Home >Common Problem >Commonly used methods of String class in Java (summary sharing)
Commonly used methods of String class in Java (summary sharing)
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-08-30 13:37:181889browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about java. The String class is a very commonly used class and is the core class of the Java language. It is used to save string constants in the code. And it encapsulates many methods for operating strings. The following summarizes the use of some common methods of the String class. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

java video tutorial"
1. Comparison of String objects1. == compares whether they refer to the same object
Note:For built-in types, == compares the value in the variable; for reference types, == compares The address in the reference.public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 10;
// 对于基本类型变量,==比较两个变量中存储的值是否相同
System.out.println(a == b); // false
System.out.println(a == c); // true
// 对于引用类型变量,==比较两个引用变量引用的是否为同一个对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("world");
String s4 = s1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s2 == s3); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s4); // true
}2. boolean equals(Object anObject)Compare in dictionary order (lexicographic order: character size order)String class overrides the parent class Object equals method. By default, equals in Object are compared according to ==. After String overrides the equals method, it is compared according to the following rules, such as: s1.equals(s2)Analysis of the equals method in String: public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
// 1. 先检测this 和 anObject 是否为同一个对象比较,如果是返回true
if (this == anObject) {
return true;
}
// 2. 检测anObject是否为String类型的对象,如果是继续比较,否则返回false
if (anObject instanceof String) {
// 将anObject向下转型为String类型对象
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = value.length;
// 3. this和anObject两个字符串的长度是否相同,是继续比较,否则返回false
if (n == anotherString.value.length) {
char v1[] = value;
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = 0;
// 4. 按照字典序,从前往后逐个字符进行比较
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
} Comparison example code: public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("Hello");
// s1、s2、s3引用的是三个不同对象,因此==比较结果全部为false
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s3); // false
// equals比较:String对象中的逐个字符
// 虽然s1与s2引用的不是同一个对象,但是两个对象中放置的内容相同,因此输出true
// s1与s3引用的不是同一个对象,而且两个对象中内容也不同,因此输出false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false
}3. int compareTo(String s)Compare in lexicographic orderDifferent from equals, equals returns boolean type, and compareTo returns an int type. Specific comparison method: First compare the size in dictionary order. If there are unequal characters, directly return the size difference of the two charactersIf the first k characters are equal (k is two character length), the return value is the length difference between the two stringspublic static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}4. int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)Same as compareTo, but ignores case for comparisonpublic static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("ABc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 不同输出字符差值-1
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 相同输出 0
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // 前k个字符完全相同,输出长度差值 -3
}2. String searchString search is also a very common operation in strings. The String class provides common search methods,
| Function | |
|---|---|
| Returns the character at the index position. If the index is a negative number or out of bounds, an IndexOutOfBoundsException is thrown. Exception | |
| Returns the position where ch first appears, without returning -1 | |
| Start from the fromIndex position to find the position where ch first appears, no -1 is returned | |
| Returns the position where str first appears, without returning -1 | |
| Start from the fromIndex position Find the position where str first appears, but -1 is not returned | |
| Search from back to front, and return the first occurrence of ch Position, no return -1 | |
| Start looking from the fromIndex position, and look for the first occurrence of ch from back to front Position, no return -1 | |
| Search from back to front, return the position where str first appears, no return -1 | |
| Start searching from the fromIndex position, and search from back to front for the position where str first appears, without returning -1 |
The above methods are all instance methods and are called through object references.
3. Conversion
1. Value and string conversion
static String valueof() value to string
Integer.parseInt() string Integer
Double.parseDouble() String to floating point
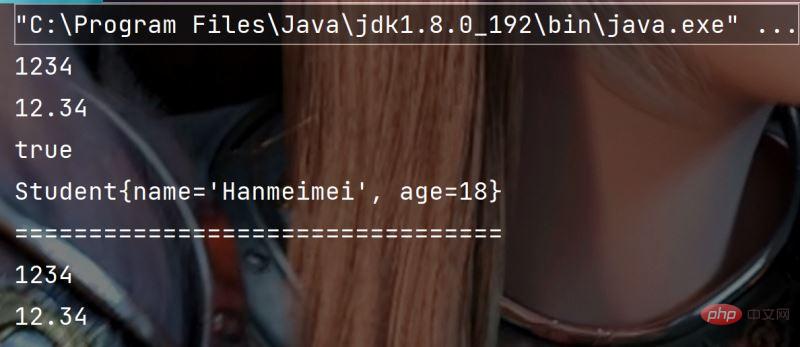
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 值转字符串
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("Hanmeimei", 18));
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println(s4);
System.out.println("=================================");
// 字符串转数字
//Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}
}
class Student{
String name;
int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}Execution result:
 2. Case conversion
2. Case conversion
String toUpperCase() Convert to uppercase
String toLowerCase() Convert to lowercase
These two functions only convert letters.
