Excel function learning: dichotomy principle of LOOKUP function
In the previous article "Excel function learning: 5 ways to use the LOOKUP function", we learned about the 5 ways to use the LOOKUP function. It is estimated that many friends don't understand it. Today I will give you details Let’s explain the dichotomy principle of LOOKUP. After understanding the principle, go back and read yesterday’s tutorial. I believe you will have a different understanding of LOOKUP.

In the previous article, we learned various routines of the LOOKUP function, and also mentioned many times that the search of the LOOKUP function is based on the dichotomy method, so in the end What is dichotomy? Let’s talk about this issue today.
Let’s still use yesterday’s example: search for results by serial number. The serial numbers are arranged in ascending order. The result of the formula =LOOKUP(J2,A2:D19) is correct.

1. Binary search principle
Binary search is to search the data in the search range according to Divide the number into two to find a piece of data in the middle, the middle value, and then compare it with our search value and the middle value. When the middle value is equal to the search value, the result is obtained directly; when the middle value is less than the search value, the binary search comparison is continued downward (that is, the binary search is continued in the lower half of the data excluding the middle value). method search); when the intermediate value is greater than the search value, the binary search comparison continues upward (that is, the binary search continues in the upper half of the data excluding the intermediate value). If no data equal to the search value is found after dichotomizing until the last data: if the last data is less than the search value, then use the position of the last data to obtain the result value; if the last data is greater than the search value, then search upwards The data whose position is closest to the last data is less than or equal to the search value, and then the result is obtained based on the position of this data.
I guess many friends will be confused by this explanation. Let’s take a look at the above example to see how to find the Chinese score of 79 through serial number 5.
First comparison: There are 18 data in the search range A2~A19, and the middle position is 18÷2=9, that is, the middle value is 9 in cell A10. Obviously the search value 5 is less than 9, so continue to search upwards in A2~A9;
Tips: If the number of data in the search range is an odd number, the middle position is (number 1) ÷ 2, for example, if it is row 11, The middle position is (11 1) ÷ 2 = 6; if the number of data is an even number, the middle position is (number) ÷ 2.

Second comparison: There are only 8 data, the middle position is 8÷2=4, the middle value is 4 in cell A5, the search value 5 is greater than 4, so Continue looking down in A6~A9. Note that there are only four numbers below at this time, and the data below 9 are directly excluded during the first search.

The third comparison: 4 data, the middle value is 6 of A7, the search value 5 is less than 6, so search upward. At this time, there is only one data left, 5 in cell A6, which is consistent with the search value, so the data 79 in column D corresponding to 5 is obtained.

It is very difficult to understand the dichotomy through just such an example. Let’s look at another example. Arrange the data in the table above in descending order of scores, or search for Chinese scores by serial number 5. The formula does not need to be modified. Because the order of the serial number column is out of order and is not arranged in ascending order, an error occurs. The actual number is 79, and the formula yields 94. What's going on? Let’s look at it through dichotomy.
The first search: the middle value (9th data) is 18, the search value 5 is less than 18, so search upward in A2~A9;

Second search: The above 8 data, the middle value (the 4th data) is 8, the search value 5 is less than 8, continue to search upward in A2~A4;

The third search: the above 3 data, the middle value is 1, the search value 5 is greater than 1, search downward:

The fourth search: Now there is only one data 7 in cell A4. The search value 5 is less than 7. Therefore, using 7 as a reference, find the data with a position closest to 7 and a value less than 5 or equal to 5, that is, 1 in cell A3, and thus obtain the corresponding The Chinese value is 94.
Through these two examples, I think everyone should have a certain understanding of the dichotomy. Regarding this principle, there is only one sentence in the function description:

In practical applications, we don’t need to worry about what the dichotomy is, what is the middle position, whether to look down or up, this is all the work of the function, we only need to remember one thing : The data must be arranged in ascending order. If it cannot be arranged in ascending order, then design the formula according to the precise search routine of LOOKUP.
2. LOOKUP implements data rounding
That’s all the introduction to the principle of dichotomy. Next, we need to solve the two problems left before.
In the article on May 12, we used LOOKUP to solve a rounding problem. As a result, everyone left messages asking for an explanation:

So what caused this? What is this formula that everyone is talking about? Look at the picture below:

#It turns out that this formula uses the LOOKUP function to remove all numbers below the hundredth place, thereby achieving percentile rounding.
After understanding the principle of dichotomy, it is time for LOOKUP to explain it to everyone. First, explain the ROW (A:A)*100 part. It actually just gets a set of numbers. In order to make it clear to everyone, let’s make the range A:A smaller. We use =ROW(A1:A31)*100 as an explanation:


3. LOOKUP for data extraction
We also use LOOKUP for data extraction, so we have a 5000-word appointment:




For beginners, the usage of LOOKUP in the above two cases is too advanced. Even through these introductions, it is estimated that they have only a partial understanding. In fact, learning functions is a process. From understanding to understanding, from understanding to mastering , which requires a lot of practice and thinking. As long as everyone maintains a positive and optimistic attitude and can experience the fun of learning functions, success is not far away.
Related learning recommendations: excel tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Excel function learning: dichotomy principle of LOOKUP function. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PM
MEDIAN formula in Excel - practical examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:08 PMThis tutorial explains how to calculate the median of numerical data in Excel using the MEDIAN function. The median, a key measure of central tendency, identifies the middle value in a dataset, offering a more robust representation of central tenden
 Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
Google Spreadsheet COUNTIF function with formula examplesApr 11, 2025 pm 12:03 PMMaster Google Sheets COUNTIF: A Comprehensive Guide This guide explores the versatile COUNTIF function in Google Sheets, demonstrating its applications beyond simple cell counting. We'll cover various scenarios, from exact and partial matches to han
 Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AM
Excel shared workbook: How to share Excel file for multiple usersApr 11, 2025 am 11:58 AMThis tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to sharing Excel workbooks, covering various methods, access control, and conflict resolution. Modern Excel versions (2010, 2013, 2016, and later) simplify collaborative editing, eliminating the need to m
 How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AM
How to convert Excel to JPG - save .xls or .xlsx as image fileApr 11, 2025 am 11:31 AMThis tutorial explores various methods for converting .xls files to .jpg images, encompassing both built-in Windows tools and free online converters. Need to create a presentation, share spreadsheet data securely, or design a document? Converting yo
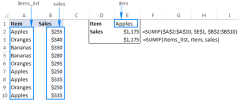 Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AM
Excel names and named ranges: how to define and use in formulasApr 11, 2025 am 11:13 AMThis tutorial clarifies the function of Excel names and demonstrates how to define names for cells, ranges, constants, or formulas. It also covers editing, filtering, and deleting defined names. Excel names, while incredibly useful, are often overlo
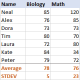 Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AM
Standard deviation Excel: functions and formula examplesApr 11, 2025 am 11:01 AMThis tutorial clarifies the distinction between standard deviation and standard error of the mean, guiding you on the optimal Excel functions for standard deviation calculations. In descriptive statistics, the mean and standard deviation are intrinsi
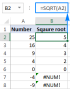 Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AM
Square root in Excel: SQRT function and other waysApr 11, 2025 am 10:34 AMThis Excel tutorial demonstrates how to calculate square roots and nth roots. Finding the square root is a common mathematical operation, and Excel offers several methods. Methods for Calculating Square Roots in Excel: Using the SQRT Function: The
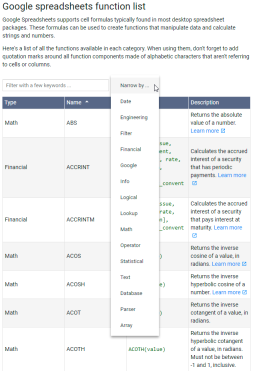 Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AM
Google Sheets basics: Learn how to work with Google SpreadsheetsApr 11, 2025 am 10:23 AMUnlock the Power of Google Sheets: A Beginner's Guide This tutorial introduces the fundamentals of Google Sheets, a powerful and versatile alternative to MS Excel. Learn how to effortlessly manage spreadsheets, leverage key features, and collaborate


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

mPDF
mPDF is a PHP library that can generate PDF files from UTF-8 encoded HTML. The original author, Ian Back, wrote mPDF to output PDF files "on the fly" from his website and handle different languages. It is slower than original scripts like HTML2FPDF and produces larger files when using Unicode fonts, but supports CSS styles etc. and has a lot of enhancements. Supports almost all languages, including RTL (Arabic and Hebrew) and CJK (Chinese, Japanese and Korean). Supports nested block-level elements (such as P, DIV),

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft







