The services provided by tcp and ip are transport layer services and network layer services respectively. In the TCP/IP architecture, tcp refers to "Transmission Control Protocol", which is a protocol of the transport layer, so the services provided by tcp are transport layer services; and ip refers to "Internet Interconnect Protocol", which is a protocol of the network layer. protocol, so the services provided by ip are network layer services.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
The services provided by tcp and ip are transport layer services and network layer services respectively.
TCP/IP architecture is divided into the following four layers:
1. Application layer, corresponding to the high level of the OSI reference model, provides users with various services required;
2. The transport layer provides end-to-end communication functions for application layer entities, ensuring the sequential transmission of data packets and the integrity of the data;
3. The network layer is responsible for the communication between adjacent nodes. Communication between;
4. Network interface layer, responsible for monitoring the exchange of data between the host and the network.
The services provided by TCP and IP are at the transport layer and the Internet layer respectively, which are transport layer services and network layer services.
TCP Protocol
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP, Transmission Control Protocol) is a connection-oriented, reliable, byte stream-based The Transport layer communication protocol is defined by the IETF's RFC 793.

TCP supplements the Internet Protocol (IP Protocol), which defines the IP address used to identify systems on the Internet, mainly ensuring end-to-end data transmission between different nodes . Internet Protocol provides instructions for transmitting data, while TCP creates connections and ensures data is delivered to the correct destination. These two protocols usually work together and are called the TCP/IP suite.
TCP works in conjunction with the Internet Protocol, which defines the logical location of remote nodes, while TCP transports and ensures data is delivered to the correct destination.
TCP is designed to accommodate a layered protocol hierarchy that supports multiple network applications. TCP is relied upon to provide reliable communication services between pairs of processes in a host computer connected to different but interconnected computer communication networks. TCP assumes that it can obtain simple, possibly unreliable datagram services from lower-level protocols. In principle, TCP should be able to operate on top of a variety of communications systems, from hardwired connections to packet-switched or circuit-switched networks.
IP Protocol
IP refers to the Internet Protocol, the abbreviation of Internet Protocol, which is the network layer in the TCP/IP system protocol. The purpose of designing IP is to improve the scalability of the network: first, to solve Internet problems and realize the interconnection of large-scale and heterogeneous networks; second, to separate the coupling relationship between top-level network applications and underlying network technologies to facilitate the two. Develop independently. According to the end-to-end design principle, IP only provides a connectionless, unreliable, best-effort packet transmission service to the host.
IP mainly includes three aspects: IP addressing scheme, packet encapsulation format and packet forwarding rules.
#Forwarding rules of IP packets
The router forwards only based on the network address. When an IP data packet is forwarded via a router, if the target network is directly connected to the local router, the data packet is delivered directly to the target host, which is called direct delivery; otherwise, the router looks up the routing information through the routing table and transfers the data packet to Specified next-hop router, this is called indirect delivery. In indirect delivery, if the router has a route to the target network in the routing table, it will deliver the data packet to the next-hop router specified in the routing table; if there is no route but there is a default route in the routing table, it will deliver the data packet. Gives the specified default router; if neither is present, the packet is dropped and an error is reported.
IP fragmentation
An IP packet may need to go through multiple different Physical network. Since the data frames of various networks have a maximum transmission unit (MTU) limit, for example, the MTU of an Ethernet frame is 1500; therefore, when the router is forwarding IP packets, if the size of the data packet exceeds the maximum size of the egress link, When transmitting units, the IP packet will be broken down into many fragments that are small enough to be transmitted on the target link. These IP fragments re-encapsulate an IP packet for independent transmission and are reassembled when it reaches the destination host.
IP packet structure
An IP packet consists of header and data. The first 20 bytes of the header are required by all IP packets and are also called fixed headers. Following the fixed part of the header are some optional fields, the length of which is variable.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What are the services provided by tcp and ip?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 ip与mac绑定什么意思Mar 09, 2023 pm 04:44 PM
ip与mac绑定什么意思Mar 09, 2023 pm 04:44 PMip与mac绑定是指将特定的IP地址与特定的MAC地址关联起来,使得只有使用该MAC地址的设备才能够使用该IP地址进行网络通信。ip与mac绑定可以防止被绑定的主机的IP地址不被假冒,前提条件:1、MAC地址是唯一的,并且不可假冒;只能绑定与路由器直接相连的网络上的主机(也就是主机的网关在路由器上)。
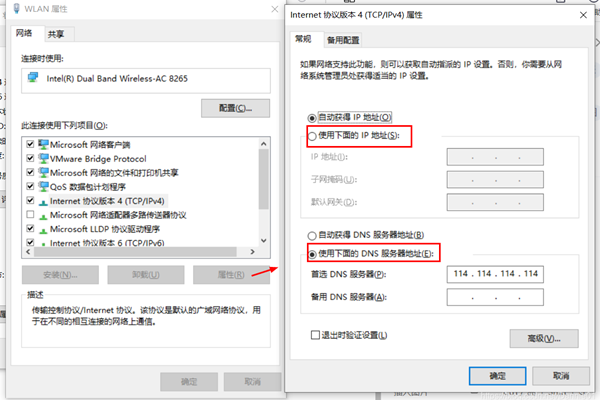 win10如何重置tcp/ip协议?windows10重置tcp/ip协议栈的方法Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
win10如何重置tcp/ip协议?windows10重置tcp/ip协议栈的方法Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AMwin10如何重置tcp/ip协议?其实方法很简单的,用户们可以直接的进入到命令提示符,然后按下ctrl+shift+enter的组合键来进行操作就可以了或者是直接的执行重置命令来进行设置,下面就让本站来为用户们来仔细的介绍一下windows10重置tcp/ip协议栈的方法吧。windows10重置tcp/ip协议栈的方法一、管理员权限1、我们使用快捷键win+R直接打开运行窗口,然后输入cmd并按住ctrl+shift+enter的组合键。2、或者我们可以直接在开始菜单中搜索命令提示符,右键点
 Java API 开发中使用 Netty4 进行 TCP 通信Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
Java API 开发中使用 Netty4 进行 TCP 通信Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PMTCP是计算机网络通信协议的一种,是一种面向连接的传输协议。在Java应用开发中,TCP通信被广泛应用于各种场景,比如客户端和服务器之间的数据传输、音视频实时传输等等。Netty4是一个高性能、高可扩展性、高性能的网络编程框架,能够优化服务器和客户端之间的数据交换过程,使其更加高效可靠。使用Netty4进行TCP通信的具体实现步骤如下:引入
 python中怎么使用TCP实现对话客户端和服务器May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
python中怎么使用TCP实现对话客户端和服务器May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PMTCP客户端一个使用TCP协议实现可连续对话的客户端示例代码:importsocket#客户端配置HOST='localhost'PORT=12345#创建TCP套接字并连接服务器client_socket=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM)client_socket.connect((HOST,PORT))whileTrue:#获取用户输入message=input("请输入要发送的消息:&
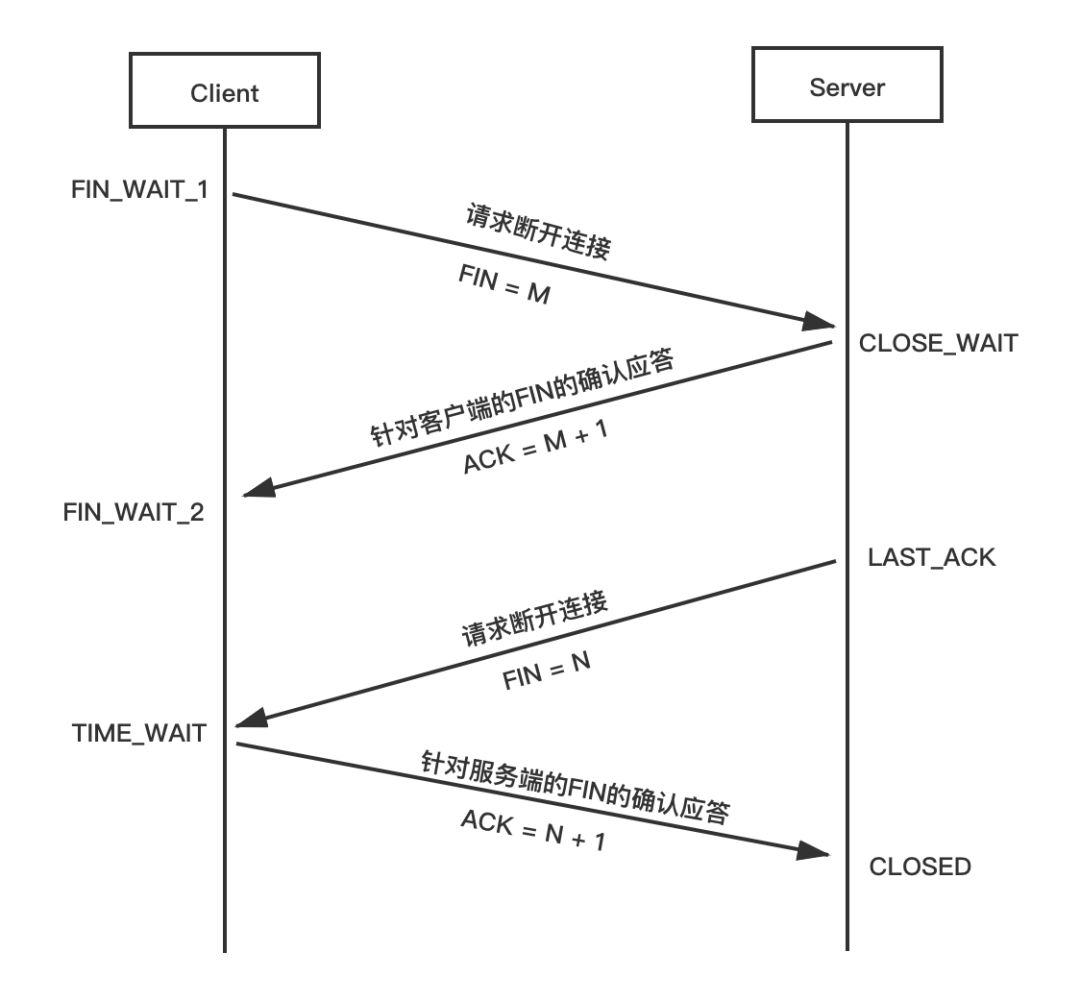
 活久见!TCP两次挥手,你见过吗?那四次握手呢?Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
活久见!TCP两次挥手,你见过吗?那四次握手呢?Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM那这里面提到的"面向连接",意味着需要 建立连接,使用连接,释放连接。建立连接是指我们熟知的TCP三次握手。而使用连接,则是通过一发送、一确认的形式,进行数据传输。还有就是释放连接,也就是我们常见的TCP四次挥手。
 Nginx对网段内ip的连接数限流如何配置May 12, 2023 am 11:07 AM
Nginx对网段内ip的连接数限流如何配置May 12, 2023 am 11:07 AMnginx中的所谓连接数限制,其实是tcp连接,也就是请求方通过三次握手后成功建立的连接状态。nginx一般为我们提供了ngx_http_limit_conn_module模块来提供限制连接功能。该模块可以根据定义的键来限制每个键值的连接数,如同一个ip来源的连接数。ngx_http_limit_conn_module指令解释syntax:limit_connzonenumber;default:—context:http,server,location该指令描述会话状态存储区域。键的状态中保存
 Linux SIGPIPE信号Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Linux SIGPIPE信号Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:00 PM在TCP通信双方中,为了描述方便,以下将通信双方用A和B代替。根据TCP协议规定,如果A关闭连接后B继续发送数据,B会收到A的RST响应。若B继续发送数据,系统会发出SIGPIPE信号告知连接已断开,停止发送。系统对SIGPIPE信号的默认处理行为是让B进程退出。操作系统对SIGPIPE信号的这种默认处理行为非常不友好,让我们来分析一下。TCP通信是全双工信道,相当于两条单工信道,连接两端各负责一条。当对端“关闭”时,虽然本意是关闭整个两条信道,但本端只是收到FIN包。根据TCP协议的规定,当一
 如何在Java中使用单个TCP连接发送多个文件?Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
如何在Java中使用单个TCP连接发送多个文件?Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM使用一个TCP连接发送多个文件为什么会有这篇博客?最近在看一些相关方面的东西,简单的使用一下Socket进行编程是没有的问题的,但是这样只是建立了一些基本概念。对于真正的问题,还是无能为力。当我需要进行文件的传输时,我发现我好像只是发送过去了数据(二进制数据),但是关于文件的一些信息却丢失了(文件的扩展名)。而且每次我只能使用一个Socket发送一个文件,没有办法做到连续发送文件(因为我是依靠关闭流来完成发送文件的,也就是说我其实是不知道文件的长度,所以只能以一个Socket连接代表一个文件)。

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool





