Home >Java >javaTutorial >One article to master the concept and use of Stream, a new feature of Java 8
One article to master the concept and use of Stream, a new feature of Java 8
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-06-23 12:03:182088browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about java, which mainly organizes the concepts and usage of Stream, including the concept of Stream, acquisition of Stream, and Stream Let’s take a look at the common methods of streaming and so on. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended study: "java video tutorial"
When we talk about streams, everyone will easily think of IO Stream, I think that Stream stream is also an IO stream, but it is not. Stream is a brand new concept introduced in Java 8 to solve some of the shortcomings of existing collection class libraries. Since we want to learn Stream flow, we have to temporarily forget the traditional concept of IO flow. Today we will explain the Stream flow in detail from the concept, characteristics, functions, usage, etc. of the Stream flow, so let me read on!
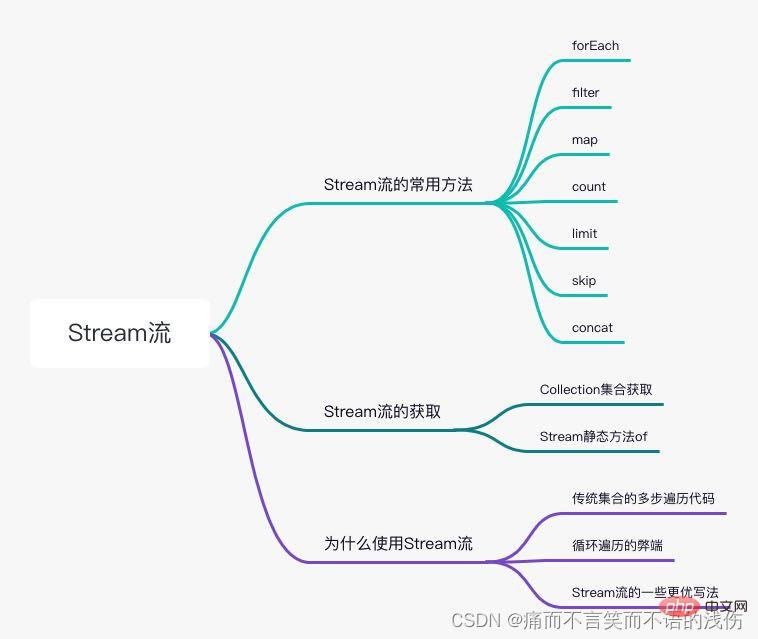
The concept of Stream flow
Why should we use Stream flow?
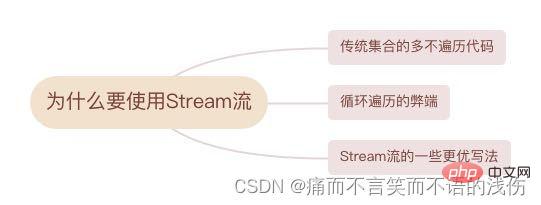
The idea of Stream flow is similar to the assembly line of a production workshop. When we need to operate multiple elements (especially multi-step operations), considering performance and convenience, we should first put together a "model" step-driven plan, and then execute it according to the plan.
Stream(Stream) is a queue of elements from the data source
The elements are Objects of a specific type, forming a queue. Stream in lava does not store elements, but calculates them on demand.
Data source The source of the stream. Can be a collection, array, etc.
Two basic characteristics of Stream:
·Pipelining:Intermediate operations will return the stream object itself. In this way, multiple operations can be connected into a pipeline, just like fluent style. Doing so can optimize operations such as laziness and short-circuiting.
Internal iteration: In the past, collection traversal was explicitly iterated outside the collection through iterator or enhanced for. This is called external iteration. Stream provides an internal iteration method, and the stream can directly call the traversal method.
When using a stream, it usually includes three basic steps: Obtain a data source (source)→Data conversion: Perform an operation to obtain the desired result. Each time the original Stream object is converted, the original Stream object is converted. Change, returning a new Stream object (which can have multiple conversions), which allows operations on it to be arranged like a chain and become a pipeline.
Acquisition of Stream stream
There are two common ways to obtain a stream:
1. Obtain through Collection collection
2.Stream interface The static method of get
Get through the Collection collection
All Collection collections can get the stream through the stream default method
//把集合转换为stream流 //list集合 List<string>list=new ArrayList(); Stream<string>stream=list.stream(); //set集合 Set<string>set=new HashSet(); Stream<string>stream2=set.stream(); //map集合(map集合需要间接的转换) Map<string>map=new HashMap(); //方法一:获取键,存储到一个set集合中 Set<string>keySet=map.keySet(); Stream<string>stream3=keySet.stream(); //方法二:获取值,存储到一个collection集合中 Collection<string>values=map.values(); Stream<string>stream4=values.stream(); //方法三:获取键值对,,键与值的映射关系,entrySet() Set<map.entry>>entries=map.entrySet(); Stream<map.entry>>stream5=entries.stream();</map.entry></map.entry></string></string></string></string></string></string></string></string></string>
2 The static method of of the .Stream interface gets
The static method of of the Stream interface can get the stream corresponding to the array.
The parameter is a variable parameter, then we can pass an array
//把数组转换成Stream流 Stream<integer>stream6=Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5); //可变参数可以传递数组 Integer[]arr={1,2,3,4,5}; Stream<integer>stream7=Stream.of(arr); String[]arr2={"a","bb","ccc"}; Stream<string>stream8=Stream.of(arr2);</string></integer></integer>
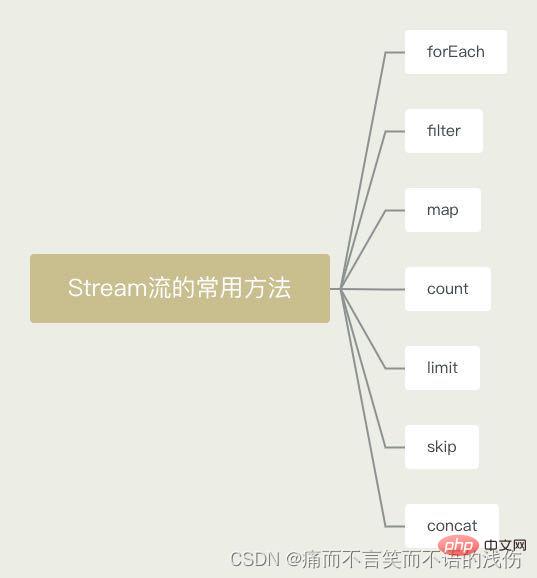
Common methods of stream stream
The common methods of stream are divided into two categories:
Delayed method: The return value type is still the method of the Stream interface itself, so chained calls are supported. (Except for the final method, all other methods are delayed methods.)
Terminator method: The return value type is no longer a method of the Stream interface's own type, so it no longer supports methods like StringBuilder Chain calls.
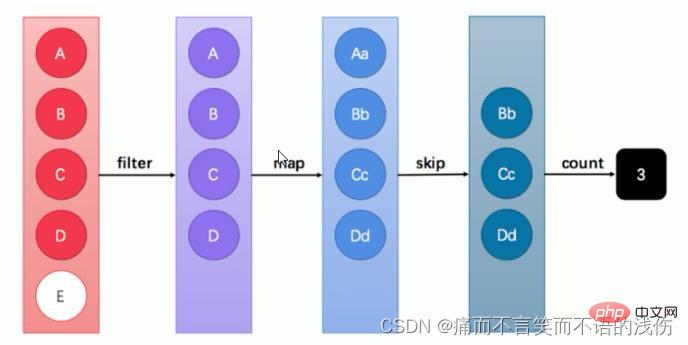
The above are some common methods of stream. Let’s learn how to use these methods in turn.
forEach traversal method
This method accepts a Consumer interface function and will hand over each stream element to the function for processing. The Consumer interface is a consumer functional interface that can pass lambda expressions and consume data.
foeeach method is used to traverse the data in the stream. It is a termination method. After traversing, other methods in the stream cannot be used.
Basic usage
public class Demo03Stream_forEach { public static void main(String[] args) { Stream<string>stream=Stream.of("张三","李四","王五","赵六","小明","小胖"); /*stream.forEach((String name)->{ System.out.println(name); });*/ stream.forEach(name->System.out.println(name)); } }</string>
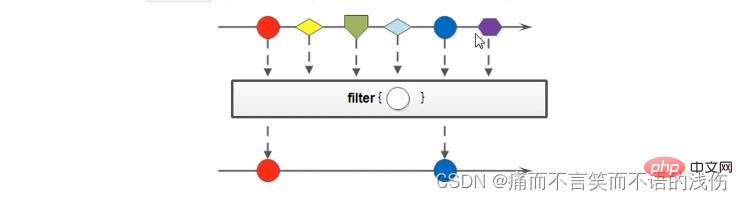
filter过滤方法
用于对Stream流中的数进行过滤。filter方法的参数Predicatehi一个函数式接口,所以可以传递lambda表达式,对数据进行过滤。可以通过filter方法将一个转换过滤为下一个流,如下图:
上面这个图把一些不也一样的元素,用filter方法进行过滤,然后成为新的流。
基本使用
public class Demo04Stream_filter { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个Stream流 Stream<string>stream=Stream .of("张三丰","赵敏","张无忌","周芷若","张三","狮王","张大牛"); //对Stream流中的元素进行过滤。只要张的人 Stream<string>stream2=stream.filter((String name)->{return name.startsWith("张");}); //遍历Stream流 stream2.forEach(name->System.out.println(name)); } }</string></string>
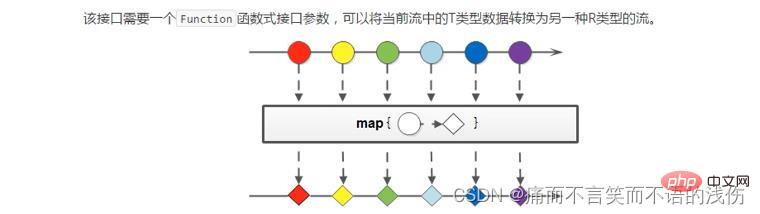
map映射方法(转换)
如果需要将流中的元素转换到另一个流中,可以使用map方法。该接口需要一个Funtion函数式接口参数,可以将当前流中的T类型数据类型转换为另一种R类型的数据流,如下图:
上面的图将不同元素的数据转换成用一种类型的元素。
基本使用
public class Demo05Stream_map { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取一个String类型的Stream流 Stream<string>stream=Stream.of("1","2","3","4","5"); //使用map方法,把字符串类型的整数,转换(映射)为integer类型的整数 Stream<integer>stream2=stream.map((String s)->{ return Integer.parseInt(s); }); //遍历Stream流 stream2.forEach(i->System.out.println(i)); } }</integer></string>
count统计元素个数方法
用于统计Stream流中的元素个数,count方法是一个终结方法,返回值是一个Long类型的整数。所以不能再继续调用Stream流中的其他方法了
基本使用
public class Demo06Stream_count { public static void main(String[] args) { //获取一个Stream流 ArrayList<integer>list=new ArrayList<integer>(); //添加元素 list.add(1); list.add(2); list.add(3); list.add(4); list.add(5); list.add(6); list.add(7); Stream<integer>stream=list.stream(); //统计stream流中的元素个数 long count=stream.count(); //打印输出 System.out.println(count);//7 } }</integer></integer></integer>
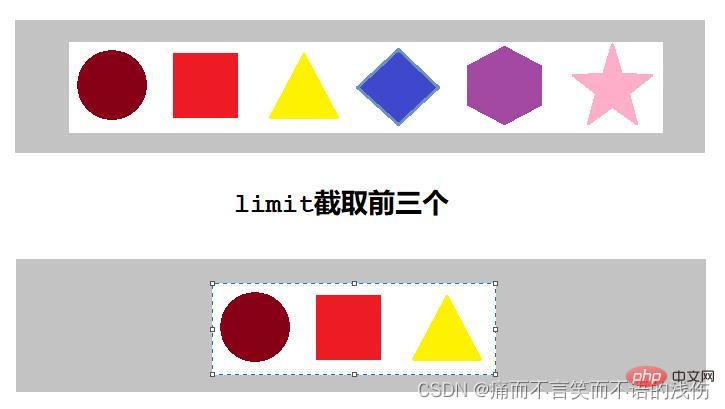
limit截取流元素方法
Limit方法可以对流进行截取,只取用前n个。参数是一个long型,如果集合当前长度大于参数则进行截取,否则不进行操作。limit方法是一个延迟方法,只是对流中的元素进行截取,返回一个新的流,使用可以继续调用stream流中的其他方法。
基本使用
public class Demo07Stream_limit { public static void main(String[] args) { show02(); } private static void show02() { //创建一个String类型的数组 String[]arr={"喜羊羊","美羊羊","沸羊羊","懒羊羊","灰太狼","红太狼"}; //集合获取一个Stream流 Stream<string>stream=Stream.of(arr); //用limit方法截取前6个元素 Stream<string>stream2=stream.limit(3); //遍历Stream2流 stream2.forEach(i->System.out.println(i)); } }</string></string>
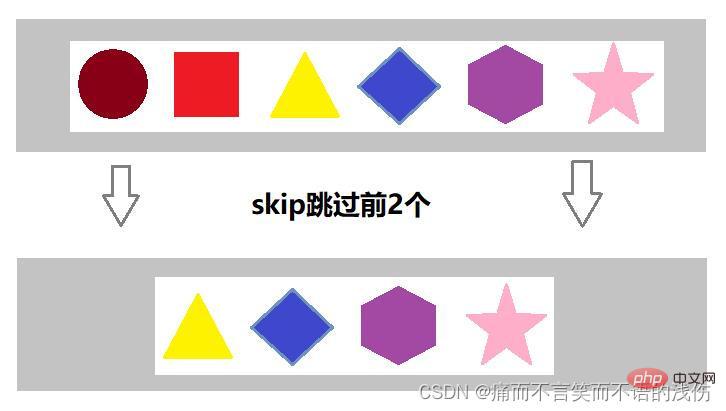
skip跳过元素方法
如果希望跳过前几个元素,可以使用skip方法获取一个截取之后的新流,如果流的当前长度大于n,则跳过前n个;否则将会得到一个长度为0的流。
基本使用
public class Demo08Stream_skip { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个String类型的数组 String[]arr={"喜羊羊","美羊羊","懒羊羊","慢羊羊","红太狼","灰太狼","小灰灰","沸羊羊","软绵绵","武大狼"}; //获取Stream流 Stream<string>stream=Stream.of(arr); //使用skip方法截取后面的元素 Stream<string>stream2=stream.skip(5); //遍历stream2流 stream2.forEach(i->System.out.println(i)); } }</string></string>
concat:合并方法
用于把流组合到一块。如果有两个流,希望合并成为一个流,就可以使用concat方法
基本使用
public class Demo09Stream_concat { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一个Stream流 Stream<string>stream=Stream.of("张三丰","张翠山","赵敏","周芷若","张无忌"); //创建一个String类型的数组 String[]arr={"喜羊羊","美羊羊","懒羊羊","慢羊羊","红太狼","灰太狼","小灰灰","沸羊羊","软绵绵","武大狼"}; //获取Stream流 Stream<string>stream2=Stream.of(arr); //使用常用方法concat方法合并流 Stream<string>stream3=Stream.concat(stream, stream2); //遍历Stream3流 stream3.forEach(i->System.out.println(i)); } }</string></string></string>
Stream流的练习
最后,我们通过下面的练习来巩固一下上面所学的内容。
现在有两个ArrayList集合存储队伍当中的多个成员姓名,
要求使用传统的for循环(或增强for循环)依次进行以下若干操作步骤:
1.第一个队伍只要名字为3个字的成员姓名:存储到一个新集合中。
2.第一个队伍筛选之后只要前3个人;存储到一个新集合中。
3.第二个队伍只要姓张的成员姓名;存储到一个新集合中。
4.第二个队伍筛选之后不要前2个人;存储到一个新集合中。
5.将两个队伍合并为一个队伍;存储到一个新集台中。
6.根据姓名创建Person对象:存储到一个新集合中,
7.打印整个队伍的Person对象信息。
示例:
第一支队伍:迪丽热巴、宋远桥、苏星河、石破天、石中玉、老子、庄子、洪七公
第二支队伍:古娜力扎、张无忌、赵丽颖、张三丰、尼古拉斯赵四、张天爱、张二狗
首先创建Person对象类
public class Person {
private String name;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + "]";
}
}
然后再根据习题要求用Stream流进行过滤
1.第一个队伍只要名字为3个字的成员姓名:存储到一个新集合中。
2.第一个队伍筛选之后只要前3个人;存储到一个新集合中。
// 第一支队伍
// 创建集合
ArrayList<string> one = new ArrayList();
// 添加元素
one.add("迪丽热巴");
one.add("宋远桥");
one.add("苏星河");
one.add("石破天");
one.add("石中玉");
one.add("老子");
one.add("庄子");
one.add("洪七公");
//1.第一个队伍只要名字为3个字的成员姓名:存储到一个新集合中。
//2.第一个队伍筛选之后只要前3个人;存储到一个新集合中。
Stream<string>oneStream=one.stream().filter(name->name.length()==3).limit(3);</string></string>
3.第二个队伍只要姓张的成员姓名;存储到一个新集合中。
4.第二个队伍筛选之后不要前2个人;存储到一个新集合中。
// 第二支队伍
// 创建集合
ArrayList<string> tow = new ArrayList();
// 添加元素
tow.add("古娜力扎");
tow.add("张无忌");
tow.add("赵丽颖");
tow.add("张三丰");
tow.add("尼古拉斯赵四");
tow.add("张天爱");
tow.add("张二狗");
//3.第二个队伍只要姓张的成员姓名;存储到一个新集合中。
//4.第二个队伍筛选之后不要前2个人;存储到一个新集合中。
Stream<string>towStream=tow.stream().filter(name->name.startsWith("张")).skip(2);</string></string>
5.将两个队伍合并为一个队伍;存储到一个新集台中。
6.根据姓名创建Person对象:存储到一个新集合中,
7.打印整个队伍的Person对象信息。
//5.将两个队伍合并为一个队伍;存储到一个新集台中。 //6.根据姓名创建Person对象:存储到一个新集合中, //7.打印整个队伍的Person对象信息。 Stream.concat(oneStream,towStream).map(name->new Person(name)).forEach(p->System.out.println(p));
最后运行结果

总结
最后,今天的内容就学到这里啦。主要熟悉和明白Stream流的一个思想概念、会使用Stream流的获取、和熟练掌握Stream流的一些常用方法。
推荐学习:《java视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of One article to master the concept and use of Stream, a new feature of Java 8. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Related articles
See more- Detailed explanation of JavaScript weak mapping and weak collection knowledge
- Learn the basics of JavaScript string objects in one article
- What are property values of javascript objects
- What is inheritance in javascript
- Detailed explanation of the basics of destructuring assignment of JavaScript objects and arrays