 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI How self-service business intelligence capabilities can improve data usage
How self-service business intelligence capabilities can improve data usage
Businesses can become more effective problem solvers and use self-service business intelligence capabilities to bring more data and tools to their users.
While self-service reporting and analytics are not new concepts, a lot has changed, from the types of data available to the nature of self-service itself.
Dan Simion, vice president of artificial intelligence and analytics at global professional services provider Capgemini, said: “What is changing is a shift from descriptive analytics to predictive and prescriptive analytics, powered by advanced analytics, data science and machine learning. Support. What needs to be done going forward is to be as flexible as possible when self-service reporting occurs so that enterprises can react to business needs as quickly as possible."
An important advancement is the ability to interact with data rather than passively consume reports or dashboard. Users can take advantage of the natural language query capabilities in the augmented analytics platform with no clicks of the keyboard and no need to know query languages such as SQL.
Even better, the answers to their questions often include an automatically generated data visualization and a narrative explaining what the data visualization means, which helps promote a shared understanding of what the data is saying.
Meanwhile, data engineering teams have been building data pipelines to ensure the right data gets to the right place at the right time for scenario decisions, while including important enterprise guardrails such as data governance and compliance sex.
The augmented analytics platform also supports self-service data preparation, allowing users to select their own data sources and combine them as needed to answer queries. Insights or dynamic data stories can also be automatically generated based on an individual's context, such as their personas and past queries run.
Microsoft Power BI, Qlik, Sisense, Tableau, Thought Spot and other leaders in the field have provided enhanced capabilities so enterprises can democratize analytics to a wider user base.
How to enable self-service
There are two general methods for enabling self-service business intelligence capabilities. One is to buy a departmental tool and get it up and running with the help of your IT team.
Another approach is to enable data experts (data scientists, data analysts, and data engineers) to provide enhanced analytical capabilities to the masses. The benefit of this approach is to see how people are using analytics in the business and to mitigate data-related risks, such as using personally identifiable information in non-compliant ways.
Large enterprises often have centers of excellence (COEs), supplemented by data scientists and data analysts assigned to specific departments or lines of business. This way, businesses can ensure their best practices while meeting the specific needs of operating units.
At the same time, as enterprises adopt cloud computing services, they are also running analytics and machine learning to enhance self-service capabilities.
Sree Majji, senior vice president of digital engineering professional service provider Apexon, said, “For example, a center of excellence (COE) can establish a dedicated discovery environment for each business group to implement business intelligence functions or data analysis. End-to-end discovery, in addition, purpose-built platforms can be instantiated for fully governed versus partially governed business intelligence environments."
The democratization of analytics enables business users to get answers to their questions faster than they could if they relied on IT. It also enables data scientists and data analysts to focus on harder problems that require specialized knowledge.
Self-service approach from industry-leading vendor
Sisense promotes a hub-and-spoke model where experts from the data team can provide support to citizen data scientists, as described above. With a center of excellence, policies and best practices are embedded in an organization's data culture.
There are some experts in the business unit, such as data scientists and analysts with domain knowledge. This approach balances the enterprise's desire to optimize business intelligence within operating units with the need for controls and standards such as governance. Specifically, the platform offers several features, including:
- Vision-based data modeling and dashboard creation.
- Interactive visualization with advanced filtering and drill paths.
- AI-driven data investigation.
- Integrate with workflow and business applications.
The Microsoft Power BI team promotes managed self-service, which divides responsibilities just like the hub-and-spoke approach, albeit differently. In this model, IT retains ownership of the data and business units can run their own reports. This approach recognizes the two-speed nature of modern organizations, where business professionals move quickly and IT moves slower.
Like Sisense, Power BI offers a drag-and-drop interface and artificial intelligence assistance for non-data experts. Enterprise business intelligence capabilities allow data scientists and data analysts to conduct more complex analyses. It also provides enterprise-level control. Customers can combine self-service and enterprise business intelligence to achieve business agility and more secure data usage.
Qlik also balances the needs of business and IT through its platform QlikSense. The company outlines five essential self-service business intelligence capabilities its platform offers. They are:
- Strike a balance between the need for data governance and timely and accurate decision-making.
- Easily integrate data sources.
- The ability to quickly share insights with stakeholders.
- Ability to create applications and reports on demand.
- Provides mobile access to analytics.
For competitive reasons, augmented analytics platforms have more similarities than differences. Often, the choice between platforms or platforms comes down to comfort level with each vendor.
