The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, react version 18.0.0, Dell G3 computer.
How to achieve scaling in react?
react image scaling and panning (position, transform implementation)
Many web pages will attach some pictures to supplement the description of the copy, for example, when talking about the address , a map will be attached next to it, and the address will be marked on the map. If the attached picture is too small and it is difficult to see the specific information of the address clearly, some product managers will design a function for panning, zooming in and out of the picture. This article will implement the above functions one by one.
Without further ado, let me show you the renderings first:

Main three functional points:
- Picture panning
- Picture zoom
- Station label
Picture panning
Picture panning can be implemented by monitoring these three events: onMouseDown, onMouseMove, onMouseUp . onMouseDownThe event records the coordinate position of each mouse press; onMouseMoveThe event calculates the distance of each translation, which is added to the distance of the picture from the parent before dragging The distance of the element is equal to the distance of the dragged image relative to the parent element; when the onMouseUp event is triggered, log out or prevent the onMouseDown and onMouseMove events from being executed to prevent the mouse from moving in The picture will pan.
These three events need to prevent the browser's default behavior, otherwise the image will be automatically opened when moving. 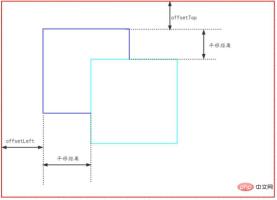
const WIDTH = 1200;const HEIGHT = 900;const DynamicStyle= () => {
const imgRef = React.createRef<HTMLImageElement>();
/** 图片样式 */ const [imgStyle, setImgStyle] = useState<React.CSSProperties>({}); /** 记录鼠标是否按下 */ const [mouseDowmFlag, setMouseDowmFlag] = useState(false); /** 记录鼠标按下的坐标 */ const [mouseDowmPos, setMouseDowmPos] = useState<{x: number, y: number}>({x: 0, y: 0}) /** 鼠标可视区域时,重置鼠标按下的布尔值为false */ useEffect(() => { document.onmouseover = () => { if (mouseDowmFlag) { setMouseDowmFlag(false);
}
}; return () => { document.onmouseover = null;
};
}, [mouseDowmFlag]) /** 平移 */ const handleMouseDown = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => { const { clientX, clientY } = event;
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); // 阻止浏览器默认行为,拖动会打开图片 setMouseDowmFlag(true); // 控制只有在鼠标按下后才会执行mousemove setMouseDowmPos({ x: clientX, y: clientY,
});
}; const handleMouseMove = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); const { clientX, clientY } = event; const diffX = clientX - mouseDowmPos.x; const diffY = clientY - mouseDowmPos.y; if (!mouseDowmFlag || (diffX === 0 && diffY === 0)) return; const { offsetLeft, offsetTop } = imgRef.current as HTMLImageElement; const offsetX = parseInt(`${diffX + offsetLeft}`, 10); const offsetY = parseInt(`${diffY + offsetTop}`, 10); setMouseDowmPos({ x: clientX, y: clientY,
}); setImgStyle({
...imgStyle, left: offsetX, top: offsetY,
});
}; const handleMouseUp = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); setMouseDowmFlag(false);
}; return ( <div className={styles.imgArea}> <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/image/987/470/885/1672193291310298.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy"
src={mapImg}
alt='part' ref={imgRef} height={HEIGHT}
style={imgStyle} onMouseDown={handleMouseDown} onMouseMove={handleMouseMove} onMouseUp={handleMouseUp}
> </img> </div>
)
}Picture zoom
Picture zoom can listen to the onWheel event. The event object event has an attribute that records the scrolling of the wheel. deltaY, when scrolling up deltaY, when scrolling down <code>deltaY>0. Each scroll modifies its scaling ratio, and at the same time changes the transform style to scale proportionally.

const WIDTH = 1200;const HEIGHT = 900;const SCALE = 0.2;const DynamicStyle= () => { const imgRef = React.createRef<HTMLImageElement>(); /** 初始化缩放比例,默认为1 */ const [rate, setRate] = useState(1); /** 图片样式 */ const [imgStyle, setImgStyle] = useState<React.CSSProperties>({}); /** 记录鼠标是否按下 */ const [mouseDowmFlag, setMouseDowmFlag] = useState(false); /** 记录鼠标按下的坐标 */ const [mouseDowmPos, setMouseDowmPos] = useState<{x: number, y: number}>({x: 0, y: 0}) /** 图片现在大小 */ const [initial, setInitial] = useState<{width: number, height: number}>({width: WIDTH, height: HEIGHT}); useEffect(() => { const { naturalWidth, naturalHeight, width, height } = imgRef.current as HTMLImageElement; setInitial({ width, height }); // eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
}, []) // console.log(natural, initial) useEffect(() => { document.onmouseover = () => { if (mouseDowmFlag) { setMouseDowmFlag(false);
}
}; return () => { document.onmouseover = null;
};
}, [mouseDowmFlag]) /** 缩放 */ const handleWheelImage = (event: React.WheelEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => { // 向上为负,向下为正 const bigger = event.deltaY > 0 ? -1 : 1; // transform偏移量 const transformX = -initial.width / 2; const transformY = -initial.height / 2; if (bigger > 0 && rate < 2) { const enlargeRate = rate + SCALE; setImgStyle({
...imgStyle, transform: `matrix(${enlargeRate}, 0, 0, ${enlargeRate}, ${transformX}, ${transformY})`, // 默认以图片中心为原点进行缩放
}); setRate(enlargeRate);
} else if (bigger < 0 && rate > 1) { const shrinkRate = rate - SCALE; setImgStyle({
...imgStyle, transform: `matrix(${shrinkRate}, 0, 0, ${shrinkRate}, ${transformX}, ${transformY})`,
}); setRate(shrinkRate);
}
} /** 平移 */ const handleMouseDown = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => { const { clientX, clientY } = event;
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); // 阻止浏览器默认行为,拖动会打开图片 setMouseDowmFlag(true); // 控制只有在鼠标按下后才会执行mousemove setMouseDowmPos({ x: clientX, y: clientY,
});
}; const handleMouseMove = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); const { clientX, clientY } = event; const diffX = clientX - mouseDowmPos.x; const diffY = clientY - mouseDowmPos.y; if (!mouseDowmFlag || (diffX === 0 && diffY === 0)) return; const { offsetLeft, offsetTop } = imgRef.current as HTMLImageElement; const offsetX = parseInt(`${diffX + offsetLeft}`, 10); const offsetY = parseInt(`${diffY + offsetTop}`, 10); setMouseDowmPos({ x: clientX, y: clientY,
}); setImgStyle({
...imgStyle, left: offsetX, top: offsetY,
});
}; const handleMouseUp = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); setMouseDowmFlag(false);
}; return ( <div className={styles.imgArea}> <img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/image/524/801/658/1672193298348581.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,p_40" class="lazy"
src={mapImg}
alt='part'
height={HEIGHT}
style={imgStyle} ref={imgRef} onWheel={handleWheelImage} onMouseDown={handleMouseDown} onMouseMove={handleMouseMove} onMouseUp={handleMouseUp}
> </img> </div>
)
}.imgArea { position: relative; width: 1200px; height: 900px; margin: auto; border: 1px solid #da2727; overflow: hidden;
& > img { position: absolute; left: 50%; top: 50%; transform: translate(-50%, -50%); cursor: move;
}
}If transformOrigin is not set, the default is to scale relative to the center of the picture, but initially in order to center the picture horizontally and vertically within the visible area , used transform: translate(-50%, -50%);, so in order to scale relative to the center point of the picture, you need to set the 5th and 6th parameter correction of matrix transformOrigin,transform: matrix(${shrinkRate}, 0, 0, ${shrinkRate}, ${transformX}, ${transformY})
Station labeling
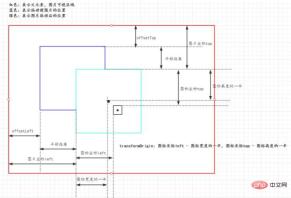
First, define a constant to represent the coordinates of the icon. This coordinate is relative to the upper left corner of the original image.
const imgInfo = { lableLeft: "1900", lableTop: "2000",}Here, explain the concept of the original picture: 
Just check out a picture element on the Internet, such as the one above. 1200 x 900 is the image size specified on the page, but the image also has a real size of 4535 x 3402.
Before calculating the initial coordinates of the icon without translation and scaling, you need to calculate the scaling ratio of the image (not the rate above):
/** 图片原始大小,默认设置为1是防止计算图片原始大小与初始大小比例出现无穷大 */const [natural, setNatural] = useState<{width: number, height: number}>({width: 1, height: 1});/** 图片现在大小 */const [initial, setInitial] = useState<{width: number, height: number}>({width: WIDTH, height: HEIGHT});useEffect(() => { const { naturalWidth, naturalHeight, width, height } = imgRef.current as HTMLImageElement; setNatural({ width: naturalWidth, height: naturalHeight }); setInitial({ width, height }); // eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps}, [])
// 初始图片缩放比例(图片有原始的图片大小)const imgScaleRateX = initial.width / natural.width;const imgScaleRateY = initial.height / natural.height;The initial coordinates of the icon are It can be calculated:
const labelLeft = parseInt(`${imgInfo.lableLeft}`, 10) * imgScaleRateX;const labelTop = parseInt(`${imgInfo.lableTop}`, 10) * imgScaleRateY;When the picture is translated, the icon also needs to be translated. This is the coordinate calculation:
// 图标相对父元素坐标 = 图标位置坐标 + 图片坐标const labelLeft = parseInt(`${imgInfo.lableLeft}`, 10) * imgScaleRateX + Number(imgStyle.left || WIDTH / 2);
const labelTop = parseInt(`${imgInfo.lableTop}`, 10) * imgScaleRateY + Number(imgStyle.top || HEIGHT / 2);
When the picture is zoomed, the icon Need to scale along with the image. If transformOrigin is not set for the icon, it will be scaled relative to the center of the icon by default. In order to ensure that the icon scales with the image, the scaling reference origin of the image and the icon must be the same, and the transformOrigin of the icon should be set to the distance relative to the origin of the image.
const labelTransformOrigin = () => { return `${initial.width / 2 - Number(imgInfo.lableLeft) * imgScaleRateX}px ${
initial.height / 2 - Number(imgInfo.lableTop) * imgScaleRateY
}px`;
}
Overall code example:
const imgInfo = {
lableLeft: "1900",
lableTop: "2000",
}
const WIDTH = 1200;
const HEIGHT = 900;
const SCALE = 0.2;
const DynamicStyle= () => {
const imgRef = React.createRef<HTMLImageElement>();
/** 初始化缩放比例,默认为1 */
const [rate, setRate] = useState(1);
/** 图片样式 */
const [imgStyle, setImgStyle] = useState<React.CSSProperties>({});
/** 记录鼠标是否按下 */
const [mouseDowmFlag, setMouseDowmFlag] = useState(false);
/** 记录鼠标按下的坐标 */
const [mouseDowmPos, setMouseDowmPos] = useState<{x: number, y: number}>({x: 0, y: 0})
/** 图片原始大小,默认设置为1是防止计算图片原始大小与初始大小比例出现无穷大 */
const [natural, setNatural] = useState<{width: number, height: number}>({width: 1, height: 1});
/** 图片现在大小 */
const [initial, setInitial] = useState<{width: number, height: number}>({width: WIDTH, height: HEIGHT});
useEffect(() => {
const { naturalWidth, naturalHeight, width, height } = imgRef.current as HTMLImageElement;
setNatural({ width: naturalWidth, height: naturalHeight });
setInitial({ width, height });
// eslint-disable-next-line react-hooks/exhaustive-deps
}, [])
useEffect(() => {
document.onmouseover = () => {
if (mouseDowmFlag) {
setMouseDowmFlag(false);
}
};
return () => {
document.onmouseover = null;
};
}, [mouseDowmFlag])
/** 缩放 */
const handleWheelImage = (event: React.WheelEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
// 向上为负,向下为正
const bigger = event.deltaY > 0 ? -1 : 1;
// transform偏移量
const transformX = -initial.width / 2;
const transformY = -initial.height / 2;
if (bigger > 0 && rate < 2) {
const enlargeRate = rate + SCALE;
setImgStyle({
...imgStyle,
transform: `matrix(${enlargeRate}, 0, 0, ${enlargeRate}, ${transformX}, ${transformY})`, // 默认以图片中心为原点进行缩放
});
setRate(enlargeRate);
} else if (bigger < 0 && rate > 1) {
const shrinkRate = rate - SCALE;
setImgStyle({
...imgStyle,
transform: `matrix(${shrinkRate}, 0, 0, ${shrinkRate}, ${transformX}, ${transformY})`,
});
setRate(shrinkRate);
}
}
/** 平移 */
const handleMouseDown = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
const { clientX, clientY } = event;
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault(); // 阻止浏览器默认行为,拖动会打开图片
setMouseDowmFlag(true); // 控制只有在鼠标按下后才会执行mousemove
setMouseDowmPos({
x: clientX,
y: clientY,
});
};
const handleMouseMove = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault();
const { clientX, clientY } = event;
const diffX = clientX - mouseDowmPos.x;
const diffY = clientY - mouseDowmPos.y;
if (!mouseDowmFlag || (diffX === 0 && diffY === 0)) return;
const { offsetLeft, offsetTop } = imgRef.current as HTMLImageElement;
const offsetX = parseInt(`${diffX + offsetLeft}`, 10);
const offsetY = parseInt(`${diffY + offsetTop}`, 10);
setMouseDowmPos({
x: clientX,
y: clientY,
});
setImgStyle({
...imgStyle,
left: offsetX,
top: offsetY,
});
};
const handleMouseUp = (event: React.MouseEvent<HTMLImageElement>) => {
event.stopPropagation();
event.preventDefault();
setMouseDowmFlag(false);
};
// 初始图片缩放比例(图片有原始的图片大小)
const imgScaleRateX = initial.width / natural.width;
const imgScaleRateY = initial.height / natural.height;
const labelTransformOrigin = () => {
return `${initial.width / 2 - Number(imgInfo.lableLeft) * imgScaleRateX}px ${
initial.height / 2 - Number(imgInfo.lableTop) * imgScaleRateY
}px`;
}
/** 图标位置计算 */
const labelStyle = (): React.CSSProperties => {
const transformX = -initial.width / 2;
const transformY = -initial.height / 2;
// 图标相对父元素坐标 = 图标初始位置坐标 + 平移量
const labelLeft = parseInt(`${imgInfo.lableLeft}`, 10) * imgScaleRateX + Number(imgStyle.left || WIDTH / 2);
const labelTop = parseInt(`${imgInfo.lableTop}`, 10) * imgScaleRateY + Number(imgStyle.top || HEIGHT / 2);
return {
left: labelLeft,
top: labelTop,
transformOrigin: labelTransformOrigin(),
transform: `matrix(${rate}, 0, 0, ${rate}, ${transformX}, ${transformY})`,
}
}
return (
<div className={styles.imgArea}>
<img
src={mapImg}
alt='part'
height={HEIGHT}
style={imgStyle}
ref={imgRef}
onWheel={handleWheelImage}
onMouseDown={handleMouseDown}
onMouseMove={handleMouseMove}
onMouseUp={handleMouseUp}
>
</img>
<span className={styles.label} style={labelStyle()}></span>
</div>
)
}Recommended learning: "react video tutorial"




























