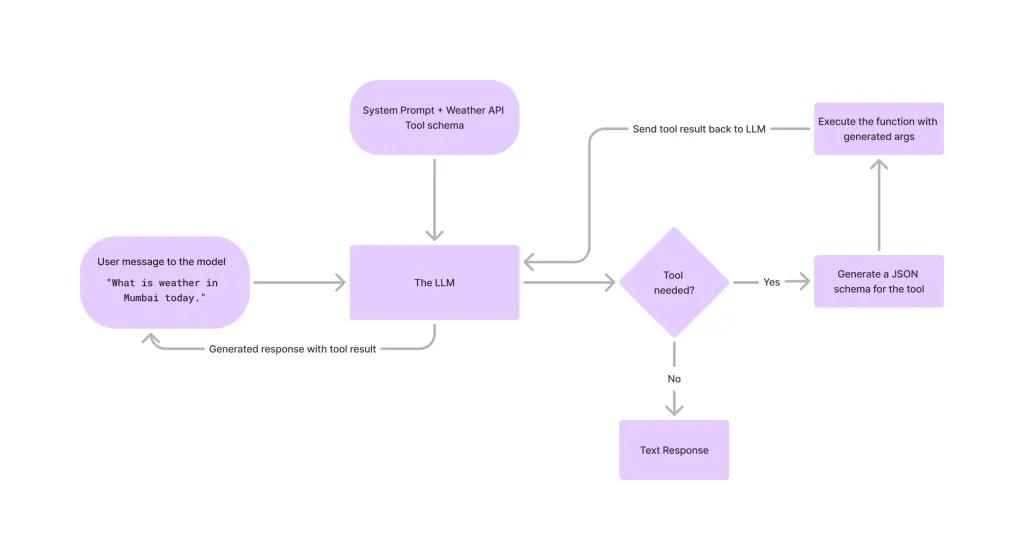 Tool Calling in LLMsApr 14, 2025 am 11:28 AM
Tool Calling in LLMsApr 14, 2025 am 11:28 AMLarge language models (LLMs) have surged in popularity, with the tool-calling feature dramatically expanding their capabilities beyond simple text generation. Now, LLMs can handle complex automation tasks such as dynamic UI creation and autonomous a
 How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global HealthApr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AM
How ADHD Games, Health Tools & AI Chatbots Are Transforming Global HealthApr 14, 2025 am 11:27 AMCan a video game ease anxiety, build focus, or support a child with ADHD? As healthcare challenges surge globally — especially among youth — innovators are turning to an unlikely tool: video games. Now one of the world’s largest entertainment indus
 UN Input On AI: Winners, Losers, And OpportunitiesApr 14, 2025 am 11:25 AM
UN Input On AI: Winners, Losers, And OpportunitiesApr 14, 2025 am 11:25 AM“History has shown that while technological progress drives economic growth, it does not on its own ensure equitable income distribution or promote inclusive human development,” writes Rebeca Grynspan, Secretary-General of UNCTAD, in the preamble.
 Learning Negotiation Skills Via Generative AIApr 14, 2025 am 11:23 AM
Learning Negotiation Skills Via Generative AIApr 14, 2025 am 11:23 AMEasy-peasy, use generative AI as your negotiation tutor and sparring partner. Let’s talk about it. This analysis of an innovative AI breakthrough is part of my ongoing Forbes column coverage on the latest in AI, including identifying and explaining
 TED Reveals From OpenAI, Google, Meta Heads To Court, Selfie With MyselfApr 14, 2025 am 11:22 AM
TED Reveals From OpenAI, Google, Meta Heads To Court, Selfie With MyselfApr 14, 2025 am 11:22 AMThe TED2025 Conference, held in Vancouver, wrapped its 36th edition yesterday, April 11. It featured 80 speakers from more than 60 countries, including Sam Altman, Eric Schmidt, and Palmer Luckey. TED’s theme, “humanity reimagined,” was tailor made
 Joseph Stiglitz Warns Of The Looming Inequality Amid AI Monopoly PowerApr 14, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Joseph Stiglitz Warns Of The Looming Inequality Amid AI Monopoly PowerApr 14, 2025 am 11:21 AMJoseph Stiglitz is renowned economist and recipient of the Nobel Prize in Economics in 2001. Stiglitz posits that AI can worsen existing inequalities and consolidated power in the hands of a few dominant corporations, ultimately undermining economic
 What is Graph Database?Apr 14, 2025 am 11:19 AM
What is Graph Database?Apr 14, 2025 am 11:19 AMGraph Databases: Revolutionizing Data Management Through Relationships As data expands and its characteristics evolve across various fields, graph databases are emerging as transformative solutions for managing interconnected data. Unlike traditional
 LLM Routing: Strategies, Techniques, and Python ImplementationApr 14, 2025 am 11:14 AM
LLM Routing: Strategies, Techniques, and Python ImplementationApr 14, 2025 am 11:14 AMLarge Language Model (LLM) Routing: Optimizing Performance Through Intelligent Task Distribution The rapidly evolving landscape of LLMs presents a diverse range of models, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. Some excel at creative content gen


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment






