 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals AI
AI Virtual-real domain adaptation method for autonomous driving lane detection and classification
Virtual-real domain adaptation method for autonomous driving lane detection and classificationVirtual-real domain adaptation method for autonomous driving lane detection and classification
arXiv paper "Sim-to-Real Domain Adaptation for Lane Detection and Classification in Autonomous Driving", May 2022, work at the University of Waterloo, Canada.

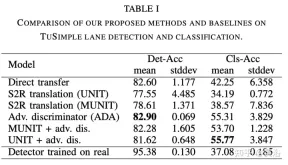
While supervised detection and classification frameworks for autonomous driving require large annotated datasets, Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) driven by synthetic data generated by illuminating real simulated environments , Unsupervised Domain Adaptation) method is a low-cost, less time-consuming solution. This paper proposes a UDA scheme of adversarial discriminative and generative methods for lane line detection and classification applications in autonomous driving.
Also introduces the Simulanes dataset generator, which takes advantage of CARLA's huge traffic scenes and weather conditions to create a natural synthetic dataset. The proposed UDA framework takes the labeled synthetic dataset as the source domain, while the target domain is the unlabeled real data. Use adversarial generation and feature discriminator to debug the learning model and predict the lane location and category of the target domain. Evaluation is performed with real and synthetic datasets.
The open source UDA framework is atgithubcom/anita-hu/sim2real-lane-detection, and the data set generator is at github.com/anita-hu/simulanes.
Real-world driving is diverse, with varying traffic conditions, weather, and surrounding environments. Therefore, the diversity of simulation scenarios is crucial to the good adaptability of the model in the real world. There are many open source simulators for autonomous driving, namely CARLA and LGSVL. This article chooses CARLA to generate the simulation data set. In addition to the flexible Python API, CARLA also contains rich pre-drawn map content covering urban, rural and highway scenes.
Simulation data generator Simulanes generates a variety of simulation scenarios in urban, rural and highway environments, including 15 lane categories and dynamic weather. The figure shows samples from the synthetic dataset. Pedestrian and vehicle participants are randomly generated and placed on the map, increasing the difficulty of the dataset through occlusion. According to the TuSimple and CULane datasets, the maximum number of lanes near the vehicle is limited to 4, and row anchors are used as labels.

Since the CARLA simulator does not directly provide lane location labels, CARLA's waypoint system is used to generate labels. A CARLA waypoint is a predefined position for the vehicle autopilot to follow, located in the center of the lane. In order to obtain the lane position label, the waypoint of the current lane is moved left and right by W/2, where W is the lane width given by the simulator. These moved waypoints are then projected into the camera coordinate system and spline-fitted to generate labels along predetermined row anchor points. The class label is given by the simulator and is one of 15 classes.
To generate a dataset with N frames, divide N evenly across all available maps. From the default CARLA map, towns 1, 3, 4, 5, 7 and 10 were used, while towns 2 and 6 were not used due to differences between the extracted lane position labels and the lane positions of the image. For each map, vehicle participants are spawned at random locations and move randomly. Dynamic weather is achieved by smoothly changing the position of the sun as a sinusoidal function of time and occasionally producing storms, which affect the appearance of the environment through variables such as cloud cover, water volume and standing water. To avoid saving multiple frames at the same location, check if the vehicle has moved from the previous frame's location and regenerate a new vehicle if it has been stationary for too long.
When the sim-to-real algorithm is applied to lane detection, an end-to-end approach is adopted and the Ultra-Fast-Lane-Detection (UFLD) model is used as the basic network. UFLD was chosen because its lightweight architecture can achieve 300 frames/second at the same input resolution while achieving performance comparable to state-of-the-art methods. UFLD formulates the lane detection task as a row-based selection method, where each lane is represented by a series of horizontal positions of predefined rows, i.e., row anchors. For each row anchor, the position is divided into w grid cells. For the i-th lane and j-th row anchor, location prediction becomes a classification problem, where the model outputs the probability Pi,j of selecting (w 1) grid cell. The additional dimension in the output is no lanes.
UFLD proposes an auxiliary segmentation branch to aggregate features at multiple scales to model local features. This is only used during training. With the UFLD method, cross-entropy loss is used for segmentation loss Lseg. For lane classification, a small branch of the fully connected (FC) layer is added to receive the same features as the FC layer for lane position prediction. The lane classification loss Lcls also uses cross-entropy loss.
In order to alleviate the domain drift problem of UDA settings, UNIT ("Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation Networks", NIPS, 2017) & MUNIT## are adopted #("Multimodal unsupervised image-to-image translation," ECCV 2018) adversarial generation method, and adversarial discriminative method using feature discriminator. As shown in the figure: an adversarial generation method (A) and an adversarial discrimination method (B) are proposed. UNIT and MUNIT are represented in (A), which shows the generator input for image translation. Additional style inputs to MUNIT are shown with dashed blue lines. For simplicity, the MUNIT-style encoder output is omitted as it is not used for image translation.


The above is the detailed content of Virtual-real domain adaptation method for autonomous driving lane detection and classification. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AM
The AI Skills Gap Is Slowing Down Supply ChainsApr 26, 2025 am 11:13 AMThe term "AI-ready workforce" is frequently used, but what does it truly mean in the supply chain industry? According to Abe Eshkenazi, CEO of the Association for Supply Chain Management (ASCM), it signifies professionals capable of critic
 How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AM
How One Company Is Quietly Working To Transform AI ForeverApr 26, 2025 am 11:12 AMThe decentralized AI revolution is quietly gaining momentum. This Friday in Austin, Texas, the Bittensor Endgame Summit marks a pivotal moment, transitioning decentralized AI (DeAI) from theory to practical application. Unlike the glitzy commercial
 Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Nvidia Releases NeMo Microservices To Streamline AI Agent DevelopmentApr 26, 2025 am 11:11 AMEnterprise AI faces data integration challenges The application of enterprise AI faces a major challenge: building systems that can maintain accuracy and practicality by continuously learning business data. NeMo microservices solve this problem by creating what Nvidia describes as "data flywheel", allowing AI systems to remain relevant through continuous exposure to enterprise information and user interaction. This newly launched toolkit contains five key microservices: NeMo Customizer handles fine-tuning of large language models with higher training throughput. NeMo Evaluator provides simplified evaluation of AI models for custom benchmarks. NeMo Guardrails implements security controls to maintain compliance and appropriateness
 AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AM
AI Paints A New Picture For The Future Of Art And DesignApr 26, 2025 am 11:10 AMAI: The Future of Art and Design Artificial intelligence (AI) is changing the field of art and design in unprecedented ways, and its impact is no longer limited to amateurs, but more profoundly affecting professionals. Artwork and design schemes generated by AI are rapidly replacing traditional material images and designers in many transactional design activities such as advertising, social media image generation and web design. However, professional artists and designers also find the practical value of AI. They use AI as an auxiliary tool to explore new aesthetic possibilities, blend different styles, and create novel visual effects. AI helps artists and designers automate repetitive tasks, propose different design elements and provide creative input. AI supports style transfer, which is to apply a style of image
 How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How Zoom Is Revolutionizing Work With Agentic AI: From Meetings To MilestonesApr 26, 2025 am 11:09 AMZoom, initially known for its video conferencing platform, is leading a workplace revolution with its innovative use of agentic AI. A recent conversation with Zoom's CTO, XD Huang, revealed the company's ambitious vision. Defining Agentic AI Huang d
 The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AM
The Existential Threat To UniversitiesApr 26, 2025 am 11:08 AMWill AI revolutionize education? This question is prompting serious reflection among educators and stakeholders. The integration of AI into education presents both opportunities and challenges. As Matthew Lynch of The Tech Edvocate notes, universit
 The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AM
The Prototype: American Scientists Are Looking For Jobs AbroadApr 26, 2025 am 11:07 AMThe development of scientific research and technology in the United States may face challenges, perhaps due to budget cuts. According to Nature, the number of American scientists applying for overseas jobs increased by 32% from January to March 2025 compared with the same period in 2024. A previous poll showed that 75% of the researchers surveyed were considering searching for jobs in Europe and Canada. Hundreds of NIH and NSF grants have been terminated in the past few months, with NIH’s new grants down by about $2.3 billion this year, a drop of nearly one-third. The leaked budget proposal shows that the Trump administration is considering sharply cutting budgets for scientific institutions, with a possible reduction of up to 50%. The turmoil in the field of basic research has also affected one of the major advantages of the United States: attracting overseas talents. 35
 All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AM
All About Open AI's Latest GPT 4.1 Family - Analytics VidhyaApr 26, 2025 am 10:19 AMOpenAI unveils the powerful GPT-4.1 series: a family of three advanced language models designed for real-world applications. This significant leap forward offers faster response times, enhanced comprehension, and drastically reduced costs compared t


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.





