Features: 1. Add new variable declaration methods const and let; 2. Template string, which solves the pain points of es5 in the string function; 3. Provides default values for parameters so that when parameters are not available Used when being passed; 4. Arrow function, which is a shortcut for writing functions; 5. Object initialization abbreviation, used to solve the problem of duplicate name of key-value pairs; 6. Destructuring; 7. Expansion operator; 8. Import and export; 9. Promise; 10. Generators; 11. async function; 12. Class.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
1. Variable declaration const and let
Before ES6, we all used varKeyword declares variables. No matter where it is declared, it is considered to be declared at the top of the function (if not at the top of the function, it is at the top of the global scope). This is function variable promotion. For example:

#Don't care whether bool is true or false. In fact, str will be created anyway. (If not declared, null is returned)
After es6, we usually use let and const to declare. let represents variables and const represents constants. Both let and const are block-level scopes. How to understand this block-level scope?
- Inside a function
- Inside a code block
Generally speaking, the code block within {} curly brackets is let and const scope.

let 's scope is in the current code block where it is located, but will not be promoted to the top of the current function.
const Declared variables will be considered constants, which means that their values cannot be modified after they are set.
If const is an object, the value contained in the object can be modified. As long as the address pointed to by the object has not changed.

2. Template string
es6 template characters are simply developed Good news for developers, it solves the pain points of es5 in the string function.
2.1 Basic string formatting
Embed expressions into strings for splicing. Use ${} to define.
//ES5
var way = 'String'
console.log('ES5:' + way)
//ES6
let way = 'String Template'
console.log(`ES6: ${way}`)
2.2 Multi-line string concatenation
In ES5, we use backslash() to do more Line string or string concatenation line by line. ES6 backtick (``) does it directly.

2.3 More methods

3. New function features
3.1 Function default parameters
In ES5, what are the default values of parameters we define for functions?
function action(num) {
num = num || 200;
//当传入num时,num为传入的值
//当没传入参数时,num即有了默认值200
return num;
}
But students who observe carefully will definitely find that when num is passed in as 0, it is false, but our actual need is to get num = 0. At this time, num = 200 is obviously different from our actual situation. The desired effect is obviously different.
ES6 provides default values for parameters. This parameter is initialized when the function is defined so that it can be used when the parameter is not passed in.
function action( num = 200 ){
console.log(num)
}
action(0); //0
action(); //200
action(300) //300
3.2 Arrow function
A very interesting part of ES6 is the shortcut way to write functions. That is the arrow function.
The three most intuitive features of arrow functions:
- No need for the function keyword to create a function
- Omit the return keyword
- Inherit the current The this keyword of the context

# tells a small detail.
When your function has one and only one parameter, you can omit the parentheses. You can omit {} and return when your function returns one and only one expression. For example:
var people = name => 'hello' + name
As a reference:

Here is a written test question: Simplify and restructure the following ES5 code into an ES6 method

4. Expanded object functions
##4.1 Object initialization abbreviation
ES5 We write objects in the form of key-value pairs, and it is possible for key-value pairs to have duplicate names. For example: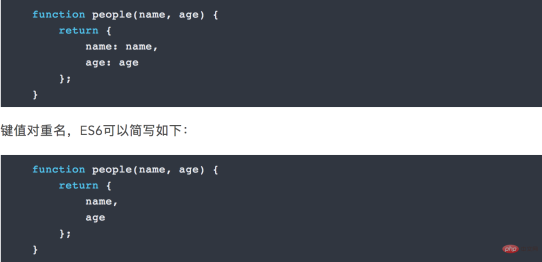

Object.assign() method to implement shallow copying.

