Browser caching is an important direction in front-end optimization. By caching static resources, the loading time of the page can be reduced, the load on the server can be reduced, and the user experience can be improved. This article will introduce the basic principles of browser caching and common caching strategies, and implement them using code under the koa framework of nodejs.

Caching principle
The basic principle of browser caching is to cache static resources (such as CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) Local, when the page requests these resources again, they are obtained directly from the local instead of downloading them from the server again. This can reduce page loading time and reduce server load, improving user experience.
In the HTTP protocol, browser caching can be implemented through two mechanisms: strong caching and negotiated caching. [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial]
Strong cache
-
Expires field:
- The value is the expiration time returned by the server, which may cause cache hit errors due to different times between the server and the client
-
Cache-Control (alternative)
public: All content is cached (both clients and proxy servers can be cached)
private: Only cached to private cache ( Client)
no-cache: Confirm with the server whether the returned response has been changed before using the response to satisfy subsequent requests for the same URL. Therefore, if the appropriate validation token (ETag) is present, no-cache initiates a round-trip communication to validate the cached response, and can avoid downloading if the resource has not been changed.
no-store: The value is not cached
must-revalidation/proxy-revalidation: If the cached content is invalidated, the request must be sent to the server Re-authentication
max-age=xxx: The cached content will expire after xxx seconds. This option can only be used in http1.1, than last-Modified Higher priority
-
last-Modified (last modified date)
last-Modified: Saved on the server , record the date when the resource was last modified (it cannot be accurate to seconds. If it is modified multiple times within a few seconds, it may cause an error to hit the cache)
if-modified-since: Save In the client, the request is carried and compared with the last-Modified of the server. If it is the same, it will directly hit the cache and return the 304 status code
koa implements strong Cache
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
// 设置 expires方案
const setExpires = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
const expires = new Date(Date.now() + 60 * 1000);
ctx.set('Expires', expires.toUTCString());
await next();
}
// Cache-Control方案(优先执行)
const setCacheControl = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
ctx.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=60');
await next();
}
// Last-Modified方案
const setLastModified = async (ctx, next) => {
// 获取资源最后修改时间
const lastModified = new Date('2021-03-05T00:00:00Z');
// 设置 Last-Modified 头
ctx.set('Last-Modified', lastModified.toUTCString());
await next();
}
const response = (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
}
// 跟Last-Modified方案相对应
const lastModifiedResponse = (ctx) => {
// 如果资源已经修改过,则返回新的资源
if (ctx.headers['if-modified-since'] !== ctx.response.get('Last-Modified')) {
response(ctx)
} else ctx.status = 304;
}
app.get('/getMes', setExpires, response);
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server started on port 3000'));Negotiation cache (the browser and the server negotiate and judge by a value)
-
Etag/if-None-Match
- Etag: The server calculates a hash value (it can also be other algorithms, representing a resource identifier) based on the requested resource and returns it to the browser. The next time the browser When requesting the resource, send Etag to the server through the if-None-Match field
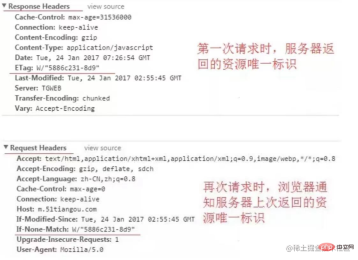
-
Last_Modified and if- Modified-Since
last-Modified: Saved in the server, records the date when the resource was last modified (it cannot be accurate to seconds. If it is modified multiple times within a few seconds, it may cause errors. Hit cache)
if-modified-since: Saved in the client, the request is carried and compared with the last-Modified of the server. If the same, the cache will be directly hit and a 304 status code will be returned.
The difference between negotiated cache ETag and Last-Modified:
ETag is the unique identifier assigned by the server to the resource, and Last-Modified is the last modified time of the resource as reported by the server.
ETag can be generated using any algorithm, such as hashing, while Last-Modified can only use a specific time format (GMT). The comparison of
ETag is a strong validator (exact-match validator) and requires an exact match, while the comparison of Last-Modified is a weak The validator (weak validator) only needs to be the same within the same second.
ETag is suitable for all types of resources, while Last-Modified is only suitable for resources that change infrequently, such as pictures, videos, etc. .
For resources that are updated frequently, ETag is more suitable because it can more accurately detect whether the resource has been modified; while for resources that are not updated frequently, Last-Modified is more suitable because It reduces server load and network traffic.
koa implements negotiation cache
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
// 设置 eTag方案
const setExpires = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
const maxAge = 60;
ctx.set('Cache-Control', `public, max-age=${maxAge}`);
// 设置 ETag 头
const etag = 'etag-123456789';
ctx.set('ETag', etag);
await next();
}
// Last-Modified方案
const setLastModified = async (ctx, next) => {
// 设置缓存时间为 1 分钟
const maxAge = 60;
ctx.set('Cache-Control', `public, max-age=${maxAge}`);
// 设置 Last-Modified 头
const lastModified = new Date('2021-03-05T00:00:00Z');
ctx.set('Last-Modified', lastModified.toUTCString());
await next();
}
const response = (ctx) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World';
}
// 跟Etag方案对应
const etagResponse = (ctx) => {
// 如果 ETag 头未被修改,则返回 304
if (ctx.headers['if-none-match'] === ctx.response.get('ETag')) {
ctx.status = 304;
} else ctx.body = 'Hello World';
}
// 跟Last-Modified方案相对应
const lastModifiedResponse = (ctx) => {
// 如果资源已经修改过,则返回新的资源
if (ctx.headers['if-modified-since'] !== ctx.response.get('Last-Modified')) {
response(ctx)
} else ctx.status = 304;
}
app.get('/getMes', setExpires, response);
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server started on port 3000'));koa uses hash to calculate Etag value:
const Koa = require('koa');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const app = new Koa();
// 假设这是要缓存的资源
const content = 'Hello, world!';
app.use(async (ctx) => {
// 计算资源的哈希值
const hash = crypto.createHash('md5').update(content).digest('hex');
// 设置 ETag 头
ctx.set('ETag', hash);
// 判断客户端是否发送了 If-None-Match 头
const ifNoneMatch = ctx.get('If-None-Match');
if (ifNoneMatch === hash) {
// 如果客户端发送了 If-None-Match 头,并且与当前资源的哈希值相同,则返回 304 Not Modified
ctx.status = 304;
} else {
// 如果客户端没有发送 If-None-Match 头,或者与当前资源的哈希值不同,则返回新的资源
ctx.body = content;
}
});
app.listen(3000);Cache execution process :
The strong cache has not expired, data is read from the cache, cache-control priority is higher than last-Modified
- ## The strong cache is invalid, negotiation cache is executed, and the priority of Etag will be higher than last-Modified
The server returns a 304 status code if the cache is not invalidated, and the client reads data from the cache
If the cache is invalidated, resources and a 200 status code are returned
The use of strong cache and negotiated cache?
Strong cache usually caches static resources (such as CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) in the browser to reduce the loading time of the page and reduce the load on the server.
Negotiation cache is usually used to cache dynamic resources (such as HTML pages, API data, etc.) to reduce the load on the server and the consumption of network bandwidth.
In actual applications, strong caching and negotiation caching can be used alone or together. For some static resources, you can only use strong caching; for some dynamic resources, you can only use negotiation caching; for some frequently changing resources, you can use strong caching and negotiation caching in combination, which can not only reduce the load on the server, but also ensure timeliness. Get the latest resources.
Conclusion
Although it is implemented using back-end nodejs, I think the front-end should also know more or less about this knowledge so that the back-end can better understand it. to interact. How to implement the front-end will be discussed later?
For more node-related knowledge, please visit: nodejs tutorial!
The above is the detailed content of What is cache? How to implement it using node?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.
 JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JavaScript Frameworks: Powering Modern Web DevelopmentMay 02, 2025 am 12:04 AMThe power of the JavaScript framework lies in simplifying development, improving user experience and application performance. When choosing a framework, consider: 1. Project size and complexity, 2. Team experience, 3. Ecosystem and community support.
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor







