Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Summarize the application of window.history object
Summarize the application of window.history object
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-08-05 11:26:261645browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces issues related to the window.history object. The History object contains the URLs visited by the user (in the browser window) , let’s take a look at it, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end]
The History object contains the user (in browser window) visited URL.
The History object is part of the window object and can be accessed through the window.history property.
Note: There is no public standard for the History object, but all browsers support it.
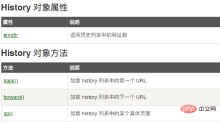
Description: Page stack object
Description: The characteristics of the stack area are (last in, first out), and the characteristics of the heap area are (first in, first out)
Content:
- (1)window.history.back() Jump to the previous page in the stack
- (2 )window.history.forward() Jump to the next page in the stack
- (3)window.history.go(num) Jump to the specified page in the stack
- (4 )window.history.length The number of pages in the stack
Note:
- a. Through the method provided in the window.history object Page jumps do not add new pages to the stack.
- Jumping through window.location.href or a tag will add a new page to the stack.
- b. The stack area feature (last in, first out) not only means that the content that comes in last is removed from the stack first, but also means that if you want to add the content in the stack to the specified location, you must first The content needs to be de-stacked.

<h2>第一页</h2>
<button>去到第二页</button>
<hr>
<h3>window.history对象提供的方法</h3>
<button>window.history.back()</button>
<button>window.history.forward()</button>
<button>window.history.go(2)</button>
<button>window.history.length</button>
<script>
var nextBut = document.querySelector('.next');
var backBut = document.querySelector('.back');
var forwardBut = document.querySelector('.forward');
var goBut = document.querySelector('.go');
var lengthBut = document.querySelector('.length');
nextBut.onclick = function() {
document.location.href = '11第2个页面.html';
}
backBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.back()
}
forwardBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.forward()
}
goBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.go(2)
}
lengthBut.onclick = function() {
console.log(window.history.length)
}
</script>

When the "Go to Second Page" button is clicked:
The second page:
<h2>第二个页面</h2>
<button>去到第三页</button>
<hr>
<h3>window.history对象提供的方法</h3>
<button>window.history.back()</button>
<button>window.history.forward()</button>
<button>window.history.go(2)</button>
<button>window.history.length</button>
<script>
var nextBut = document.querySelector('.next');
var backBut = document.querySelector('.back');
var forwardBut = document.querySelector('.forward');
var goBut = document.querySelector('.go');
var lengthBut = document.querySelector('.length');
nextBut.onclick = function() {
document.location.href = '11第3个页面.html';
}
backBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.back()
}
forwardBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.forward()
}
goBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.go(2)
}
lengthBut.onclick = function() {
console.log(window.history.length)
}
</script>
When clicking the "Go to the third page" button:

Of course, you can click on the buttons below , if you are interested, try it yourself and give it a try!
The third page:
<h2>第三个页面</h2>
<button>去到第四页</button>
<hr>
<h3>window.history对象提供的方法</h3>
<button>window.history.back()</button>
<button>window.history.forward()</button>
<button>window.history.go(2)</button>
<button>window.history.length</button>
<script>
var nextBut = document.querySelector('.next');
var backBut = document.querySelector('.back');
var forwardBut = document.querySelector('.forward');
var goBut = document.querySelector('.go');
var lengthBut = document.querySelector('.length');
nextBut.onclick = function() {
document.location.href = '11第4个页面.html';
}
backBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.back()
}
forwardBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.forward()
}
goBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.go(2)
}
lengthBut.onclick = function() {
console.log(window.history.length)
}
</script>
The rendering is as follows: When clicking the "Go to the fourth page" button:

The fourth page:
<h2>第四个页面</h2>
<button>回到首页</button>
<hr>
<h3>window.history对象提供的方法</h3>
<button>window.history.back()</button>
<button>window.history.forward()</button>
<button>window.history.go(2)</button>
<button>window.history.length</button>
<script>
var nextBut = document.querySelector('.next');
var backBut = document.querySelector('.back');
var forwardBut = document.querySelector('.forward');
var goBut = document.querySelector('.go');
var lengthBut = document.querySelector('.length');
nextBut.onclick = function() {
document.location.href = '11window.history对象.html';
}
backBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.back()
}
forwardBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.forward()
}
goBut.onclick = function() {
window.history.go(2)
}
lengthBut.onclick = function() {
console.log(window.history.length)
}
</script>
The rendering is as follows: When clicking the "Return to Home Page" button:

[Related recommendations: javascript Video tutorial、web front-end】
The above is the detailed content of Summarize the application of window.history object. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

