Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >A brief analysis of some APIs of the path module in node
A brief analysis of some APIs of the path module in node
- 青灯夜游forward
- 2022-05-26 13:00:122129browse
This article will introduce you to the path path module of node, introduce some APIs of the path built-in module, and also prepare a case for practice. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

1. First introduction to path module
path module is officially provided by Node.js and is used for processing Path to module . It provides a series of methods and attributes to meet users' needs for path processing.
2.path module API
2.1 path.join()
path.join() method, used to combine multiple path fragments Spliced into a complete path string
The syntax format is

...paths(string) The sequence of path fragments is you All path series that need to be spliced
It should be noted that the returned value is string
//引入path模块
const path=require("path")
//书写要拼接的路径
const pathStr=path.join('/a','/b/c','../','./d','e')
console.log(pathStr)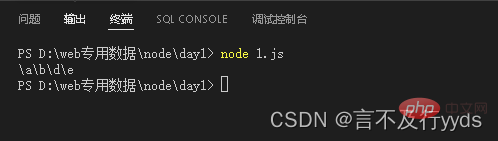
##2.2 path. basename()
Use the path.basename() method to get the last part of the path. This method is often used to get the file name in theSyntax formatpath

- path required parameter, a string representing a path
- Optional parameter, representing the file extension The name
- represents the last part of the path
const path=require("path") const fpath='./a/b/c/index.html' var fullname=path.basename(fpath) console.log(fullname) //获取指定后缀的文件名 const namepath=path.basename(fpath,'.html') console.log(namepath)
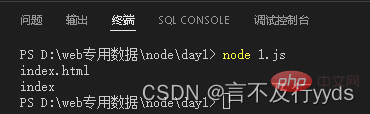
path.extname() is used to get the file extension in the path
The format is

