Home >Operation and Maintenance >Linux Operation and Maintenance >Why use select in linux
Why use select in linux
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2023-01-30 19:04:541445browse
Because select allows developers to wait for multiple file buffers at the same time, it can reduce IO waiting time and improve the IO efficiency of the process. The select() function is an IO multiplexing function that allows the program to monitor multiple file descriptors and wait for one or more of the monitored file descriptors to become "ready"; the so-called "ready" state is Refers to: the file descriptor is no longer blocked and can be used for certain types of IO operations, including readable, writable, and exceptions.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
select is a computer function located in the header file #include
1. Introduction to select function
The select function is an IO multiplexing function. Its main function is to wait for the event in the file descriptor to be ready. , select can allow us to wait for multiple file buffers at the same time, reduce IO waiting time, and improve the IO efficiency of the process.
The select() function allows the program to monitor multiple file descriptors and wait for one or more of the monitored file descriptors to become "ready". The so-called "ready" state means that the file descriptor is no longer in a blocking state and can be used for certain types of IO operations, including readable, writable, and exception occurrence
2. Introduction to select function parameters
int select(int nfds, fd_set *readfds, fd_set *writefds,
fd_set *exceptfds, struct timeval *timeout);ndfs
The maximum value of the file descriptor waiting for is 1, for example: the application process wants to wait for the file For events of descriptors 3, 5, and 8, the
nfds=max(3,5,8)+1;
fd_set type
readfds and writefds, exceptfds types are all fd_set, so what is the fd_set type?
- The fd_set type is essentially a bitmap , the position of the bitmap represents the phase The content of the corresponding file descriptor indicates whether the file descriptor is valid. 1 means that the file descriptor at this location is valid, and 0 means that the file descriptor at this location is invalid.
- If file descriptors 2 and 3 are set in the bitmap, the bitmap represents 1100.
- The upper limit of fd_set is 1024 file descriptors.
readfds
- readfds is the set of file descriptors waiting for read events,.If If you don't care about read events (there is data in the buffer), you can pass NULL value.
- Both the application process and the kernel can set readfds, Application processSetting readfds is in order to notify the kernel to wait for the read event of the file descriptor in readfds.And KernelSetting readfds isIn order to tell the application process which read events take effect
writefds
Similar to readfds, writefds is a collection waiting for write events (Is there space in the buffer)If you don't care When writing an event, you can pass the value NULL.
exceptfds
If an exception occurs while the kernel is waiting for the corresponding file descriptor, then will The failed file descriptor is set into exceptfds . If you don't care about error events, you can pass the value NULL.
timeout
Set the time select blocks in the kernel. If you want to set it to non-blocking, set it to NULL. If you want select to block for 5 seconds, you will create a struct timeval time={5,0};
The structure type of struct timeval is:
struct timeval {
long tv_sec; /* seconds */
long tv_usec; /* microseconds */
};Return value
- If no file descriptor is ready, return 0;
- If the call fails, return -1;
- If an event occurs in readfds in timeout, return the remaining time of timeout.
3.Select workflow
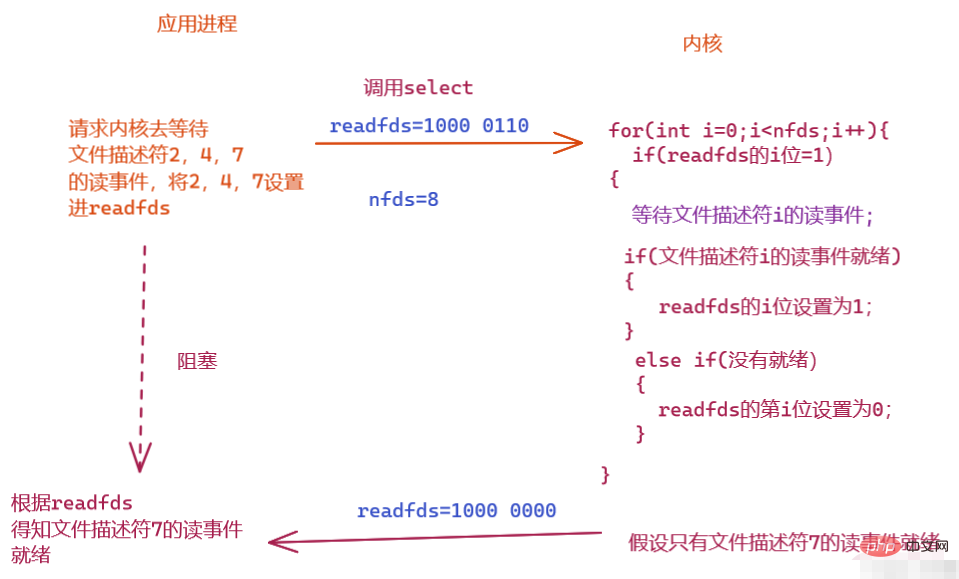
Application processandKernelBoth need to obtain information from readfds and writefds. Among them, the kernel needs to know which file descriptors need to wait from readfds and writefds, and the application process needs to know which file descriptor events are ready from readfds and writefds.

