 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI The driver's 'divine assist” on the road! BIT develops hybrid brain-computer interface driving assistance system to improve driving safety
The driver's 'divine assist” on the road! BIT develops hybrid brain-computer interface driving assistance system to improve driving safetyThe driver's 'divine assist” on the road! BIT develops hybrid brain-computer interface driving assistance system to improve driving safety
With the improvement of people’s living standards, cars have entered thousands of households. However, while vehicles provide travel convenience, traffic accidents have also become an important threat to the life safety of drivers and pedestrians.
According to incomplete statistics from the World Health Organization in 2018, road traffic accidents are one of the important factors causing casualties and economic losses. Traffic accidents cause nearly 1.35 million deaths and 20-50 million injuries every year. Nearly 3% of the GDP is consumed by traffic accidents every year.
Among them, fatigue driving is an important factor causing traffic accidents, second only to speeding. Therefore, driving safety is no small matter, even if you are an "experienced driver".
Based on driving safety issues, recently, Assistant Professor Luo Longxi and doctoral student Ju Jiawei from the intelligent human-machine system team of Professor Bi Luzheng from the School of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering of Beijing Institute of Technology proposed a method Intelligent Driving Assistance Systems (IDAS), or synchronized sequential hybrid brain-computer interfaces (hBCIs), combine electroencephalography (EEG) and electromyography (EMG) signals to classify the driver's braking and normal driving intentions.
To put it simply and crudely, this intelligent assistance system can indirectly affect vehicle control by identifying emergencies that the driver may encounter, or it can directly control the vehicle after discovering the emergency. Effectively improve driving safety.
The research was published in the form of a paper in the English science and technology journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems.

Hybrid brain-computer interface——hBCI
Currently, the input information of IDAS mainly includes vehicles Information related to environment, behavior, and biological signals. Vehicle and surrounding environment information mainly comes from vehicle parameters and traffic information. Some IDAS need to detect the driver's drowsiness state, while other systems rely on driving behavior detection and driving intention prediction.
So where does the driver’s relevant information come from? The answer is obtained by monitoring the activity of the driver's feet, limbs and nerves.
Sources of biological information include electroencephalography (EEG) signals and electromyography (EMG) signals. Due to the early emergence of EEG signals, brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) based on EEG signals have been used in driving behavior research. Although these EEG interfaces have made great progress in braking intention detection, their detection performance is not stable due to the characteristics of the EEG signal itself. As an effective solution, hybrid brain-computer interface (hBCI) can solve the shortcomings of EEG-based BCIs such as low stability, poor performance, and insufficient reliability.
Based on how signals are combined, hbci can be divided into two modes, using feature-level fusion strategy (hBCI-FL) and classifier-level fusion strategy (hbci-cl). The first mode combines two or more EEG signals, and the other mode combines EEG with other signals such as EMG signals and ECG signals.
The researchers invited 13 subjects aged between 24 and 30 to participate in the experiment. By collecting EEG signals, EMG signals and vehicle information during simulated driving, the detection of driver's hard braking intention in virtual driving scenarios was studied. Then, they used the hBCI model that combines EEG signals, EMG signals, and vehicle information to detect the upcoming emergency braking intention.

Three driving intention classifications
In the experiment, the R&D team compared and analyzed several simultaneous The sexual and temporal hBCI models use spectral features and temporal features respectively, as well as one VS rest or decision tree classification strategies to perform multiple classifications of the three driving intentions.

The "one VS rest" classification strategy decomposes the three categories into three parallel binary classifications, including normal driving vs. other, soft braking vs. other, and hard braking vs. other. For the one VS rest classification strategy, the final result is obtained based on the maximum value of all two classifiers.
Experimental results show that the R&D team’s hBCI system recognizes hard braking intentions 130 m/s faster than the model based on pedal deflection. The hBCI-SE1 classification algorithm and one-on-one classification strategy based on spectral features have the highest classification accuracy, and the average system accuracy is 96.37%. Finally, the team selected optimal order hBCI, optimal order hBCI and models based on single brain electrical signals or electromyographic signals for comparison.

The results show that optimal simultaneity and sequential hbci are significantly better than those based on single EEG or EMG signal method. In the test, the results obtained were in good agreement with the offline test results.
This research has certain reference value for human-centered intelligent assisted driving systems to improve driving safety and driving comfort. However, the project currently has certain limitations. For example, there are various stimulus factors that induce hard braking and soft braking, the impact of subject differences, the inconvenience of the collection device, etc. Next, the team will solve the above limitations and explore more effective feature and strategy fusion to improve performance.
This research was partially funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51975052) and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation of China (3222021).
Paper address:
https://downloads.spj.sciencemag.org/cbsystems/aip/9847652.pdf
The above is the detailed content of The driver's 'divine assist” on the road! BIT develops hybrid brain-computer interface driving assistance system to improve driving safety. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Let's Dance: Structured Movement To Fine-Tune Our Human Neural NetsApr 27, 2025 am 11:09 AMScientists have extensively studied human and simpler neural networks (like those in C. elegans) to understand their functionality. However, a crucial question arises: how do we adapt our own neural networks to work effectively alongside novel AI s
 New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AM
New Google Leak Reveals Subscription Changes For Gemini AIApr 27, 2025 am 11:08 AMGoogle's Gemini Advanced: New Subscription Tiers on the Horizon Currently, accessing Gemini Advanced requires a $19.99/month Google One AI Premium plan. However, an Android Authority report hints at upcoming changes. Code within the latest Google P
 How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How Data Analytics Acceleration Is Solving AI's Hidden BottleneckApr 27, 2025 am 11:07 AMDespite the hype surrounding advanced AI capabilities, a significant challenge lurks within enterprise AI deployments: data processing bottlenecks. While CEOs celebrate AI advancements, engineers grapple with slow query times, overloaded pipelines, a
 MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AM
MarkItDown MCP Can Convert Any Document into Markdowns!Apr 27, 2025 am 09:47 AMHandling documents is no longer just about opening files in your AI projects, it’s about transforming chaos into clarity. Docs such as PDFs, PowerPoints, and Word flood our workflows in every shape and size. Retrieving structured
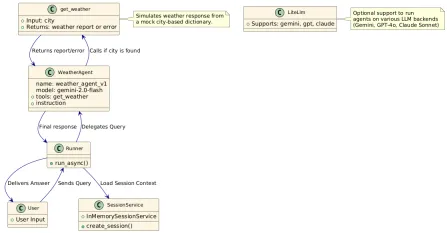 How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How to Use Google ADK for Building Agents? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:42 AMHarness the power of Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK) to create intelligent agents with real-world capabilities! This tutorial guides you through building conversational agents using ADK, supporting various language models like Gemini and GPT. W
 Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AM
Use of SLM over LLM for Effective Problem Solving - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:27 AMsummary: Small Language Model (SLM) is designed for efficiency. They are better than the Large Language Model (LLM) in resource-deficient, real-time and privacy-sensitive environments. Best for focus-based tasks, especially where domain specificity, controllability, and interpretability are more important than general knowledge or creativity. SLMs are not a replacement for LLMs, but they are ideal when precision, speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Technology helps us achieve more with fewer resources. It has always been a promoter, not a driver. From the steam engine era to the Internet bubble era, the power of technology lies in the extent to which it helps us solve problems. Artificial intelligence (AI) and more recently generative AI are no exception
 How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AM
How to Use Google Gemini Models for Computer Vision Tasks? - Analytics VidhyaApr 27, 2025 am 09:26 AMHarness the Power of Google Gemini for Computer Vision: A Comprehensive Guide Google Gemini, a leading AI chatbot, extends its capabilities beyond conversation to encompass powerful computer vision functionalities. This guide details how to utilize
 Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AM
Gemini 2.0 Flash vs o4-mini: Can Google Do Better Than OpenAI?Apr 27, 2025 am 09:20 AMThe AI landscape of 2025 is electrifying with the arrival of Google's Gemini 2.0 Flash and OpenAI's o4-mini. These cutting-edge models, launched weeks apart, boast comparable advanced features and impressive benchmark scores. This in-depth compariso


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

SecLists
SecLists is the ultimate security tester's companion. It is a collection of various types of lists that are frequently used during security assessments, all in one place. SecLists helps make security testing more efficient and productive by conveniently providing all the lists a security tester might need. List types include usernames, passwords, URLs, fuzzing payloads, sensitive data patterns, web shells, and more. The tester can simply pull this repository onto a new test machine and he will have access to every type of list he needs.