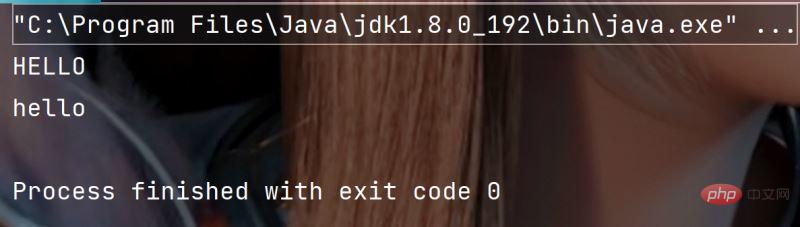
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO";
// 小写转大写
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase());
// 大写转小写
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase());
}Execution result:
 3. Conversion of strings and arrays
3. Conversion of strings and arrays
char[ ] toCharArray() String to array
new String (array reference) array to string
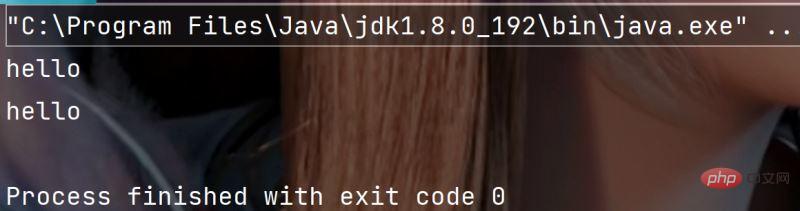
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
// 字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
System.out.println();
// 数组转字符串
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2);
}Execution result:
 4. Formatting
4. Formatting
static String format( );
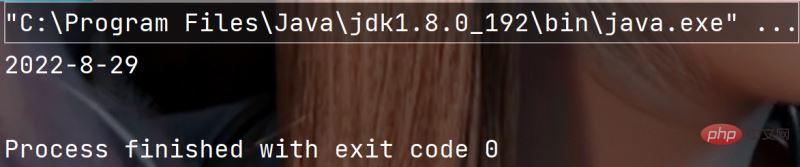
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2022, 8, 29);
System.out.println(s);
}Execution result:
 4. String replacement
4. String replacement
Use a specified new string Replace existing string data. The available methods are as follows:
| Function | |
|---|---|
| Replace all specified content | |
| Replace the first specified content content |
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String[] split(String regex) | 将字符串全部拆分 |
| String[] split(String regex, int limit) | 将字符串以指定的格式,拆分为limit组 |
如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用"|"作为连字符.
代码示例:
实现字符串的拆分处理
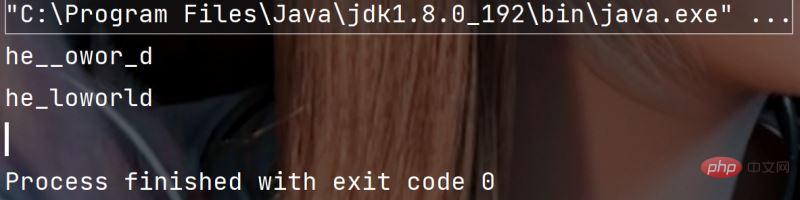
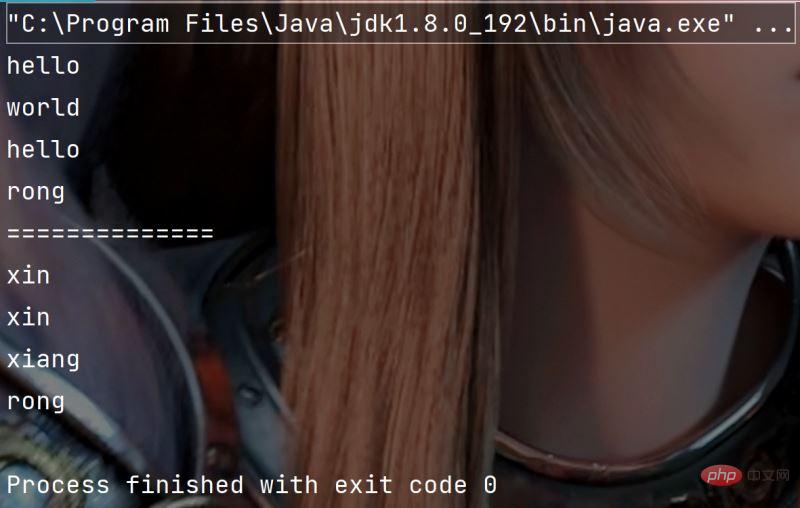
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello rong";
String[] result = str.split(" ") ; // 按照空格拆分
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("==============");
String str1 = "xin&xin=xiang&rong";
String[] str2 = str1.split("&|=");//按照=和&拆分
for(String s: str2) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}执行结果:
代码示例:
字符串的部分拆分
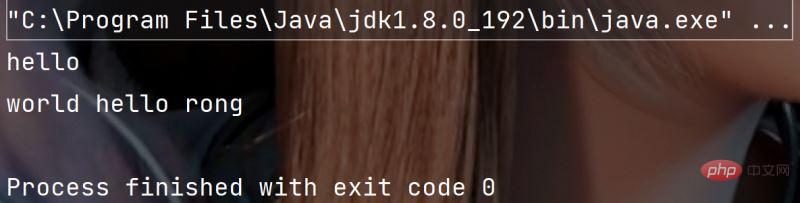
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello world hello rong" ;
String[] result = str.split(" ",2) ;
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}执行结果:
有些特殊字符作为分割符可能无法正确切分, 需要加上转义.
字符"|“,”*“,”+“,”."都得加上转义字符,前面加上 “” .
而如果是 “” ,那么就得写成 “\” ; 使用split来切分字符串时,遇到以反斜杠\作为切分的字符串,split后传入的内容是\\,这么写是因为第一和第三是个斜杠是字符串的转义符。转义后的结果是\,split函数解析的不是字符串而是正则,正则表达式中的\结果对应\,所以分隔反斜杠的时候要写四个反斜杠。
代码示例:
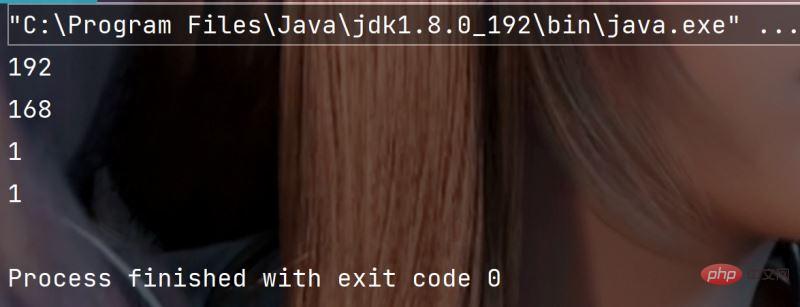
拆分IP地址
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "192.168.1.1" ;
String[] result = str.split("\\.") ;
for(String s: result) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}执行结果:
代码中的多次拆分:
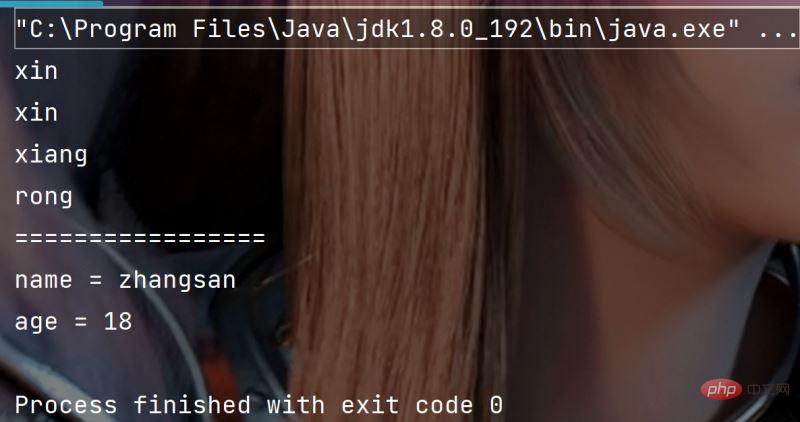
ppublic static void main(String[] args) {
//字符串多次拆封
String str = "xin&xin=xiang&rong";
String[] str1 = str.split("&");
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {
String[] str2 = str1[i].split("=");
for (String x:str2) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
String s = "name=zhangsan&age=18" ;
String[] result = s.split("&") ;
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
String[] temp = result[i].split("=") ;
System.out.println(temp[0]+" = "+temp[1]);
}
}执行结果:
六. 字符串截取
从一个完整的字符串之中截取出部分内容。可用方法如下 :
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String substring(int beginIndex) | 从指定索引截取到结尾 |
| String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 截取部分内容 |
代码示例:
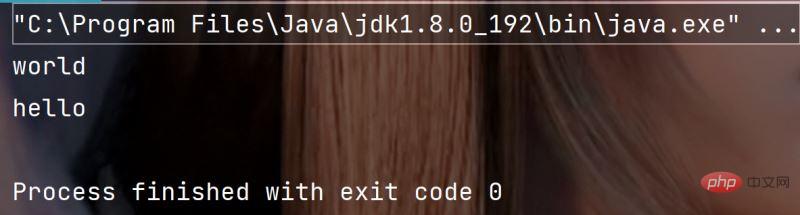
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld" ;
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));
}执行结果:
注意事项:
索引从0开始
注意前闭后开区间的写法, substring(0, 5) 表示包含 0 号下标的字符, 不包含 5 号下标,即(0,4)
七. 其他操作方法
1. String trim()
去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格
trim 会去掉字符串开头和结尾的空白字符(空格, 换行, 制表符等).
示例代码:
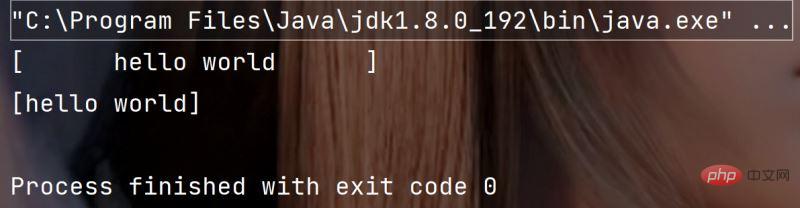
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello world " ;
System.out.println("["+str+"]");
System.out.println("["+str.trim()+"]");
}执行结果:
2. boolean isEmpty ()
isEmpty() 方法用于判断字符串是否为空
示例代码:
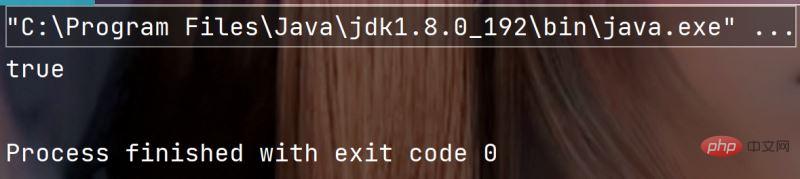
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "";
System.out.println(str.isEmpty());
}执行结果:
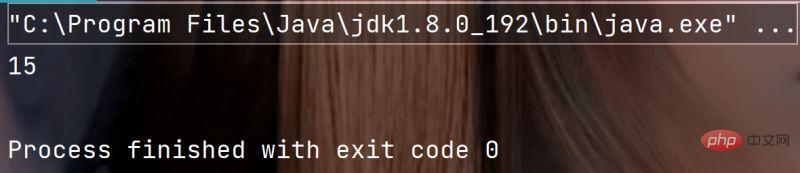
3. int length()
用于求字符串的长度
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "xinxinxiangrong";
System.out.println(str.length());
}执行结果:
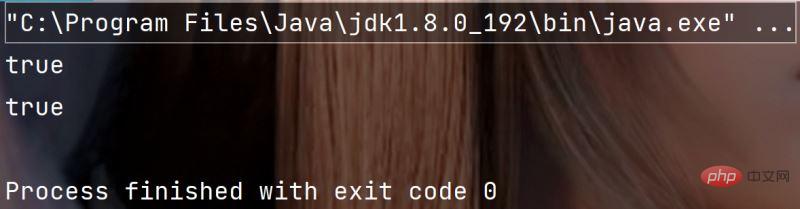
4. 判断字符串开头结尾
boolean startsWith(String prefix) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串开头的
boolean endWith(String sufix) 判断字符串是否以某个字符串结尾的
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "xinxinxianrong";
System.out.println(str.startsWith("xin"));
System.out.println(str.endsWith("rong"));
}执行结果:
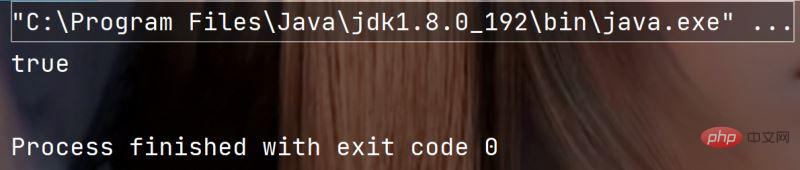
5. boolean contains(String str)
判断字符串中是否包含某个字符串
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "xinxinxianrong";
System.out.println(str.contains("inx"));
}执行结果:
推荐学习:《java视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Commonly used methods of String class in Java (summary sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!