The definition of a robot highlights the function of imitating humans; the definition of a robot is an individual with three elements: brain, hands, and feet, with non-contact sensors and contact sensors, and a sense of balance and inherent sense. Sensors, this definition emphasizes that the robot should have human-like characteristics, that is, it relies on its hands to operate, its feet to move, and its brain to complete unified command tasks.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 10 system, DELL G3 computer.
What is highlighted in the definition of a robot
What is highlighted in the definition of a robot is the function of imitating humans
has the following 3 conditions The machine can be called a robot:
An individual with three elements: brain, hands, and feet;
Has non-contact sensors (eyes) , the ear receives distant information) and contact sensors;
Sensors with balance sense and intrinsic sense.
This definition emphasizes that the robot should have humanoid characteristics, that is, it relies on its hands to operate, its feet to move, and its brain to complete unified command tasks. Non-contact sensors and contact sensors are equivalent to human facial features, allowing robots to recognize the external environment, while balance sense and intrinsic sense are indispensable sensors for robots to perceive their own status.
Expand knowledge
Robot is an intelligent machine that can work semi-autonomously or fully autonomously. Robots are capable of performing tasks such as homework or movement through programming and automatic control.
The earliest robot in history can be seen in the puppet robot built by Emperor Yang of the Sui Dynasty according to the image of Liu Peng. It was equipped with mechanisms and had the ability to sit, stand up, worship, and lie down.
Robots have basic characteristics such as perception, decision-making, and execution. They can assist or even replace humans in completing dangerous, heavy, and complex tasks, improve work efficiency and quality, serve human life, and expand or extend the scope of human activities and abilities.
Classification of robots
Regarding the classification of robots, there is no unified international standard, and there can be different classifications from different perspectives.
Development stage
First generation robot:
Teaching reproducible robot. In 1947, in order to transport and process nuclear fuel, the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the United States developed the world's first remotely controlled robot. In 1962, the United States successfully developed the PUMA universal teaching and reproduction robot. This robot uses a computer to control a machine with multiple degrees of freedom. It stores programs and information through teaching, reads the information during work, and then issues instructions. In this way, the robot can repeatedly reproduce this action based on the results of the human's teaching at that time. For example, a car's spot welding robot will always repeat this kind of work after teaching the spot welding process.
Second generation robot:
Sensing robot. The teaching and reproduction robot has no perception of the external environment. It does not know the size of the operating force, the existence of the workpiece, or whether the welding is good or bad. Therefore, in the late 1970s, people began to study the second generation Robots are called sensory robots. This type of robot has a sense similar to that of humans in certain functions, such as force sense, touch, sliding sense, vision, hearing, etc. It can feel and identify the shape, size, and color of workpieces through senses.
The third generation robot:
Intelligent robot. Robots invented since the 1990s. This kind of robot is equipped with a variety of sensors and can perform complex logical reasoning, judgment and decision-making, and independently determine its own behavior in changing internal states and external environments.
Control method
Operational robot: can be automatically controlled, can be programmed repeatedly, is multi-functional, has several degrees of freedom, can be fixed or Motion, used in related automation systems.
Programmable robot: Control the mechanical movements of the robot in sequence according to the pre-required order and conditions.
Teaching reproducible robot: Through guidance or other methods, first teach the robot movements, input the work program, and the robot will automatically repeat the operation.
CNC-type robot: There is no need to move the robot. The robot is taught through numerical values, language, etc., and the robot performs operations based on the taught information.
Sensation-controlled robot: Uses information obtained from sensors to control the robot's movements.
Adaptable control robot: The robot can adapt to changes in the environment and control its own actions.
Learning-controlled robot: The robot can "understand" the work experience, has a certain learning function, and uses the "learned" experience at work.
Intelligent robot: A robot that uses artificial intelligence to determine its actions.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What is highlighted in the definition of robot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 机器人学我表情的样子,让人感到一丝恐惧Apr 09, 2023 am 10:11 AM
机器人学我表情的样子,让人感到一丝恐惧Apr 09, 2023 am 10:11 AM通常,机器人的主要功能是完成一些简单的操作任务,我们希望机器人可以模仿人,让能力尽可能接近人类水平。不论是小米的 CyberOne 还是特斯拉的 Optimus,人们关心的主要是其机械关节数量,控制算法和行走速度。不过在这个领域,有些人探索的方向更加脑洞大开:现在,有一种机器人把模仿真人表情做到了极致:先尝试一下自拍。从「嫌弃」到「惊讶」,都可以做到完全同步:这个机器人名叫 Ameca,是个表情怪。除了模仿,它自己也能照镜子做很多小表情,看起来非常像真人。Ameca「假装」第一次见到镜子,首
 拿破仑、孔子在线陪聊!AI聊天机器人「复活」历史名人,网友:真上头!Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:11 PM
拿破仑、孔子在线陪聊!AI聊天机器人「复活」历史名人,网友:真上头!Apr 08, 2023 pm 12:11 PM和活生生的已故历史名人聊天是个什么感觉?近日,就有一群开发者利用语言模型,把千百年来各行各业的历史名人全部「复活」成了聊天机器人,做进了一款手机app里,起名叫「你好,历史」!开发者声称,这个与古代名人聊天的app涉及的内容几乎无所不包。比如可以:与玛丽莲·梦露聊好莱坞八卦与弗里达·卡洛讨论现代艺术问问圣诞老人他有多少只驯鹿问问科特·科本为什么自杀向穴居人学习如何生火与宇宙意识辩论生命的意义不过他们也没忘记提醒用户,这些对话是由人工智能生成的,所以不要太认真。而且每个对话都是独一无二的,你永远不
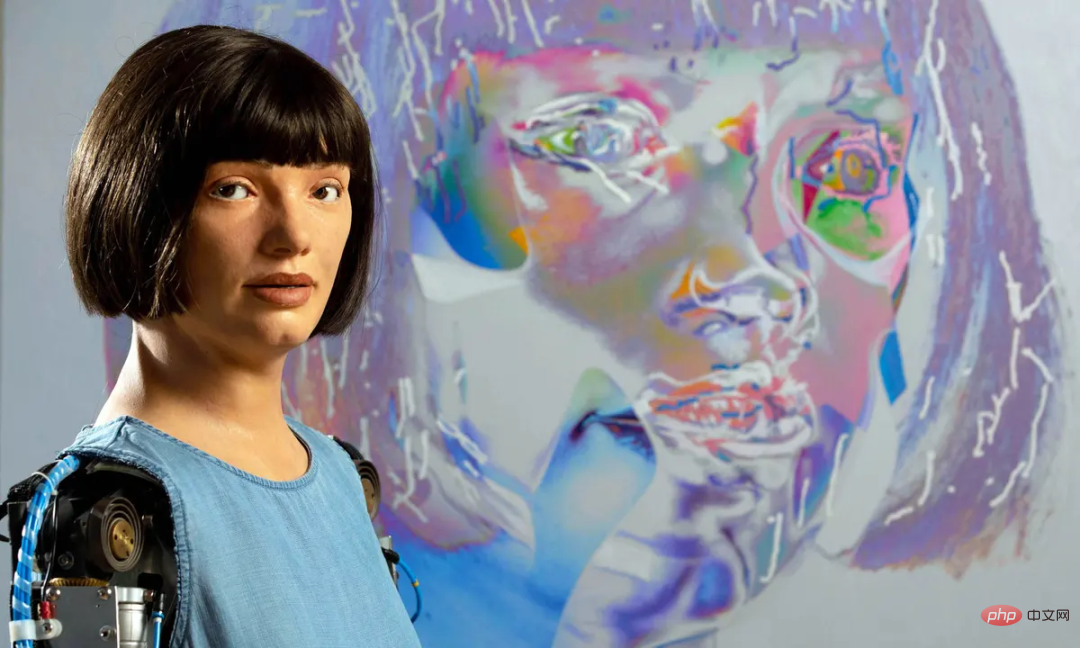 女王登基70周年,世上首个超逼真人形机器艺术家献上肖像画作,被锐评“缺少信念”Apr 08, 2023 pm 08:11 PM
女王登基70周年,世上首个超逼真人形机器艺术家献上肖像画作,被锐评“缺少信念”Apr 08, 2023 pm 08:11 PM大数据文摘出品作者:Caleb为庆祝英国女王伊丽莎白二世登基70周年,英国也是早早就洋溢出了庆典的味道。据了解,英国将于6月2日至5日连放4天公众假期,并在期间举行多项庆祝活动。英国皇家铸币厂也在精心打造有史以来最大的硬币,直径220毫米,重15公斤,面值15000英镑,耗时近400小时打造,是该厂1100年来生产的最大硬币。这枚金币一面雕刻着代表英国女王伊丽莎白二世的符号EⅡR,周围环绕着代表英国的玫瑰、水仙、蓟和三叶草。另一面有女王骑在马背上的图案。在这么热闹的日子里,AI当然也必须来凑一凑
 人类与人工智能如何建立关系Apr 09, 2023 pm 07:41 PM
人类与人工智能如何建立关系Apr 09, 2023 pm 07:41 PM人类与人工智能相比,哪个更擅长建立关系?事实上,这项革命性的技术已经存在了很长一段时间。然而,直到最近人们才意识到人工智能对人类的重要性。人工智能利用算法模拟人类,并随着时间的推移从经验中学习的能力,为这项技术与人类建立关系开辟道路。人类如何建立人际关系作为人类,我们倾向于只与少数人建立关系。我们试图确保不需要的和不相干的人从我们的生活中消失。在将我们的关系限制在少数人的同时,我们确保与那些对我们真正重要的人建立高质量的关系。然而,同样的方法在商业用语中可能不是理想的,并可能适得其反。尽管知道这
 盘点全球不错的七所机器人工程专业学校Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:31 PM
盘点全球不错的七所机器人工程专业学校Apr 08, 2023 pm 01:31 PM有抱负的工程师应该了解世界各地著名的机器人工程学院。现在是从事机器人和工程事业的最佳时机——从人工智能到太空探索,这一领域充满了令人兴奋的创新和进步。美国劳工统计局估计,未来10年,机械工程领域的职业总体上将保持7%的稳定增长率,确保毕业生将有大量的就业机会。机器人工程专业的学生平均工资超过9万美元,无需担心还助学贷款的问题。对于那些考虑投身机器人工程领域的人来说,选择一所合适的大学是非常重要的。世界上许多顶尖的机器人工程学院都在美国,尽管国外也有一些很棒的项目。这是7所世界上最好的机器人工程学
 让机器人学会咖啡拉花,得从流体力学搞起!CMU&MIT推出流体模拟平台Apr 07, 2023 pm 04:46 PM
让机器人学会咖啡拉花,得从流体力学搞起!CMU&MIT推出流体模拟平台Apr 07, 2023 pm 04:46 PM机器人也能干咖啡师的活了!比如让它把奶泡和咖啡搅拌均匀,效果是这样的:然后上点难度,做杯拿铁,再用搅拌棒做个图案,也是轻松拿下:这些是在已被ICLR 2023接收为Spotlight的一项研究基础上做到的,他们推出了提出流体操控新基准FluidLab以及多材料可微物理引擎FluidEngine。研究团队成员分别来自CMU、达特茅斯学院、哥伦比亚大学、MIT、MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab、马萨诸塞大学阿默斯特分校。在FluidLab的加持下,未来机器人处理更多复杂场景下的流体工作也都
 四足机器人学会“双腿站立下楼梯”!效率比腿式系统高83%Apr 09, 2023 am 11:21 AM
四足机器人学会“双腿站立下楼梯”!效率比腿式系统高83%Apr 09, 2023 am 11:21 AM还记得那个和特斯拉飙车的机器人吗?这是瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院衍生公司研发的与公司同名的四足轮腿式机器人——Swiss-Mile,前身是ANYmal四足机器人。距离它和特斯拉飙车还不到半年的时间,它又实现了重大升级。这次升级改进了机器人的算法,运动能力直接UP UP UP ! 可以双腿站立下楼梯:(小编内心OS:如果是我穿轮滑鞋下楼梯可能会摔个狗吃屎)楼梯爬累了,坐个电梯吧,用前脚按开电梯门:面对障碍物应对自如:它还能知道什么时候该站起来,什么时候该“趴下”,双腿直立与四足运动之间的切换更丝滑:
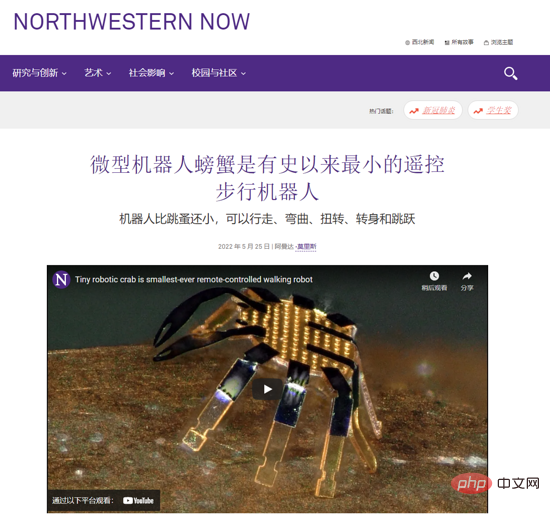 科学家展示世界上有史以来超小的“螃蟹”遥控步行机器人,体积比跳蚤还小Apr 09, 2023 pm 10:41 PM
科学家展示世界上有史以来超小的“螃蟹”遥控步行机器人,体积比跳蚤还小Apr 09, 2023 pm 10:41 PM日前,美国西北大学工程师开发出有史以来最小的遥控步行机器人,它以一种小巧可爱的螃蟹形式出现。这种微小的“螃蟹”机器人宽度只有半毫米,可以弯曲、扭曲、爬行、行走、转弯甚至跳跃,无需液压或电力。IT之家了解到,相关研究成果发表在《科学・机器人》上。据介绍,这种机器人是用形状记忆合金材料所制造的,然后可以变成所需的形状,当你加热后又会变回原来的形状,而热量消失时可以再次弹回变形时的样子。据介绍,其热量是由激光所带来的。激光通过“螃蟹”加热合金,但因为它们非常小,所以热量传播非常快,这使得它们的响应速度

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.