Start with the Business Case
Ease of use drives many business intelligence platform decisions as enterprises look to provide data-driven insights to more employees. When operating units purchase their own analytics platform, they are typically solving a specific problem. Over time, an enterprise may end up with multiple platforms or multiple instances of the same platform.
Other considerations should include the scalability of the platform, how it fits into the enterprise's current and planned architecture, and whether the platform has adequate security, governance and compliance controls. The major platforms offer these features and in many ways offer similar functionality, so vendor choice may depend on the user's relative comfort with the vendor's team.
Cost and IT impact are other considerations
Understanding the cost of ownership and architectural impact of any business intelligence solution is key for business leaders. Total cost of ownership includes software licensing hardware costs, development costs, and maintenance costs. Majji said this could be 5 to 10 times the initial supplier sales.
Majji said, "A good business intelligence architecture can minimize manual intervention, protect static and dynamic data, and reduce the overhead of data movement. Before purchasing any business intelligence solution themselves, business leaders should Recognize these impacts."
Majji advises that if business intelligence tools already exist in the enterprise, it needs to keep pace with the changing environment and have a technology assessment framework to regularly evaluate the tools the enterprise already has versus what is available. tool. This includes identifying gaps in current tools based on required business capabilities. All tools should have a framework for divestiture, maintenance or investment assessment and valuation techniques.
Simion said, “If the tools are flexible enough and can effectively solve new challenges in the business, then they are good enough to continue to be used. Do the tools adapt to real-time or near-real-time data? Examples like this can Helping businesses assess their position and make the difficult decision of whether to make changes.”
The above is the detailed content of How self-service business intelligence capabilities can improve data usage. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PMVibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
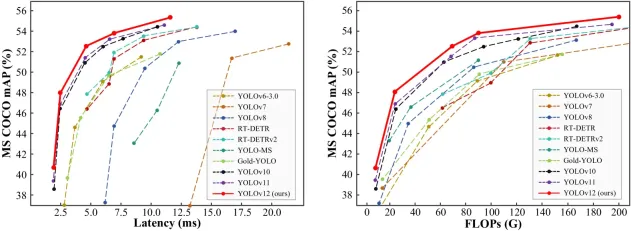 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AMYOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AMFebruary 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
 How to Use DALL-E 3: Tips, Examples, and FeaturesMar 09, 2025 pm 01:00 PM
How to Use DALL-E 3: Tips, Examples, and FeaturesMar 09, 2025 pm 01:00 PMDALL-E 3: A Generative AI Image Creation Tool Generative AI is revolutionizing content creation, and DALL-E 3, OpenAI's latest image generation model, is at the forefront. Released in October 2023, it builds upon its predecessors, DALL-E and DALL-E 2
 Elon Musk & Sam Altman Clash over $500 Billion Stargate ProjectMar 08, 2025 am 11:15 AM
Elon Musk & Sam Altman Clash over $500 Billion Stargate ProjectMar 08, 2025 am 11:15 AMThe $500 billion Stargate AI project, backed by tech giants like OpenAI, SoftBank, Oracle, and Nvidia, and supported by the U.S. government, aims to solidify American AI leadership. This ambitious undertaking promises a future shaped by AI advanceme
 Google's GenCast: Weather Forecasting With GenCast Mini DemoMar 16, 2025 pm 01:46 PM
Google's GenCast: Weather Forecasting With GenCast Mini DemoMar 16, 2025 pm 01:46 PMGoogle DeepMind's GenCast: A Revolutionary AI for Weather Forecasting Weather forecasting has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving from rudimentary observations to sophisticated AI-powered predictions. Google DeepMind's GenCast, a groundbreak
 Sora vs Veo 2: Which One Creates More Realistic Videos?Mar 10, 2025 pm 12:22 PM
Sora vs Veo 2: Which One Creates More Realistic Videos?Mar 10, 2025 pm 12:22 PMGoogle's Veo 2 and OpenAI's Sora: Which AI video generator reigns supreme? Both platforms generate impressive AI videos, but their strengths lie in different areas. This comparison, using various prompts, reveals which tool best suits your needs. T
 Which AI is better than ChatGPT?Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
Which AI is better than ChatGPT?Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PMThe article discusses AI models surpassing ChatGPT, like LaMDA, LLaMA, and Grok, highlighting their advantages in accuracy, understanding, and industry impact.(159 characters)


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools






