 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI How much do you know about autonomous driving inertial navigation technology?
How much do you know about autonomous driving inertial navigation technology?How much do you know about autonomous driving inertial navigation technology?
Inertial navigation is generally integrated into GPS equipment and is integrated by suppliers. So what is the need to discuss here? We must know that when the vehicle is driving, we can get the yawrate and speed signals of the GPS. Moreover, the vehicle itself has a set of sensors to obtain yawrate and speed, and because trajectory estimation is an important part of autonomous driving, understanding the working principle of inertial navigation can help us do vehicle body-based trajectory estimation.
Inertial Navigation
At present, the integrated navigation system composed of GNSS IMU is the mainstream positioning system solution, and the inertial navigation system is the only one that can output complete The equipment with six degrees of freedom data has high data update frequency and is the fusion center of positioning information.
The core algorithms used in inertial navigation mainly include three types: 1. Inertial navigation solution algorithm; 2. Kalman filter coupling of integrated navigation. 3. Integration of environmental feature information and inertial navigation.
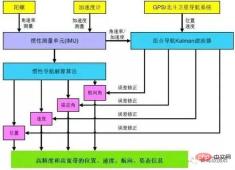
Integrated navigation system core algorithm framework
Hardware and principle
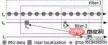
The inertial navigation system (INS) uses the inertial sensor (IMU) to measure the specific force and angular velocity information of the carrier, combined with the given initial conditions, and integrates it with information from systems such as GNSS to perform real-time An autonomous navigation system that estimates speed, position, attitude and other parameters. Specifically, the inertial navigation system is a type of dead reckoning navigation. That is, the position of the next point is deduced from the position of a known point based on the continuously measured heading angle and speed of the carrier, so that the current position of the moving body can be continuously measured.
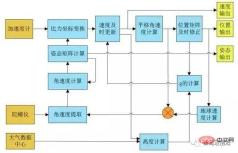
Inertial system working principle diagram
The inertial navigation system uses an accelerometer and gyro sensors to measure the motion parameters of the carrier. Three vertically arranged gyroscopes are used to measure the angular velocity of the carrier around its three coordinate axes, and are also sensitive to the angular velocity of the earth's rotation.
The accelerometer is based on Newton's second law and uses capacitive, piezoresistive or thermal convection principles to obtain the acceleration value by measuring the corresponding inertial force of the mass block during the acceleration process. Used to measure the acceleration of each axis on the moving body coordinate system.
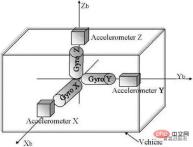
Inertial system working principle diagram
Inertial navigation through the gyroscope The measured angular velocity is integrated and transformed to calculate the attitude angle (roll, pitch angle) and azimuth angle of the vehicle body. The components of gravity acceleration on each coordinate axis can be calculated based on the attitude angle. The acceleration of each axis measured by the accelerometer is integrated after subtracting the gravity acceleration component to obtain the velocity and position. The state calculated by inertial navigation is used to predict the current position of the vehicle, and then compared with the position (or observation data) obtained by the satellite positioning receiver. The compared deviation includes the inertial navigation estimation error and the satellite receiver positioning error. After weighting through the data fusion algorithm, it is used to correct the inertial navigation prediction, making the inertial navigation prediction more and more accurate.
Inertial navigation solution algorithm
Usually divided into the following steps:
- Attitude update: Integrate the angular velocity output by the gyroscope to obtain the attitude increment, which is superimposed on the last attitude;
- Coordinate conversion: from IMU From the carrier coordinate system to the position and velocity solution coordinate system (inertial coordinate system);
- Speed update: it is necessary to consider the removal of gravity acceleration to obtain the acceleration in the inertial system, and obtain the velocity through integration;
- Position update: get the position through velocity integration.
Principle diagram of inertial navigation solution algorithm
In In inertial navigation, each iteration of the navigation equation needs to use the last navigation result as the initial value, so the initialization of inertial navigation is one of the more important parts. Attitude alignment refers to obtaining the roll, pitch, and yaw of the IMU. The alignment process of roll and pitch is generally called leveling. When the car is stationary, the specific force measured by the accelerometer is only caused by gravity, which can be solved by f=C*g; for a very high-precision IMU, the compass alignment method can be used. When the car is stationary, the specific force measured in the carrier system is The rotation of the earth is used to determine the orientation (yaw) of the carrier.
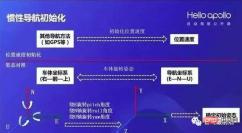
Inertial navigation initialization schematic
Kalman filtering of combined navigation The coupling of the filter
uses the coupling of the Kalman filter to fuse the IMU and GNSS point cloud positioning results. It can be divided into two methods: loose coupling and tight coupling.
The loose coupling filter uses the difference between the position and velocity measurements and the calculated position and velocity as the input of the combined navigation filter, which is the quantity measurement of the Kalman filter. Tightly coupled data include GNSS navigation parameters, pseudoranges in positioning, distance changes, etc.
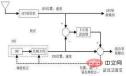
Loose coupling schematic diagram of Kalman filter
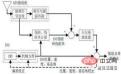
Tight coupling schematic diagram of Kalman filter

Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of loose coupling and tight coupling of Kalman filter
Taking the inertial navigation system used by Baidu Apollo as an example, the loose coupling method is adopted. And an error Kalman filter is used. The results of the inertial navigation solution are used for the time update of the Kalman filter, that is, prediction; while the GNSS and point cloud positioning results are used for the measurement update of the Kalman filter. The Kalman filter will output the position, speed, and attitude errors to correct the inertial navigation module, and the errors during the IMU period are used to compensate for the original IMU data.
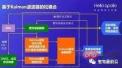
Loose coupling of Baidu Apollo Kalman filter
Kalman filter fusion diagram
Integration of environmental feature information and inertial navigation
The positioning accuracy and stability of the currently commonly used GNSS IMU combined inertial navigation solution in some scenarios still cannot fully meet the requirements of autonomous driving . For example, in scenarios where GNSS signals are weak for a long time, such as urban building groups and underground garages, relying on GNSS signals to update precise positioning is not stable enough. Therefore, new precise positioning update data sources must be introduced, and lidar/lidar/ It has become an inevitable trend to integrate visual sensing positioning and other environmental information for positioning.
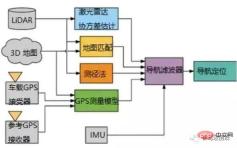
Schematic diagram of an architecture for integrated navigation and environmental awareness information fusion
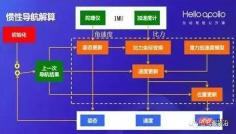
Take Baidu Apollo's multi-sensor fusion positioning system solution as an example. The inertial navigation system is at the center of the positioning module. The module fuses IMU, GNSS, Lidar and other positioning information, and the final output after solving and correcting the inertial navigation system satisfies High-precision position information with 6 degrees of freedom required for autonomous driving.
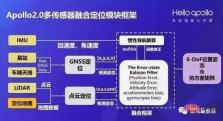
Baidu Apollo’s inertial fusion positioning module framework
The above is the detailed content of How much do you know about autonomous driving inertial navigation technology?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
![Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/242/473/174717025174979.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40) Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AM
Can't use ChatGPT! Explaining the causes and solutions that can be tested immediately [Latest 2025]May 14, 2025 am 05:04 AMChatGPT is not accessible? This article provides a variety of practical solutions! Many users may encounter problems such as inaccessibility or slow response when using ChatGPT on a daily basis. This article will guide you to solve these problems step by step based on different situations. Causes of ChatGPT's inaccessibility and preliminary troubleshooting First, we need to determine whether the problem lies in the OpenAI server side, or the user's own network or device problems. Please follow the steps below to troubleshoot: Step 1: Check the official status of OpenAI Visit the OpenAI Status page (status.openai.com) to see if the ChatGPT service is running normally. If a red or yellow alarm is displayed, it means Open
 Calculating The Risk Of ASI Starts With Human MindsMay 14, 2025 am 05:02 AM
Calculating The Risk Of ASI Starts With Human MindsMay 14, 2025 am 05:02 AMOn 10 May 2025, MIT physicist Max Tegmark told The Guardian that AI labs should emulate Oppenheimer’s Trinity-test calculus before releasing Artificial Super-Intelligence. “My assessment is that the 'Compton constant', the probability that a race to
 An easy-to-understand explanation of how to write and compose lyrics and recommended tools in ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 05:01 AM
An easy-to-understand explanation of how to write and compose lyrics and recommended tools in ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 05:01 AMAI music creation technology is changing with each passing day. This article will use AI models such as ChatGPT as an example to explain in detail how to use AI to assist music creation, and explain it with actual cases. We will introduce how to create music through SunoAI, AI jukebox on Hugging Face, and Python's Music21 library. Through these technologies, everyone can easily create original music. However, it should be noted that the copyright issue of AI-generated content cannot be ignored, and you must be cautious when using it. Let’s explore the infinite possibilities of AI in the music field together! OpenAI's latest AI agent "OpenAI Deep Research" introduces: [ChatGPT]Ope
 What is ChatGPT-4? A thorough explanation of what you can do, the pricing, and the differences from GPT-3.5!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AM
What is ChatGPT-4? A thorough explanation of what you can do, the pricing, and the differences from GPT-3.5!May 14, 2025 am 05:00 AMThe emergence of ChatGPT-4 has greatly expanded the possibility of AI applications. Compared with GPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4 has significantly improved. It has powerful context comprehension capabilities and can also recognize and generate images. It is a universal AI assistant. It has shown great potential in many fields such as improving business efficiency and assisting creation. However, at the same time, we must also pay attention to the precautions in its use. This article will explain the characteristics of ChatGPT-4 in detail and introduce effective usage methods for different scenarios. The article contains skills to make full use of the latest AI technologies, please refer to it. OpenAI's latest AI agent, please click the link below for details of "OpenAI Deep Research"
 Explaining how to use the ChatGPT app! Japanese support and voice conversation functionMay 14, 2025 am 04:59 AM
Explaining how to use the ChatGPT app! Japanese support and voice conversation functionMay 14, 2025 am 04:59 AMChatGPT App: Unleash your creativity with the AI assistant! Beginner's Guide The ChatGPT app is an innovative AI assistant that handles a wide range of tasks, including writing, translation, and question answering. It is a tool with endless possibilities that is useful for creative activities and information gathering. In this article, we will explain in an easy-to-understand way for beginners, from how to install the ChatGPT smartphone app, to the features unique to apps such as voice input functions and plugins, as well as the points to keep in mind when using the app. We'll also be taking a closer look at plugin restrictions and device-to-device configuration synchronization
 How do I use the Chinese version of ChatGPT? Explanation of registration procedures and feesMay 14, 2025 am 04:56 AM
How do I use the Chinese version of ChatGPT? Explanation of registration procedures and feesMay 14, 2025 am 04:56 AMChatGPT Chinese version: Unlock new experience of Chinese AI dialogue ChatGPT is popular all over the world, did you know it also offers a Chinese version? This powerful AI tool not only supports daily conversations, but also handles professional content and is compatible with Simplified and Traditional Chinese. Whether it is a user in China or a friend who is learning Chinese, you can benefit from it. This article will introduce in detail how to use ChatGPT Chinese version, including account settings, Chinese prompt word input, filter use, and selection of different packages, and analyze potential risks and response strategies. In addition, we will also compare ChatGPT Chinese version with other Chinese AI tools to help you better understand its advantages and application scenarios. OpenAI's latest AI intelligence
 5 AI Agent Myths You Need To Stop Believing NowMay 14, 2025 am 04:54 AM
5 AI Agent Myths You Need To Stop Believing NowMay 14, 2025 am 04:54 AMThese can be thought of as the next leap forward in the field of generative AI, which gave us ChatGPT and other large-language-model chatbots. Rather than simply answering questions or generating information, they can take action on our behalf, inter
 An easy-to-understand explanation of the illegality of creating and managing multiple accounts using ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 04:50 AM
An easy-to-understand explanation of the illegality of creating and managing multiple accounts using ChatGPTMay 14, 2025 am 04:50 AMEfficient multiple account management techniques using ChatGPT | A thorough explanation of how to use business and private life! ChatGPT is used in a variety of situations, but some people may be worried about managing multiple accounts. This article will explain in detail how to create multiple accounts for ChatGPT, what to do when using it, and how to operate it safely and efficiently. We also cover important points such as the difference in business and private use, and complying with OpenAI's terms of use, and provide a guide to help you safely utilize multiple accounts. OpenAI


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