##5. More convenient data access--deconstructing the
array and objects are the most commonly used and important representation forms in JS. To simplify extracting information, ES6 adds destructuring, which is the process of breaking a data structure into smaller parts.
ES5 we extract the information in the object in the following form:
 Does it feel familiar? Yes, this is how we obtained object information before ES6 , obtained one by one. Now, destructuring allows us to retrieve data from an object or array and store it as a variable, for example:
Does it feel familiar? Yes, this is how we obtained object information before ES6 , obtained one by one. Now, destructuring allows us to retrieve data from an object or array and store it as a variable, for example:
 Interview question:
Interview question:

6. Spread Operator Spread operator
Another interesting feature in ES6 is that Spread Operator also has three dots
... Next, we will show its use. Assemble objects or arrays:
 For Object, it can also be used to combine into new Object. (ES2017 stage-2 proposal) Of course, if there are duplicate attribute names, the right side will overwrite the left side.
For Object, it can also be used to combine into new Object. (ES2017 stage-2 proposal) Of course, if there are duplicate attribute names, the right side will overwrite the left side.

##7. Import and export
7.1 import import module, export export module
What is the difference between importing with or without curly brackets. The following is a summary: 
- export default people
- , use
import people
There can be only one export default in a file. But there can be multiple exports.to import (without braces). - When using export name, use import{name}
- to import (remember to bring the curly brackets).
When there is one export default people and multiple export names or export ages in a file, use import people,{name,age} - to import.
When there are n multiple exports in a file to export many modules, in addition to importing one by one, you can also use import * asexample
8. Promise
Too many callbacks or nesting of code before promise, poor readability and coupling High degree and low scalability. Through the Promise mechanism, the flat code structure greatly improves the readability of the code; using synchronous programming to write asynchronous code and preserve the linear code logic greatly reduces the code coupling and improves the scalability of the program. .
To put it bluntly, it is to write asynchronous code in a synchronous way. Initiate an asynchronous request:
##9. Generators
A generator is a function that returns an iterator. The generator function is also a kind of function. The most intuitive manifestation is that it has one more asterisk * than the ordinary function. The yield keyword can be used in its function body. What is interesting is that the function will pause after each yield. Here is a more vivid example in life. When we go to the bank to handle business, we have to get a queuing number from the machine in the lobby. Once you get your queue number, the machine will not automatically issue the next ticket for you. In other words, the ticket machine is "paused" and will not continue to spit out tickets until the next person wakes it up again.
OK. Let’s talk about iterators. When you call a generator, it returns an iterator object. This iterator object has a method called next to help you restart the generator function and get the next value. The next method not only returns a value, the object it returns has two properties: done and value. value is the value you obtained, and done is used to indicate whether your generator has stopped providing values. Continuing to use the example of just picking up tickets, each queue number is the value here, and whether the paper for printing tickets is used up is the done here.

What are the uses of generators and iterators?
Much of the excitement surrounding generators is directly related to asynchronous programming. Asynchronous calls are very difficult for us. Our function does not wait for the asynchronous call to complete before executing. You may think of using a callback function (of course there are other solutions such as Promise such as Async/await).
The generator allows our code to wait. There is no need for nested callback functions. Using a generator ensures that the execution of the function is paused when the asynchronous call completes before our generator function runs a line of code.
Then the problem is, we can’t manually call the next() method all the time. You need a method that can call the generator and start the iterator. Something like this:

#Perhaps the most interesting and exciting aspect of generators and iterators is the ability to create clean-looking code for asynchronous operations. Instead of using callback functions everywhere, you can create code that looks synchronous but actually uses yield to wait for the asynchronous operation to complete.
10. async function
es6 introduces the async function, making asynchronous operations more convenient.
What is the async function? In a word, it is syntactic sugar for the Generator function.

After comparison, you will find that the async function is to replace the asterisk (*) of the Generator function with async, and replace yield with await, and that's it.
The improvement of the async function to the Generator function is reflected in the following four points:
Built-in executor
Better Semantics
Wider applicability
The return value is Promise
11. Basic Grammar of Class
In JavaScript language, the traditional way to generate instance objects is through the constructor:

es6 provides a writing method that is closer to traditional languages and introduces the concept of Class as a template for objects. Classes can be defined through the class keyword.
Basically, es6's %(red)[class] can be regarded as just a syntactic sugar. Most of its functions can be achieved by es5. The new %(red)[class] writing method is just It just makes the writing of object prototypes clearer and more like the syntax of object-oriented programming. The above code is rewritten using es6's %(red)[class], as follows.

The above code defines a "class". You can see that there is a constructor method in it. This is the constructor method, and the this keyword represents the instance object. In other words, the constructor Point of es5 corresponds to the constructor of the Point class of es6.
In addition to the construction method, the Point class also defines a toString method. Note that when defining a "class" method, you do not need to add the keyword function in front, just put the function definition directly. In addition, there is no need to separate the methods with commas, otherwise an error will be reported.
es6 classes can be regarded as another way of writing constructors.
[Recommended learning: javascript video tutorial]



Built-in executor
Better Semantics
Wider applicability
The return value is Promise


The above is the detailed content of What are the characteristics of front-end development es6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 es6怎么判断是否为数组Apr 25, 2022 pm 06:43 PM
es6怎么判断是否为数组Apr 25, 2022 pm 06:43 PM在es6中,可以利用“Array.isArray()”方法判断对象是否为数组,若判断的对象是数组,返回的结果是true,若判断对象不是数组,返回的结果是false,语法为“Array.isArray(需要检测的js对象)”。
 es6中遍历跟迭代的区别是什么Apr 26, 2022 pm 02:57 PM
es6中遍历跟迭代的区别是什么Apr 26, 2022 pm 02:57 PMes6中遍历跟迭代的区别是:遍历强调的是要把整个数据依次全部取出来,是访问数据结构的所有元素;而迭代虽然也是依次取出数据,但是并不保证取多少,也不保证把所有的数据取完,是遍历的一种形式。
 es6中怎么判断两个对象是否相等Apr 19, 2022 pm 03:34 PM
es6中怎么判断两个对象是否相等Apr 19, 2022 pm 03:34 PM在es6中,可用Object对象的is()方法来判断两个对象是否相等,该方法检测两个变量的值是否为同一个值,判断两个对象的引用地址是否一致,语法“Object.is(对象1,对象2)”;该方法会返回布尔值,若返回true则表示两个对象相等。
 es6怎么将数字转为字符串Apr 19, 2022 pm 06:38 PM
es6怎么将数字转为字符串Apr 19, 2022 pm 06:38 PM转换方法:1、利用“+”给数字拼接一个空字符,语法“数字+""”;2、使用String(),可把对象的值转换为字符串,语法“String(数字对象)”;3、用toString(),可返回数字的字符串表示,语法“数字.toString()”。
 es6中assign的用法是什么May 05, 2022 pm 02:25 PM
es6中assign的用法是什么May 05, 2022 pm 02:25 PM在es6中,assign用于对象的合并,可以将源对象的所有可枚举属性复制到目标对象;若目标对象与源对象有同名属性,或多个源对象有同名属性,则后面的属性会覆盖前面的属性,语法为“Object.assign(...)”
 es6怎么改变数组数据Apr 26, 2022 am 10:08 AM
es6怎么改变数组数据Apr 26, 2022 am 10:08 AM改变方法:1、利用splice()方法修改,该方法可以直接修改原数组的内容,语法为“数组.splice(开始位置,修改个数,修改后的值)”;2、利用下标访问数组元素,并重新赋值来修改数组数据,语法为“数组[下标值]=修改后的值;”。
 sort排序是es6中的吗Apr 25, 2022 pm 03:30 PM
sort排序是es6中的吗Apr 25, 2022 pm 03:30 PMsort排序是es6中的;sort排序是es6中用于对数组的元素进行排序的方法,该方法默认不传参,按照字符编码顺序进行排序,排序顺序可以是字母或数字,并按升序或降序,语法为“array.sort(callback(a,b))”。
 import as在es6中的用法是什么Apr 25, 2022 pm 05:19 PM
import as在es6中的用法是什么Apr 25, 2022 pm 05:19 PM在es6中,import as用于将若干export导出的内容组合成一个对象返回;ES6的模块化分为导出与导入两个模块,该方法能够将所有的导出内容包裹到指定对象中,语法为“import * as 对象 from ...”。


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor







