This article brings you relevant knowledge about Redis, which mainly organizes issues related to the basic use of Jedis, including basic Jedis operations, use of Jedis connection pools, etc., as follows Let's take a look, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: Redis video tutorial
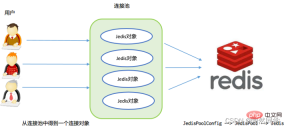
1. Introduction to Jedis
Jedis = Java Redis
Redis can not only be operated using commands, but now basically mainstream languages have API support, such as Java, C#, C, PHP, Node.js, Go, etc. There are some Java clients listed on the official website, including Jedis, Redisson, Jredis, JDBC-Redis, etc. Among them, Jedis and Redisson are officially recommended.
To use Jedis to operate redis, you need to import the jar package as follows:

2. Basic operations of Jedis
2.1 Commonly used APIs for Jedis objects
Note: Each method is the command name in redis, and the parameters of the method are the parameters of the command
Method |
Function |
|||||||||||||||||||||
new Jedis(host, port) |
##CreateJedis connection, parameters: host name, port number 6379 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
## set(key,value) |
Add a string key and value |
|||||||||||||||||||||
get(key) |
##Get the specified key Value
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Delete the specified key and value||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Add a |
hash type key-field-value | ##hget(key,field)|||||||||||||||||||||
Get its value through the |
hash key-field | lpush(key,values)|||||||||||||||||||||
|
##Add a # from the left | ##List type keys and elements##lpop(key) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Pop an element from the left |
##rpop(key) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
Pop an element from the right |
close() |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ##Close the connection
|
##JedisPoolConfig configuration class |
Function Description |
| JedisPoolConfig() |
Create a configuration object and just use the parameterless constructor |
void setMaxTotal() |
Set the maximum number of connections in the connection pool |
void setMaxWaitMillis() |
Set the maximum waiting time to get the connection object Jedis |
##JedisPool connection pool class |
##Description |
||||||
, Port number)Create connection pool | Parameter 1: The above configuration object, Parameter 2: Server name, Parameter 3: 6379|||||||
Get a Jedis connection object from the connection pool |
##void close() | ||||||
Connection pool closing method, usually does not close the connection pool |
3.3JedisPool的基本使用需求: 使用连接池优化jedis操作 开发步骤 创建连接池配置对象,设置最大连接数10,设置用户最大等待时间2000毫秒 通过配置对象做为参数,创建连接池对象 从连接池里面获取jedis连接对象,执行redis命令。 执行redis命令sadd写入set集合类型的数据:students=白骨精,孙悟空,猪八戒 执行redis命令smembers读取集合中的数据 输出读取的数据 关闭连接对象(通常连接池不关闭) 运行效果
执行代码 package com.itheima.jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 创建Jedis连接池
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1) 创建连接池配置对象,设置最大连接数10,设置用户最大等待时间2000毫秒
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxTotal(10);
config.setMaxWaitMillis(2000);
//2) 通过配置对象做为参数,创建连接池对象
JedisPool pool = new JedisPool(config, "localhost", 6379);
//3) 从连接池里面获取jedis连接对象,执行redis命令。
Jedis jedis = pool.getResource();
//4) 执行redis命令sadd写入set集合类型的数据:students=白骨精,孙悟空,猪八戒
jedis.sadd("students", "白骨精", "孙悟空", "猪八戒");
//5) 执行redis命令smembers读取集合中的数据
Set<string> students = jedis.smembers("students");
//6) 输出读取的数据
System.out.println(students);
//7) 关闭连接对象(通常连接池不关闭)
jedis.close();
pool.close();
}
}</string>
4.案例:编写jedis连接池工具类4.1相应API的学习java.util.ResourceBundle类是专门用于:读取类路径下Properties配置文件的类
案例:得到druid.properties中的url属性 package com.itheima.jedis;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* 读取属性文件
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//得到资源绑定对象
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("druid");
System.out.println(bundle.getString("url"));
}
}
4.2连接池工具类的实现需求: 实现连接池工具类,通过工具类得到Jedis连接对象,配置参数写在属性文件中 调用工具类,对Redis数据库进行操作 执行效果:
实现步骤: 在src目录下创建连接池的工具类: jedis.properties 创建静态成员变量JedisPool对象 在静态代码块中,读取src下的配置文件,得到ResourceBundle对象 得到上面的四个参数,其中host是字符串类型,其它参数要转成整数类型 实例化配置对象,实例化连接池对象 编写静态方法getJedis()返回Jedis对象 创建hash对象:键employee,添加字段名:name,值:NewBoy;字段名: salary,值:3000 使用hgetall读取hash对象输出 关闭jedis对象 jedis.properties配置文件 # 主机名 host=localhost # 端口号 port=6379 # 最大连接数 maxTotal=20 # 最长等待时间 maxWaitMillis=3000 JedisUtils.java package com.itheima.utils;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* 连接池工具类
*/
public class JedisUtils {
//创建一个连接对象
private static JedisPool pool;
static {
//创建连接池的配置对象
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
//设置最大连接数和最长等待时间
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jedis");
//得到配置文件中的属性值
String host = bundle.getString("host");
int port = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("port"));
int maxTotal = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("maxTotal"));
int maxWaitMillis = Integer.parseInt(bundle.getString("maxWaitMillis"));
//设置配置对象的参数
config.setMaxTotal(maxTotal);
config.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWaitMillis);
//创建连接池对象
pool = new JedisPool(config, host, port);
}
/**
* 得到redis连接对象
* @return
*/
public static Jedis getJedis() {
return pool.getResource();
}
}
使用工具类: package com.itheima.jedis;
import com.itheima.utils.JedisUtils;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 使用工具类
*/
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//从工具类中得到Jedis对象
Jedis jedis = JedisUtils.getJedis();
//创建hash对象:键employee,添加字段名:name,值:NewBoy;字段名: salary,值:3000
jedis.hset("employee", "name","NewBoy");
jedis.hset("employee", "salary","3000");
//使用hgetall读取hash对象输出
Map<string> employee = jedis.hgetAll("employee");
System.out.println(employee);
//关闭jedis对象
jedis.close();
}
}</string>
推荐学习:Redis视频教程 |
The above is the detailed content of Redis Learning: Basic Use of Jedis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Redis: Beyond SQL - The NoSQL PerspectiveMay 08, 2025 am 12:25 AM
Redis: Beyond SQL - The NoSQL PerspectiveMay 08, 2025 am 12:25 AMRedis goes beyond SQL databases because of its high performance and flexibility. 1) Redis achieves extremely fast read and write speed through memory storage. 2) It supports a variety of data structures, such as lists and collections, suitable for complex data processing. 3) Single-threaded model simplifies development, but high concurrency may become a bottleneck.
 Redis: A Comparison to Traditional Database ServersMay 07, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Redis: A Comparison to Traditional Database ServersMay 07, 2025 am 12:09 AMRedis is superior to traditional databases in high concurrency and low latency scenarios, but is not suitable for complex queries and transaction processing. 1.Redis uses memory storage, fast read and write speed, suitable for high concurrency and low latency requirements. 2. Traditional databases are based on disk, support complex queries and transaction processing, and have strong data consistency and persistence. 3. Redis is suitable as a supplement or substitute for traditional databases, but it needs to be selected according to specific business needs.
 Redis: Introduction to a Powerful In-Memory Data StoreMay 06, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Redis: Introduction to a Powerful In-Memory Data StoreMay 06, 2025 am 12:08 AMRedisisahigh-performancein-memorydatastructurestorethatexcelsinspeedandversatility.1)Itsupportsvariousdatastructureslikestrings,lists,andsets.2)Redisisanin-memorydatabasewithpersistenceoptions,ensuringfastperformanceanddatasafety.3)Itoffersatomicoper
 Is Redis Primarily a Database?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Is Redis Primarily a Database?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMRedis is primarily a database, but it is more than just a database. 1. As a database, Redis supports persistence and is suitable for high-performance needs. 2. As a cache, Redis improves application response speed. 3. As a message broker, Redis supports publish-subscribe mode, suitable for real-time communication.
 Redis: Database, Server, or Something Else?May 04, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Redis: Database, Server, or Something Else?May 04, 2025 am 12:08 AMRedisisamultifacetedtoolthatservesasadatabase,server,andmore.Itfunctionsasanin-memorydatastructurestore,supportsvariousdatastructures,andcanbeusedasacache,messagebroker,sessionstorage,andfordistributedlocking.
 Redis: Unveiling Its Purpose and Key ApplicationsMay 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Redis: Unveiling Its Purpose and Key ApplicationsMay 03, 2025 am 12:11 AMRedisisanopen-source,in-memorydatastructurestoreusedasadatabase,cache,andmessagebroker,excellinginspeedandversatility.Itiswidelyusedforcaching,real-timeanalytics,sessionmanagement,andleaderboardsduetoitssupportforvariousdatastructuresandfastdataacces
 Redis: A Guide to Key-Value Data StoresMay 02, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Redis: A Guide to Key-Value Data StoresMay 02, 2025 am 12:10 AMRedis is an open source memory data structure storage used as a database, cache and message broker, suitable for scenarios where fast response and high concurrency are required. 1.Redis uses memory to store data and provides microsecond read and write speed. 2. It supports a variety of data structures, such as strings, lists, collections, etc. 3. Redis realizes data persistence through RDB and AOF mechanisms. 4. Use single-threaded model and multiplexing technology to handle requests efficiently. 5. Performance optimization strategies include LRU algorithm and cluster mode.
 Redis: Caching, Session Management, and MoreMay 01, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Redis: Caching, Session Management, and MoreMay 01, 2025 am 12:03 AMRedis's functions mainly include cache, session management and other functions: 1) The cache function stores data through memory to improve reading speed, and is suitable for high-frequency access scenarios such as e-commerce websites; 2) The session management function shares session data in a distributed system and automatically cleans it through an expiration time mechanism; 3) Other functions such as publish-subscribe mode, distributed locks and counters, suitable for real-time message push and multi-threaded systems and other scenarios.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor