512g solid state drive refers to the storage capacity of the solid state drive is 512GB; 512GB generally refers to the form capacity of the hard disk, and the actual capacity is about 500GB. The capacity of the hard disk in the operating system does not match the official nominal capacity. It is both less than the nominal capacity. The larger the capacity, the greater the difference. This is because the hard disk manufacturer’s calculation method of capacity is different from that of the operating system. Caused by different unit conversion relationships.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
512g solid state drive refers to the storage capacity of the solid state drive is 512GB. 512GB generally refers to the formal capacity of the hard disk, and the actual capacity is about 500GB.
Solid State Drive Introduction
Solid State Disk (Solid State Disk or Solid State Drive, referred to as SSD), also known as solid state drive, is a solid state drive. A hard drive made from an array of electronic memory chips. It is a primary flash memory (NAND Flash) computer storage device used as permanent memory.
Solid state drives are composed of control units and storage unit controls (FLASH chips, DRAM chips), and are widely used in industrial control, video surveillance, network monitoring, network terminals, navigation equipment and other fields. Compared with mechanical hard drives, solid-state drives have higher read and write speeds, but the cost is also relatively high. The new generation of solid state drives adopts the new generation of solid state drives SATA-III, PCIex8 or mSATA, M.2, ZIF, IDE, U.2, CF, CFast and other interfaces.

Flash-based SSD is the main category of SSD, and its internal structure is very simple. The main body of a solid-state drive is actually a PCB board. The most basic accessories on the PCB board are a control chip, a cache chip (some low-end hard drives do not have a cache chip), and a flash memory chip for storing data.
Solid-state drives are exactly the same as ordinary hard drives in terms of interface specifications and definitions, functions and usage methods, and their product appearance and size are basically the same as ordinary hard drives (emerging U.2, M.2 and other forms The size and shape of solid-state drives are completely different from SATA mechanical hard drives). It is widely used in military, vehicle, industrial control, video surveillance, network monitoring, network terminals, electric power, medical, aviation, navigation equipment and many other fields.
Advantages:
Fast reading and writing speed: Using flash memory as the storage medium, the reading speed is faster than that of a mechanical hard disk. SSDs do not use magnetic heads and their seek time is almost zero. The continuous writing speed is very amazing. Most solid-state drive manufacturers will claim that their solid-state drives have a continuous reading and writing speed of more than 500MB/s. In recent years, NVMe solid-state drives can reach around 2000MB/s, or even more than 4000MB/s.
The speed of solid-state drives is not only reflected in continuous reading and writing. Fast random reading and writing speed is the ultimate secret of solid-state drives, which is most directly reflected in most daily operations. Related to this is extremely low access time. The seek time of the most common 7200-rpm mechanical hard drive is generally 12-14 milliseconds, while solid-state drives can easily reach 0.1 milliseconds or even lower.
Classification of solid-state drives
Classification method:
The storage media of solid-state drives are divided into two types, one is flash memory (FLASH chip) As a storage medium, another method is to use DRAM as a storage medium. The latest is Intel's XPoint particle technology.
-
Flash-based solid-state drives:
Flash-based solid-state drives (IDEFLASH DISK, Serial ATA Flash Disk): use FLASH chips as storage media, which is usually Talking about SSD. Its appearance can be made into a variety of shapes, such as laptop hard drive, micro hard drive, memory card, USB flash drive, etc. The biggest advantage of this kind of SSD solid state drive is that it can be moved, and the data protection is not controlled by the power supply. It can be adapted to various environments and is suitable for individual users. Longer lifespan varies with different flash media. SLC flash memory generally reaches tens of thousands of PE times, MLC can reach more than 3,000 times, TLC has also reached about 1,000 times, and the latest QLC can also ensure a lifespan of 300 times. The average user's write volume in a year does not exceed 50 times that of the hard disk. Overall size, even the cheapest QLC flash memory can provide a write life of 6 years. Reliability is very high, and high-quality home solid-state drives can easily achieve one-tenth the failure rate of ordinary home mechanical hard drives.
-
DRAM-based category:
DRAM-based solid state drive: uses DRAM as the storage medium and has a narrow application range. It imitates the design of a traditional hard disk, can be volume set up and managed by file system tools of most operating systems, and provides industry-standard PCI and FC interfaces for connecting to hosts or servers. Application methods can be divided into two types: SSD hard disk and SSD hard disk array. It is a high-performance memory that can theoretically be written infinitely. The only drawback is that it requires an independent power supply to protect data security. DRAM solid-state drives are relatively non-mainstream devices.
-
Based on 3D XPoint class
Solid state drive based on 3D XPoint: In principle, it is close to DRAM, but it is non-volatile storage. The read latency is extremely low, easily one hundredth that of existing solid-state drives, and has a near-infinite storage life. The disadvantage is that the density is lower than NAND and the cost is extremely high. It is mostly used in enthusiast-level desktop computers and data centers.
Expand knowledge:
Inside the computer, information is stored, calculated, and stored in binary form. processed and transmitted. Information storage units include bits, bytes and words. The storage capacity units of various storage devices include KB, MB, GB, and TB. It can be based on byte conversion
Unit conversion:
The conversion rate is approximately equal to 1000 (1024), and the order from large to small is T, GB, MB, KB, B. The smaller it is, the bit .
Computer storage units are generally represented by bit, B, KB, MB, GB, TB, PB, EB, ZB, YB, BB, NB, DB... The relationship between them is:

For hard disk capacity, general manufacturers always use decimal counting. Generally, computer operating systems use binary counting, so you will often find that the hard drive capacity you see on your computer is smaller than the actual available capacity on the hard drive. For example, a 20GB hard drive only shows 18.6GB.

Usually the hard drive we buy has a capacity of 1TB, and when plugged into the computer, it displays about 931G. This is normal. What is used in the computer is Binary algorithm. After purchasing a hard drive, careful people will find that the capacity of the hard drive in the operating system does not match the official nominal capacity, and is both less than the nominal capacity. The larger the capacity, the greater the difference.
The nominal 8GB hard drive displays only 7.4GB in the operating system; This is caused by the different calculation methods of hard drive manufacturers and operating systems for calculating capacity, and different unit conversion relationships. . The computer system uses the binary calculation method, while the hard disk manufacturer uses the international unit. In the international unit system, TB, GB, MB, and KB are the counting units of "base 1000". 1000 bytes is 1KB, and every 1000KB is 1MB. Every 1000MB is 1GB and every 1000GB is 1TB.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What does 512g solid state drive mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 修复 Windows 11 无法识别 PC 上的 NVMe SSDMay 18, 2023 am 11:38 AM
修复 Windows 11 无法识别 PC 上的 NVMe SSDMay 18, 2023 am 11:38 AMWindows11的发布非常坎坷。于2021年10月推出,用户报告了他们遇到的几种类型的问题,例如Windows11无法识别NVMeSSD、功能损坏、兼容性问题等。总而言之,微软长期以来非常不稳定和不发达的版本。虽然微软正在努力工作并且一直在缓慢地发布更新来解决这些问题,但Windows11中存在的问题数量是压倒性的。在这里,我们尝试帮助解决可能会破坏您使用最新Windows版本Windows11体验的问题。继续阅读以了解有关如何让您的PC检测到NVMeSSD
 如何使 SSD 成为 Windows 11 中的主驱动器May 15, 2023 pm 10:52 PM
如何使 SSD 成为 Windows 11 中的主驱动器May 15, 2023 pm 10:52 PM为什么让SSD成为Windows11中的主驱动器?优点说明HDD和SSD之间的区别不是程度的问题,而是种类的问题。HDD有很多运动部件——主轴、旋转磁盘、读/写臂等——损坏其中任何一个都可能导致磁盘失效。因此,耐用性并不是HDD的强项。它们也无法与SSD提供的速度相提并论。HDD使用机械组件,而SSD使用闪存来保存和访问数据。由于没有移动部件,它们坚固耐用,不易因坠落而损坏,同时也使它们速度更快、更省电。在大多数情况下,SSD的使用寿命也将比其传统同类产品更长。如果您经常向SSD引入新文件,SS
 使用 DriveDX 检查 Mac SSD 的健康状况Apr 16, 2023 pm 10:28 PM
使用 DriveDX 检查 Mac SSD 的健康状况Apr 16, 2023 pm 10:28 PM了解磁盘的健康状况很重要,原因有很多,但现在大多数现代Mac都将SSD驱动器焊接到逻辑板上,这意味着如果SSD出现故障,则必须更换整个逻辑板-比简单地更换驱动器更昂贵的维修。通过检查SSD的健康状态,您可以提前解决问题、备份数据,并至少在没有灾难性情况的情况下考虑您的修复选项。从开发商BinaryFruit获取DriveDXDriveDX提供免费试用,可让您查看SSD当前的健康状况。如果您想在两周试用期后继续使用DriveDX,您可以付费。打开DriveDX,您将获得驱
 安装win11找不到固态硬盘解决方法Jan 06, 2024 pm 09:02 PM
安装win11找不到固态硬盘解决方法Jan 06, 2024 pm 09:02 PM我们在安装win11系统后,可能会出现找不到原本固态硬盘的问题,这大概率是由于系统重置但是没有重新扫描硬盘,所以我们只要重新扫描一下即可。安装win11找不到固态硬盘解决方法1、首先,右键点击此电脑图标,打开“管理”选项。2、然后,点击进入左边栏“磁盘管理”选项页面。3、再该页面查看上方是否有固态硬盘,若有,右键点击选择“更改驱动器号和路径”选项。4、然后,再点击该页面的左下角“添加”按钮。5、接着点击“浏览”按钮并在弹出来的页面中添加驱动器号即可。方法二:1、若无,该页面的下面显示“unkno
 如何在新的 SSD 上安装 macOSApr 13, 2023 pm 04:01 PM
如何在新的 SSD 上安装 macOSApr 13, 2023 pm 04:01 PM如何使用 macOS Recovery 在新的 SSD 上安装 macOS在 2009 年之后生产的任何 Mac 上,都有一个内置的恢复系统。这允许您将 Mac 启动到恢复模式。在此模式下,您可以修复内部磁盘、从 Time Machine 备份恢复文件、获取在线帮助或重新安装 macOS。您必须能够连接到互联网才能使用这些工具。您可以使用 macOS 安装工具在计算机中安装的新 SSD 上安装 macOS。要使用 Internet Recovery 在 SSD 上安装 macOS:按照制造商针对
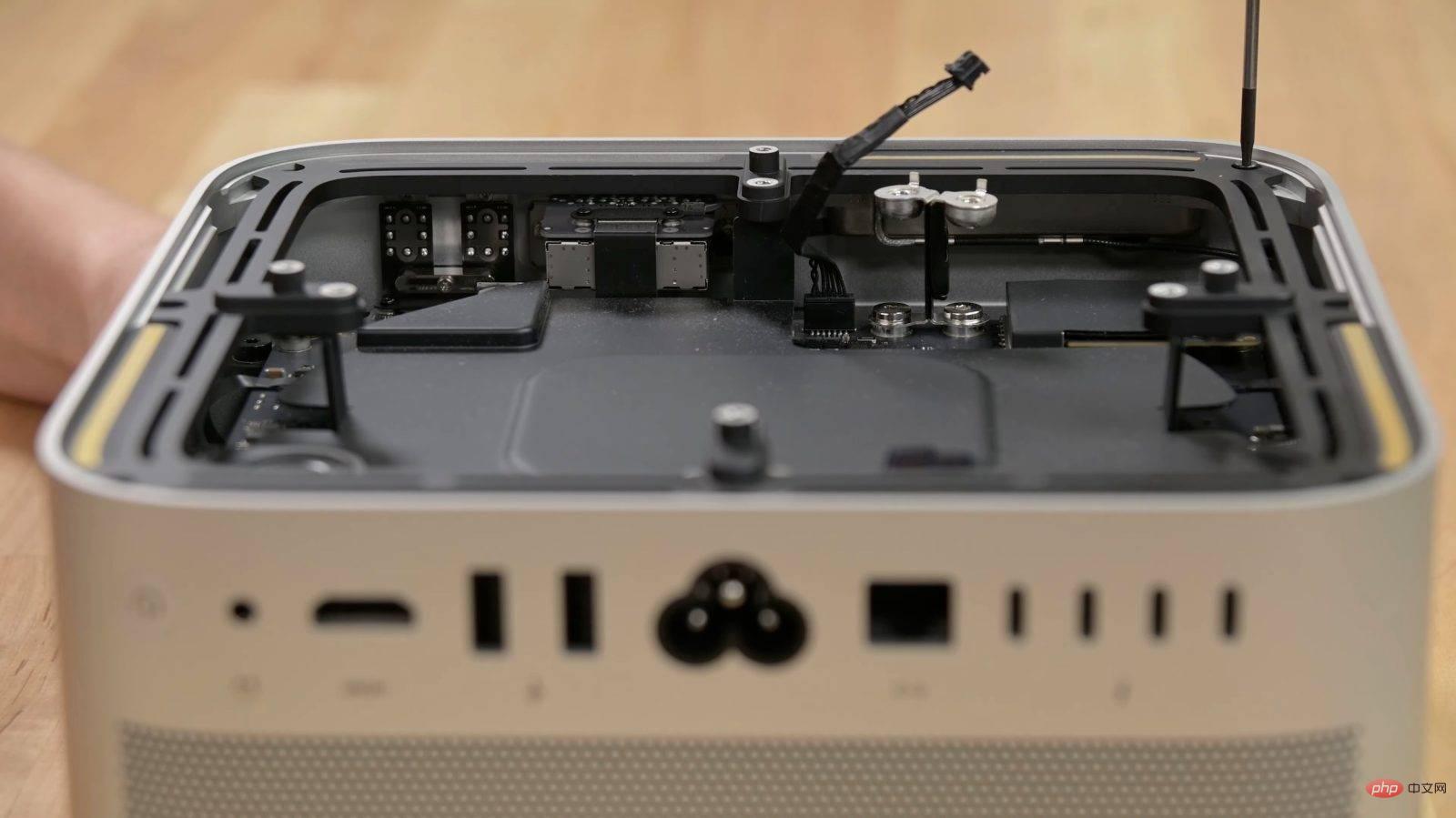 iFixit 拆解显示 Mac Studio 的内部存储可更换但不可升级Apr 19, 2023 pm 02:28 PM
iFixit 拆解显示 Mac Studio 的内部存储可更换但不可升级Apr 19, 2023 pm 02:28 PM上周MacStudio上市后,我们看到一些拆解展示了机器内部的所有东西。尽管MacStudio有免费的存储插槽已经很明显,但用户是否可以自行升级尚不清楚。现在iFixit已经能够确认MacStudio的内部存储虽然是可更换的,但不可升级。与MacPro类似,MacStudio内部有两个相对容易访问的SSD端口。不幸的是,这并不意味着用户可以购买特定配置的MacStudio,然后添加具有更多存储空间的新SSD。经iFixit测试,MacStudio无法识别出不同
 如何升级 Surface Laptop 5 中的存储/硬盘Apr 13, 2023 pm 08:22 PM
如何升级 Surface Laptop 5 中的存储/硬盘Apr 13, 2023 pm 08:22 PM第 1 步:备份您的数据要开始更换过程,您需要准备 Surface Laptop 5。最重要的是备份所有数据。我们建议使用 OneDrive 之类的服务或使用外部 SSD 或硬盘驱动器之类的离线解决方案。您将安装新的 SSD 和干净的 Windows 版本。该过程完成后,您可以将这些文件复制并恢复回 Surface Laptop 5。如果您正在寻找用于备份的外部存储,三星 T5
 加装固态硬盘需要重新装系统吗Nov 07, 2022 am 10:39 AM
加装固态硬盘需要重新装系统吗Nov 07, 2022 am 10:39 AM加装固态硬盘不一定要重新装系统;如果添加的硬盘,只是用来扩展存储容量,那么就没有必要重装系统;如果添加的固态硬盘,是用来作为系统盘的,就必须重装系统。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),






