Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >In-depth analysis of the event object Event in JS
In-depth analysis of the event object Event in JS
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2022-08-04 19:56:002311browse
After the event occurs, an event object (Event) will be generated, representing the status of the event. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event object Event in JS and a detailed interpretation of it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

1. What is an event object Event
When every event is triggered, a corresponding event object will be generatedevent, which includes the element that triggered the event, the status of the keyboard and mouse, the position, etc.
Whenever the user triggers an event, JS will automatically generate an event object. Depending on the triggering event, this object contains different contents. For example, a click event is triggered by the mouse. A MouseEvent object will be generated, which contains the mouse position and other contents; triggering an event through the keyboard will generate a KeyboardEvent object which contains key-related information.
-
eventThe object represents the status of the event, such as the element that triggered the event, the status of the keyboard button, the position of the mouse, the status of the mouse button, etc.; -
eventThe object is an implicit parameter and is only valid during the event; -
eventThe object will have different properties depending on the triggering method. That is to say, some properties are only valid for specific events, but all contents are inherited from theEventobject; the eventobject is inIEThe behavior of browsers such asChromeis different. For example,event.targetrepresents the element that triggers the event. InIE, you need to useevent.srcElementGet;
EventThe object itself is a constructor that can be used to generate new instances.
event = new Event(type, options);
EventThe constructor accepts two parameters. The first parameter type is a string, indicating the name of the event; the second parameter options is an object, indicating the configuration of the event object. This object mainly has the following two properties.
bubbles: Boolean value, optional, defaults to false, indicating whether the event object bubbles.cancelable: Boolean value, optional, defaults to false, indicating whether the event can be canceled, that is, whether it can be canceled usingEvent.preventDefault()Cancel this event. Once an event is canceled, it is as if it never occurred and the browser's default behavior for that event will not be triggered.
var ev = new Event(
'look',
{
'bubbles': true,
'cancelable': false
}
);
document.dispatchEvent(ev);The above code creates a new look event instance, and then uses the dispatchEvent method to trigger the event.
Note that if the bubbles attribute is not explicitly specified as true, the generated event can only trigger the listening function in the "capture phase".
// HTML 代码为
// <div><p>Hello</p></div>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
var p = document.querySelector('p');
function callback(event) {
var tag = event.currentTarget.tagName;
console.log('Tag: ' + tag); // 没有任何输出
}
div.addEventListener('click', callback, false);
var click = new Event('click');
p.dispatchEvent(click);In the above code, the p element emits a click event, which does not bubble by default. div.addEventListenerThe method specifies listening during the bubbling phase, so the listening function will not be triggered. If it is written as div.addEventListener('click', callback, true), then this event can be monitored during the "capture phase".
On the other hand, if this event fires on a div element.
div.dispatchEvent(click);
Then, no matter whether the div element is listening in the bubbling stage or in the capturing stage, the listening function will be triggered. Because the div element is the target of the event at this time, there is no question of whether it bubbles up. The div element will always receive the event, thus causing the listening function to take effect.
