Four major components: 1. Activity component, which is a separate window and the program flow must be run in [Activity], so it is the most basic module. 2. The service component is used to complete user-specified operations in the background. 3. The content provider component will prepare a content window for all applications and retain databases and files. 4. The broadcast receiver component is a mechanism for transmitting information between programs. Its function is to receive or send notifications.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: Android 13 system, Xiaomi 12 mobile phone.
The four major components of Android are activity, service, content provider, and broadcast receiver.
1. Detailed explanation of the four major components of android
1. Activity
Activity It can be regarded as the foundation of the Android system. Only on this foundation can other work be carried out, because all programs running in the Android system must run in [Activity], so it is the most basic module. . It functions as a frame or page, and each program will be composed of multiple [Activities].
(1) An Activity is usually a separate screen (window).
(2) Activities communicate through Intent.
(3) Every Activity in the android application must be declared in the AndroidManifest.xml configuration file, otherwise the system will not recognize or execute the Activity.
2. service
Service is a very important component in Android. Its status and priority are similar to activities. However, Service cannot run by itself. It only runs in the background on Android. Its function is to interact with other components of Android. For example, when we open the music player on the phone and put it in the background, the music played at this time is controlled by the Service.
1) Service is used to complete user-specified operations in the background. Service is divided into two types:
started (started): When an application component (such as activity) calls the startService() method to start the service, the service is in the started state.
bound (binding): When the application component calls the bindService() method to bind to the service, the service is in the bound state.
2) The difference between startService() and bindService():
started service (start service) is the startService() method called by other components Started, which causes the service's onStartCommand() method to be called. When a service is in the started state, its life cycle is independent of the component that started it and can run in the background indefinitely, even if the component that started the service has been destroyed. Therefore, the service needs to be stopped by calling the stopSelf() method after completing the task, or by other components calling the stopService() method.
Use the bindService() method to enable the service. The caller and the service are bound together. Once the caller exits, the service will terminate. "death" characteristics.
3) Developers need to declare all services in the application configuration file, using the
4) Service usually runs in the background. It generally does not need to interact with users, so the Service component does not have a graphical user interface. Service components need to inherit the Service base class. Service components are usually used to provide background services for other components or monitor the running status of other components.
3. Content provider (content provider)
The content provider component is specially designed for third-party applications. It is very flexible and very important. , it will prepare a content window for all applications, and retain databases and files. Its function is that when we use these third-party software, we can effectively access and protect the data inside.
1) The android platform provides Content Provider to provide the specified data set of an application to other applications. Other applications can obtain or store data from this content provider through the ContentResolver class.
2) Content providers are only needed if data needs to be shared between multiple applications. For example, address book data is used by multiple applications and must be stored in a content provider. Its benefit is to unify the way data is accessed.
3) ContentProvider implements data sharing. ContentProvider is used to save and obtain data and make it visible to all applications. This is the only way to share data between different applications because Android does not provide a common storage area that all applications can access.
4) Developers will not directly use objects of the ContentProvider class. Most of them implement operations on ContentProvider through ContentResolver objects.
5) ContentProvider uses URI to uniquely identify its data set. The URI here is prefixed with content://, indicating that the data is managed by ContentProvider.
4. broadcast receiver
In the Android system, the broadcast receiver is not directly visible. It is a mechanism for transmitting information between programs. Its function is to receive or send notifications. In layman's terms, a broadcast receiver is more like a delivery component. It can receive information and even filter it and then respond.
1) Your application can use it to filter external events and only receive and respond to external events of interest (such as when a phone call comes in, or when the data network is available). Broadcast receivers have no user interface. However, they can start an activity or service in response to the information they receive, or use a NotificationManager to notify the user. Notifications can be used in many ways to attract the user's attention, such as flashing the backlight, vibrating, playing sounds, etc. Generally speaking, you put a persistent icon on the status bar that the user can open and get the message.
2) There are two methods for registering broadcast receivers, namely dynamic registration in the program and static registration in the AndroidManifest file.
3) The characteristic of dynamically registered broadcast receivers is that when the Activity used to register is turned off, the broadcast will become invalid. Static registration does not need to worry about whether the broadcast receiver is turned off. As long as the device is turned on, the broadcast receiver is also turned on. That is to say, even if the app itself is not started, the broadcast subscribed by the app will affect it when triggered.
2. Summary of the four major components of android:
1. Registration of the four major components
4 The major basic components need to be registered before they can be used. Each Activity, service, and Content Provider need to be configured in the AndroidManifest file. Activities, services, and content providers that are not declared in the AndroidManifest file will not be visible to the system and therefore will not be available. The registration of broadcast receivers is divided into static registration (configured in the AndroidManifest file) and dynamic creation through code and registration to the system by calling Context.registerReceiver(). It should be noted that the broadcast receiver configured in the AndroidManifest file will remain active as the system starts, and will be triggered as long as an interested broadcast is received (even if the program is not running).
2. Activation of the 4 major components
Activation of content provider: After receiving a request from ContentResolver, the content provider is activated. The other three components activities, services and broadcast receivers are activated by an asynchronous message called an intent.
3. Closing of the 4 major components
The content provider is only activated in response to a request from ContentResolver. A broadcast receiver is only activated in response to broadcast messages. Therefore, there is no need to explicitly close these components. Activity closure: You can close an activity by calling its finish() method. Service shutdown: For services started through the startService() method, the Context.stopService() method must be called to shut down the service. For services started using the bindService() method, the Contex.unbindService() method must be called to shut down the service.
4. Tasks (activity stack) in android
a) A task is actually a stack of activities. It consists of one or more Activities, which together complete a complete user experience. The bottom of the stack is the Activity that starts the entire task, and the top of the stack is the currently running Activity that the user can interact with. When one activity starts another, the new activity is pushed onto the stack and becomes the currently running activity. The previous activity remains on the stack. When the user presses the BACK key, the current activity pops off the stack and the previous one returns to the currently running activity. What is saved in the stack is actually an object. The activities in the stack will never be rearranged, but will only be pushed or popped.
b) All activities in the task move as a whole. The entire task (i.e. activity stack) can be moved to the foreground or retreated to the background.
c) The Android system is a multi-task (Multi-Task) operating system, which can execute multiple other programs while listening to music on your mobile phone. Every time an additional application is executed, more system memory will be consumed. When too many programs are executed at the same time, or the closed program does not release memory correctly, the system will feel slower and slower, or even unstable. In order to solve this problem, Android introduced a new mechanism, namely Life Cycle.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What are the four major components of android. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 如何在 iPhone 和 Android 上关闭蓝色警报Feb 29, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
如何在 iPhone 和 Android 上关闭蓝色警报Feb 29, 2024 pm 10:10 PM根据美国司法部的解释,蓝色警报旨在提供关于可能对执法人员构成直接和紧急威胁的个人的重要信息。这种警报的目的是及时通知公众,并让他们了解与这些罪犯相关的潜在危险。通过这种主动的方式,蓝色警报有助于增强社区的安全意识,促使人们采取必要的预防措施以保护自己和周围的人。这种警报系统的建立旨在提高对潜在威胁的警觉性,并加强执法机构与公众之间的沟通,以共尽管这些紧急通知对我们社会至关重要,但有时可能会对日常生活造成干扰,尤其是在午夜或重要活动时收到通知时。为了确保安全,我们建议您保持这些通知功能开启,但如果
 在Android中实现轮询的方法是什么?Sep 21, 2023 pm 08:33 PM
在Android中实现轮询的方法是什么?Sep 21, 2023 pm 08:33 PMAndroid中的轮询是一项关键技术,它允许应用程序定期从服务器或数据源检索和更新信息。通过实施轮询,开发人员可以确保实时数据同步并向用户提供最新的内容。它涉及定期向服务器或数据源发送请求并获取最新信息。Android提供了定时器、线程、后台服务等多种机制来高效地完成轮询。这使开发人员能够设计与远程数据源保持同步的响应式动态应用程序。本文探讨了如何在Android中实现轮询。它涵盖了实现此功能所涉及的关键注意事项和步骤。轮询定期检查更新并从服务器或源检索数据的过程在Android中称为轮询。通过
 如何在Android中实现按下返回键再次退出的功能?Aug 30, 2023 am 08:05 AM
如何在Android中实现按下返回键再次退出的功能?Aug 30, 2023 am 08:05 AM为了提升用户体验并防止数据或进度丢失,Android应用程序开发者必须避免意外退出。他们可以通过加入“再次按返回退出”功能来实现这一点,该功能要求用户在特定时间内连续按两次返回按钮才能退出应用程序。这种实现显著提升了用户参与度和满意度,确保他们不会意外丢失任何重要信息Thisguideexaminesthepracticalstepstoadd"PressBackAgaintoExit"capabilityinAndroid.Itpresentsasystematicguid
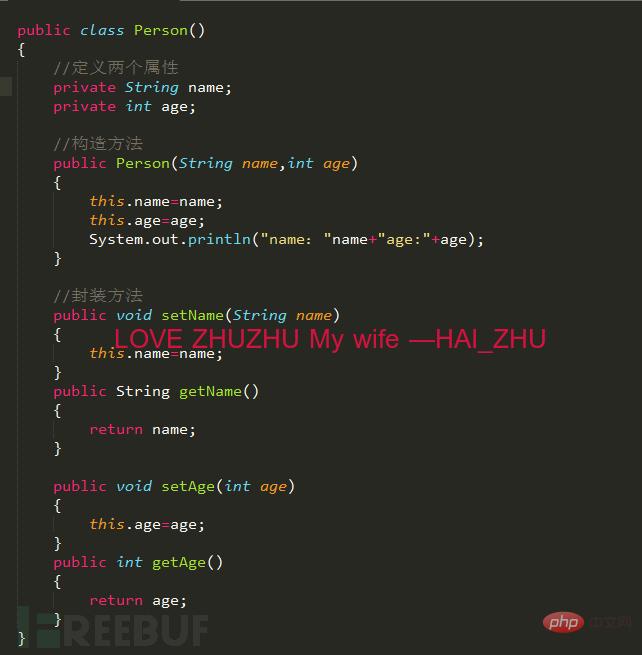 Android逆向中smali复杂类实例分析May 12, 2023 pm 04:22 PM
Android逆向中smali复杂类实例分析May 12, 2023 pm 04:22 PM1.java复杂类如果有什么地方不懂,请看:JAVA总纲或者构造方法这里贴代码,很简单没有难度。2.smali代码我们要把java代码转为smali代码,可以参考java转smali我们还是分模块来看。2.1第一个模块——信息模块这个模块就是基本信息,说明了类名等,知道就好对分析帮助不大。2.2第二个模块——构造方法我们来一句一句解析,如果有之前解析重复的地方就不再重复了。但是会提供链接。.methodpublicconstructor(Ljava/lang/String;I)V这一句话分为.m
 如何在2023年将 WhatsApp 从安卓迁移到 iPhone 15?Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:37 PM
如何在2023年将 WhatsApp 从安卓迁移到 iPhone 15?Sep 22, 2023 pm 02:37 PM如何将WhatsApp聊天从Android转移到iPhone?你已经拿到了新的iPhone15,并且你正在从Android跳跃?如果是这种情况,您可能还对将WhatsApp从Android转移到iPhone感到好奇。但是,老实说,这有点棘手,因为Android和iPhone的操作系统不兼容。但不要失去希望。这不是什么不可能完成的任务。让我们在本文中讨论几种将WhatsApp从Android转移到iPhone15的方法。因此,坚持到最后以彻底学习解决方案。如何在不删除数据的情况下将WhatsApp
 同样基于linux为什么安卓效率低Mar 15, 2023 pm 07:16 PM
同样基于linux为什么安卓效率低Mar 15, 2023 pm 07:16 PM原因:1、安卓系统上设置了一个JAVA虚拟机来支持Java应用程序的运行,而这种虚拟机对硬件的消耗是非常大的;2、手机生产厂商对安卓系统的定制与开发,增加了安卓系统的负担,拖慢其运行速度影响其流畅性;3、应用软件太臃肿,同质化严重,在一定程度上拖慢安卓手机的运行速度。
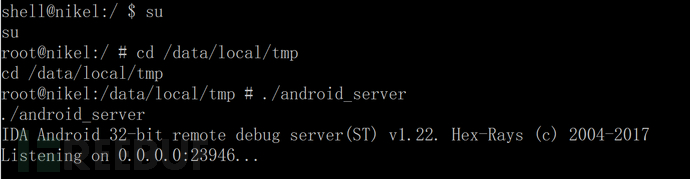 Android中动态导出dex文件的方法是什么May 30, 2023 pm 04:52 PM
Android中动态导出dex文件的方法是什么May 30, 2023 pm 04:52 PM1.启动ida端口监听1.1启动Android_server服务1.2端口转发1.3软件进入调试模式2.ida下断2.1attach附加进程2.2断三项2.3选择进程2.4打开Modules搜索artPS:小知识Android4.4版本之前系统函数在libdvm.soAndroid5.0之后系统函数在libart.so2.5打开Openmemory()函数在libart.so中搜索Openmemory函数并且跟进去。PS:小知识一般来说,系统dex都会在这个函数中进行加载,但是会出现一个问题,后
 Android APP测试流程和常见问题是什么May 13, 2023 pm 09:58 PM
Android APP测试流程和常见问题是什么May 13, 2023 pm 09:58 PM1.自动化测试自动化测试主要包括几个部分,UI功能的自动化测试、接口的自动化测试、其他专项的自动化测试。1.1UI功能自动化测试UI功能的自动化测试,也就是大家常说的自动化测试,主要是基于UI界面进行的自动化测试,通过脚本实现UI功能的点击,替代人工进行自动化测试。这个测试的优势在于对高度重复的界面特性功能测试的测试人力进行有效的释放,利用脚本的执行,实现功能的快速高效回归。但这种测试的不足之处也是显而易见的,主要包括维护成本高,易发生误判,兼容性不足等。因为是基于界面操作,界面的稳定程度便成了

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function