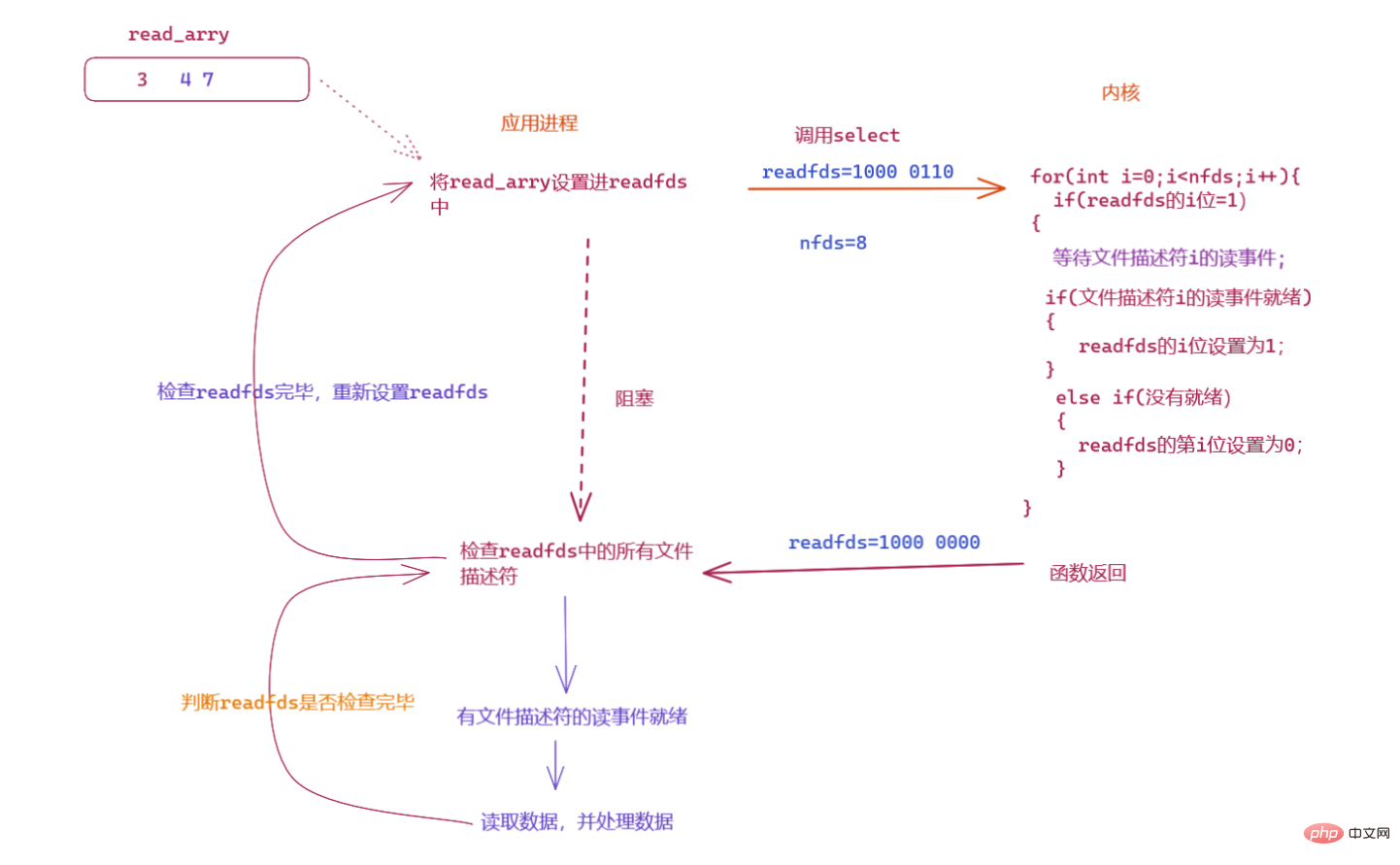
如果我们要不断轮询等待文件描述符,则应用进程需要不断的重新设置readfds和writefds,因为每一次调用select,内核会修改readfds和writefds,所以我们需要在 应用程序 中 设置一个数组 来保存程序需要等待的文件描述符,保证调用 select 的时候readfds 和 writefds中的将如下:
4.Select服务器
如果是一个select服务器进程,则服务器进程会不断的接收有新链接,每个链接对应一个文件描述符,如果想要我们的服务器能够同时等待多个链接的数据的到来,我们监听套接字listen_sock读取新链接的时候,我们需要将新链接的文件描述符保存到read_arrys数组中,下次轮询检测的就会将新链接的文件描述符设置进readfds中,如果有链接关闭,则将相对应的文件描述符从read_arrys数组中拿走。
一张图看懂select服务器:
简易版的select服务器:
server.hpp文件:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<string.h>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
#define BACKLOG 5
namespace sjp{
class server{
public:
static int Socket(){
int sock=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
if(sock>0)
return sock;
if(sock<0)
exit(-1);
}
static bool Bind(int sockfd,short int port){
struct sockaddr_in lock;
memset(&lock,'\0',sizeof(lock));
lock.sin_family=AF_INET;
lock.sin_port=htons(port);
lock.sin_addr.s_addr=INADDR_ANY;
if(bind(sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&lock,(socklen_t)sizeof(lock))<0){
exit(-2);
}
return true;
}
static bool Listen(int sockfd){
if(listen(sockfd,BACKLOG)<0){
exit(-3);
}
return true;
}
};
}select_server.hpp文件
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include"server.hpp"
#include<unistd.h>
#include<time.h>
namespace Select{
class select_server{
private:
int listen_sock;//监听套接字
int port;
public:
select_server(int _port):port(_port){}
//初始化select_server服务器
void InitServer(){
listen_sock=sjp::server::Socket();
sjp::server::Bind(listen_sock,port);
sjp::server::Listen(listen_sock);
}
void Run(){
std::vector<int> readfds_arry(1024,-1);//readfds_arry保存读事件的文件描述符
readfds_arry[0]=listen_sock;//将监听套接字保存进readfds_arry数组中
fd_set readfds;
while(1){
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
int nfds=0;
//将read_arry数组中的文件描述符设置进程readfds_arry位图中
for(int i=0;i<1024;i++)
{
if(readfds_arry[i]!=-1){
FD_SET(readfds_arry[i],&readfds);
if(nfds<readfds_arry[i]){
nfds=readfds_arry[i];
}
}
}
//调用select对readfds中的文件描述符进行等待数据
switch(select(nfds+1,&readfds,NULL,NULL,NULL)){
case 0:
//没有一个文件描述符的读事件就绪
cout<<"select timeout"<<endl;
break;
case -1:
//select失败
cout<<"select error"<<endl;
default:
{
//有读事件发生
Soluation(readfds_arry,readfds);
break;
}
}
}
}
void Soluation(std::vector<int>& readfds_arry,fd_set readfds){
for(int i=0;i<readfds_arry.size();i++){
if(FD_ISSET(readfds_arry[i],&readfds))
{
if(readfds_arry[i]==listen_sock){
//有新链接到来
struct sockaddr peer;
socklen_t len;
int newfd=accept(listen_sock,&peer,&len);
cout<<newfd<<endl;
//将新链接设置进readfds_arry数组中
AddfdsArry(readfds_arry,newfd);
}
else{
//其他事件就绪
char str[1024];
int sz=recv(readfds_arry[i],&str,sizeof(str),MSG_DONTWAIT);
switch(sz){
case -1:
//读取失败
cout<<readfds_arry[i]<<": recv error"<<endl;
break;
case 0:
//对端关闭
readfds_arry[i]=-1;
cout<<"peer close"<<endl;
break;
default:
str[sz]='\0';
cout<<str<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
void AddfdsArry(std::vector<int>& fds_arry,int fd){
for(int i=0;i<fds_arry.size();i++){
if(fds_arry[i]==-1){
fds_arry[i]=fd;
break;
}
}
}
};
}select_server.cc文件
#include"select_server.hpp"
int main(int argv,char* argc[]){
if(argv!=2){
cout<<"./selectserver port"<<endl;
exit(-4);
}
int port=atoi(argc[1]);//端口号
Select::select_server* sl=new Select::select_server(port);
sl->InitServer();
sl->Run();
}测试:

5.Select的缺陷
- 由于fd_set的上限是1024,所以select能等待的读事件的文件描述符和写事件的文件描述是有上限的,如果作为一个大型服务器,能够同时链接的客户端是远远不够的。
- 每次应用进程调用一次select之前,都需要重新设定writefds和readfds,如果进行轮询调用select,这对影响cpu效率。
- 内核每一次等待文件描述符 都会重新扫描所有readfds或者writefds中的所有文件描述符,如果有较多的文件描述符,则会影响效率。
推荐学习:Linux视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Why use select in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Is the command to mount a hard disk in Linux the mount command?
- What are the commands to run files in Linux?
- How to use yum to install php on linux
- Detailed explanation of how to add a Linux security group port (command line method)
- Detailed explanation of the differences between systemctl, service and chkconfig commands under Linux