2. Event attributes
We mentioned earlier that objects will have different attributes depending on the triggering method. We can It is roughly divided into four parts:
General properties (properties owned whether triggered by keyboard or mouse)
- bubbles
Whether the event will bubble, Boolean;
- cancelable
Whether the event has default behavior, Boolean Value;
Default behavior refers to some behaviors specified in the browser, such as
The link will jump after clicking on the label,<form></form>Click within the label Enter will automatically submit and so on. - currentTarget
The element where the event handler is currently processing the event returns an
Elementobject; - defaultPrevented
Whether the event cancels the default behavior, Boolean value;
- detail
Returns a number containing event details
In theclick
,mousedownandmouseupevents, this number represents the current number of clicks. In thedblclickevent, this number is always 2 . In keyboard events and mouse over events, this number is always 0. eventPhase返回一个代表事件处理程序发生时所在阶段的数字;
0表示当前阶段未发生其他事件;1表示当前事件在捕获阶段发生;2表示当前事件处于目标阶段;3表示当前事件处于冒泡阶段;isTrusted表示该事件是由用户行为触发的,还是由 JS 代码触发的,布尔值;
当事件是由用户行为(点击等)触发时,值为true,当事件是通过EventTarget.dispatchEvent()派发的时候,这个属性的值为false。
- 列表1
- 列表2
- 列表3
- 列表4
点击列表1后,控制台打印如下结果: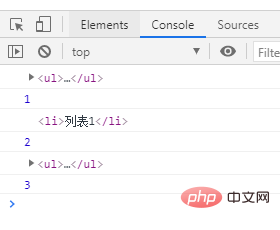
target返回触发该事件的目标节点,返回一个Element对象;
target并不一定与this指向相同,this指向的是当前发生事件的元素,而target指向的是触发该事件的元素,可以将上方代码中的console.log(event.eventPhase);换成console.log(event.target);来具体体验一下两者的不同。
在IE浏览器中应使用srcElement来代替target。type返回触发的事件名称,例click,keydown等;
鼠标属性
-
button当事件被触发时,哪个鼠标按钮被点击; -
clientX当事件被触发时,鼠标指针的 x 轴坐标; -
clientY当事件被触发时,鼠标指针的 y 轴坐标; -
screenX当事件被触发时,鼠标指针的 x 轴坐标; -
screenY当事件被触发时,鼠标指针的 y 轴坐标;
键盘属性
-
altKey当事件被触发时,“Alt” 是否被按下; -
ctrlKey当事件被触发时,“Ctrl” 是否被按下; -
metaKey当事件被触发时,“meta” 是否被按下; -
shiftKey当事件被触发时,“Shift” 是否被按下; -
Location返回按键在设备上的位置; -
charCode当事件被触发时,触发键值的字母代码; -
key按下按键时返回按键的标识符; -
keyCode返回keypress事件触发的键的值的字符代码,或者keydown或keyup事件的键的代码; -
which返回keypress事件触发的键的值的字符代码,或者keydown或keyup事件的键的代码; -
relatedTarget返回与事件的目标节点相关的节点。
IE属性
-
cancelBubble如果想阻止事件冒泡,必须把该属性设为true; -
fromElement对于mouseover和mouseout事件,fromElement引用移出鼠标的元素; -
returnValue等同于defaultPrevented; -
srcElement等同于target; -
toElement对于mouseover和mouseout事件,该属性引用移入鼠标的元素; -
x事件发生的位置的 x 坐标; -
y事件发生的位置的 y 坐标;
三、Event 方法
-
initEvent()初始化新创建的Event对象的属性; -
preventDefault()阻止触发事件元素的默认行为; -
stopPropagation()阻止事件冒泡;
如果想要阻止事件元素的默认行为,例如点击 <a></a> 标签时执行点击事件,不要跳转链接,需要在事件处理程序中调用 preventDefault 方法:
<a>百度一下,你就知道</a>
<script>
document.querySelector("a").onclick = function () {
event.preventDefault();
// do something
}
</script>
如果想要阻止事件冒泡,例如点击子元素标签时执行子元素的点击事件,而不想要执行父级元素的事件处理程序,则需要调用 stopPropagation 方法:
- 不要触发 ul 的点击事件处理程序
其他相关方法
-
addEventListener()给目标元素注册监听事件; -
createEvent()创建一个Event对象; -
dispatchEvent()将事件发送到目标元素的监听器上; -
handleEvent()把任意对象注册为事件处理程序; -
initMouseEvent()初始化鼠标事件对象的值; -
initKeyboardEvent()初始化键盘事件对象的值; -
initMutationEvent()初始变动事件和HTML事件对象的值; -
initCustomEvent()初始自定义事件对象的值; -
removeEventListener()删除目标元素上的某个监听事件;
另外关于 createEvent 方法,根据传入参数的不同,会返回不同的 event 对象:
-
MouseEvents创建鼠标事件对象,返回的对象中包含initMouseEvent()方法; -
KeyboardEvent创建键盘事件对象,返回的对象中包含initKeyEvent()方法; -
KeyEvents在firefox中创建键盘事件对象需要传入该参数; -
MutationEvents模拟变动事件和 HTML 事件的事件对象,返回的对象中包含initMutationEvent方法; -
CustomEvent创建自定义事件对象,返回的对象中包含initCustomEvent()方法;
四、模拟事件
4.1 模拟鼠标事件
我们可以通过 createEvent() 方法可以创建一个新的 event 对象,借助 initMouseEvent() 方法来对这个鼠标事件对象的值进行初始化,该方法接受十五个参数,分别与鼠标事件中的各个属性一一对应,按照 type、bubbles、cancelable、view、detail、screenX、screenY、clientX、clientY、ctrlKey、altKey、shiftKey、、metaKey、button、relatedTarget 的顺序传入即可:
var oBtn = document.querySelector("button");
// 为 button 绑定事件处理程序
oBtn.addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log(event);
})
var event = document.createEvent("MouseEvents");
// 通过 initMouseEvent() 方法初始化鼠标事件的 event 对象
event.initMouseEvent("click", true, true, document.defaultView, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, false, false, false, false, 0, null);
// 通过 dispatchEvent() 方法来触发 oBtn 上绑定的点击事件,此时浏览器打印的 event 对象为自定义的 event
oBtn.dispatchEvent(event);
初始化事件对象时,最重要的是前四个参数,因为浏览器在触发事件时,这四个参数是必须的,而剩余的参数只有在事件处理程序中才会被使用,target 会在执行 dispatchEvent 方法时自动赋值;
4.2 模拟键盘事件
同样需要先使用 createEvent() 方法可以创建一个新的 event 对象,但需要使用 initKeyEvent 来对键盘事件对象的值进行初始化,该方法接收八个参数,分别于键盘事件对象中的各个属性一一对应,按照 type、bubbles、cancelable、view、key、location、modifiers、repeat的顺序传入即可。但在 firefox 中,需要按照 type、bubbles、cancelable、view、ctrlKey、altKey、shiftKey metaKey keyCode charCode ` 的顺序传入十个参数
document.onkeydown = function () {
console.log(event);
}
var event = document.createEvent("KeyboardEvent");
event.initKeyboardEvent("keydown", false, false, document.defaultView, "a", 0, "Shift", 0);
document.dispatchEvent(event);
4.3 模拟其他事件
如果想要模拟其他事件,诸如 submit、focus 等 HTML 和变动事件,则需要通过 MutationEvents 方法来创建事件,通过 initEvent 方法来进行初始化,按照type、bubbles、cancelable、relatedNode、preValue、newValue、attrName、attrChange的顺序传入参数。
<input>
<script>
var oInput = document.querySelector("input");
oInput.addEventListener("focus", function () {
this.style.background = "#ccc"
})
var event = document.createEvent("HTMLEvents");
event.initEvent("focus", true, false);
oInput.dispatchEvent(event);
</script>
4.4 自定义 DOM 事件
自定义事件不是由 DOM 原生触发的,它的目的是让开发人员创建自己的事件。要创建新的自定义事件,可以调用 createEvent("CustomEvent"),返回的对象有一个名为 initCustomEvent() 的方法,接收 type、bubbles、cancelable、detail 四个参数。
var oInput = document.querySelector("input");
oInput.addEventListener("myEvent", function () {
console.log(event);
})
var event = document.createEvent("CustomEvent");
event.initCustomEvent("myEvent", true, false, "自定义事件myEvent");
oInput.dispatchEvent(event);
上方代码创建了一个自定义事件,事件名为 myEvent , 该事件可以向上冒泡,不可以执行在浏览器中的默认行为, detail 属性的值为 自定义事件myEvent,可以在绑定该事件的元素或者元素的父级元素上绑定事件处理程序来查看 event 对象。
5. Event Compatibility Processing
mainly takes into account the difference in event objects between IE browsers and Chrome and other browser event objects. Special processing is required for the following four properties:
Get the
eventobjectvar event = event || window.event;Get
targetobjectvar target = event.target || event.srcElement;Prevent browser default behavior
event.preventDefault? event.preventDefault(): (event.returnValue = false);Prevent Event bubbling
event.stopPropagation ? event.stopPropagation() : (event.cancelBubble = true);
[Related recommendations:javascript Study tutorial】
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of the event object Event in JS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- What is an anonymous function in JavaScript? Brief analysis of application scenarios
- Detailed explanation of JavaScript numerical methods and properties
- Let's analyze JavaScript exception handling methods together
- Let's talk about how to use the Object() function to create objects in JavaScript
- What is this? An in-depth analysis of this in JavaScript
- Detailed explanation of 5 loop traversal methods of Javascript objects