- path is a required parameter, a string representing a path
- Return: Returns the obtained extension string
-
const path=require("path") const fpath='./a/b/c/d/index.html' const ftext =path.extname(fpath) console.log(ftext)
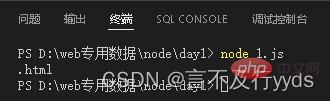
Split the provided code (one file has html, css, and js at the same time)
Split into three files: index.html index.css index.js and store them in a prepared fileSource code:3.1 Implementation stepshttp://127.0. 0.1:5500/node/day1/static/index.html
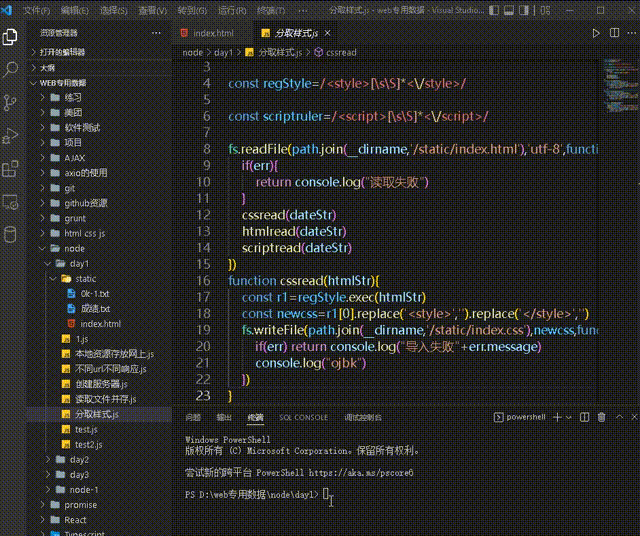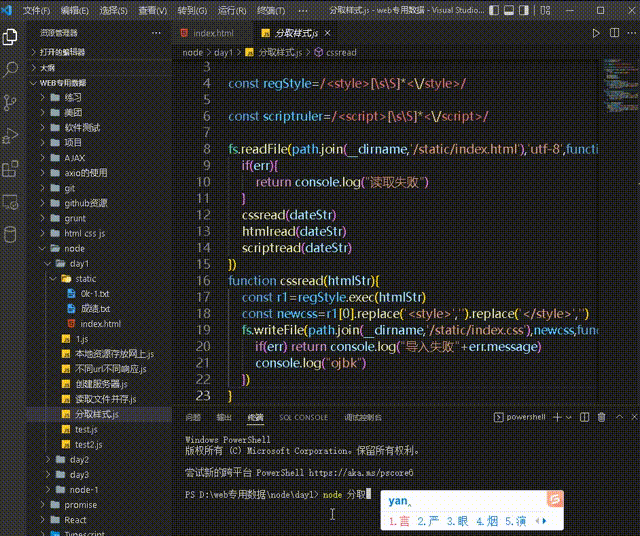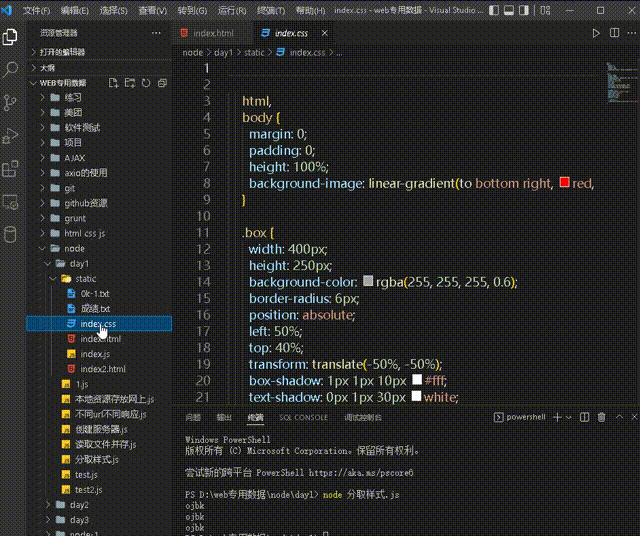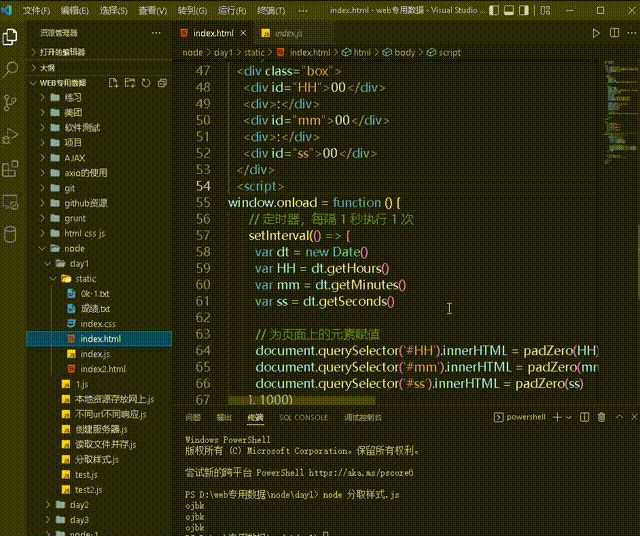
1. Create two regular expressions, respectively Used to match 3.1.1 Step 1 - Import the required modules and create regular expressions
const path=require('path')
const fs=require('fs')
const regStyle=/<style>[\s\S]*<\/style>/
const scriptruler=/<script>[\s\S]*<\/script>/
//需要读取的文件
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,'/static/index.html'),'utf-8',function(err,dateStr){
if(err){
return console.log("读取失败")
}
resolveCSS(dateStr)
resolveHTML(dateStr)
resolveJS (dateStr)
})
3.1.2 Custom resolveCSS resolveHTML resolveJS method
function resolveCSS(htmlStr){
const r1=regStyle.exec(htmlStr)
const newcss=r1[0].replace('<style>','').replace('</style>','')
//将匹配的css写入到指定的index.css文件中
fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname,'/static/index.css'),newcss,function(err){
if(err) return console.log("导入失败"+err.message)
console.log("ojbk")
})
}
function resolveJS(htmlStr){
const r2=scriptruler.exec(htmlStr)
const newcss=r2[0].replace('<script>','').replace('</script>','')
//将匹配的css写入到指定的index.js文件中
fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname,'/static/index.js'),newcss,function(err){
if(err) return console.log("导入失败"+err.message)
console.log("ojbk")
})
}
function resolveHTML(htmlStr){
const newhtml=htmlStr
.replace(regStyle,'<link rel="stylesheet" href="./index.css">')
.replace(scriptruler,'<script src="./index.js"></script>')
//将匹配的css写入到指定的index.html文件中
fs.writeFile(path.join(__dirname,'/static/index2.html'),newhtml,function(err){
if(err) return console.log("导入失败"+err.message)
console.log("ojbk")
})
}The final result is to separate the styles in the specified file
But the initial index.html contains all the code, and thenthe styles are split. The storage location is still the original, so the final index.html code remains unchanged
 For more node-related knowledge, please visit:
For more node-related knowledge, please visit:
The above is the detailed content of A brief analysis of some APIs of the path module in node. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

