Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings
A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-05-25 11:59:052877browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces the relevant knowledge about strings, which mainly introduces the commonly used basic methods as well as special characters and A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings internal representation methods. Let’s take a look at the content below, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

[Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end]
No matter what programming language In , strings are important data types. Follow me to learn moreJavaScript string knowledge!
Preface
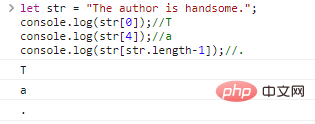
A string is a string composed of characters. If you have studied C, Java, you should know that the characters themselves can also independently become a type. However, JavaScript does not have a single character type, only a string of length 1. The string of
JavaScript uses a fixed UTF-16 encoding. No matter what encoding we use when writing the program, it will not be affected.
Writing
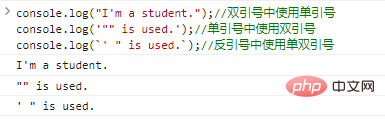
There are three ways to write strings: single quotes, double quotes, and backticks.
let single = 'abcdefg';//单引号let double = "asdfghj";//双引号let backti = `zxcvbnm`;//反引号
Single and double quotation marks have the same status, we do not make a distinction.
String formatting
Backticks allow us to use ${...}elegantly format strings instead of using strings Addition operation.
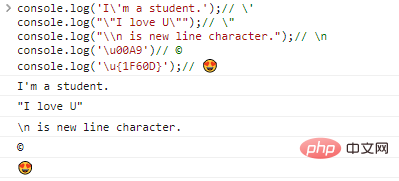
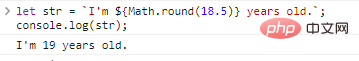
let str = `I'm ${Math.round(18.5)} years old.`;console.log(str);
Code execution result:
Multi-line string
Backticks can also allow strings to span lines , very useful when we write multi-line strings.
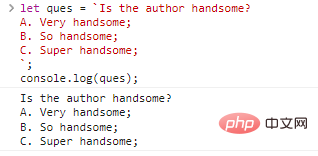
let ques = `Is the author handsome? A. Very handsome; B. So handsome; C. Super handsome;`;console.log(ques);
Code execution result:
Doesn’t it seem like there is nothing? However, this cannot be achieved using single and double quotes. If you want to get the same result, you can write:
let ques = 'Is the author handsome?\nA. Very handsome;\nB. So handsome;\nC. Super handsome;';console.log(ques);
The above code contains a special character \n, which is used in our programming process The most common special characters.
Special characters
Characters\n, also known as "newline character", supports single and double quotes to output multi-line strings. When the engine outputs a string, if it encounters \n, it will continue to output on another line, thereby realizing a multi-line string.
Although \n looks like two characters, it only occupies one character position. This is because \ is the escape character in the string. , characters modified by escape characters become special characters.
Special character list
| Special character | Description | |
|---|---|---|
\n |
Newline character, used to start a new line of output text. | |
\r |
Carriage return character, move the cursor to the beginning of the line, use ## in Windows system #\r\n represents a line break, which means that the cursor needs to go to the beginning of the line first, and then to the next line before it can change to a new line. For other systems, just use \n.
|
|
\' \" | Single and double quotation marks, mainly because single and double quotation marks are special characters, we want When using single and double characters in a string, escape them. ||
\\ | Backslash, also because \ is a special character. If we just want to output \ itself, we must escape it.
|
|
\b \ f \v | Backspace, page feed, vertical tabs - are no longer used. ||
\xXX | is a hexadecimal Unicode character encoded as XX, for example: \x7A means z ( The hexadecimal Unicode encoding of z is 7A).
|
|
\uXXXX
| is a hexadecimal Unicode character encoded as XXXX, for example: \u00A9 means ©.
|
|
\u{X...X} (1-6 hexadecimal characters)
|
UTF-32The Unicode symbol encoded as X...X.
|
| 方法 | 描述 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
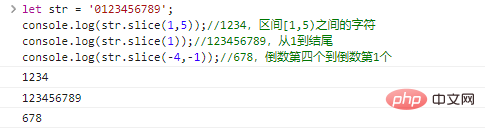
.slice(start,end) |
[start,end) |
可负 |
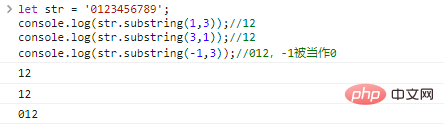
.substring(start,end) |
[start,end) |
负值为0
|
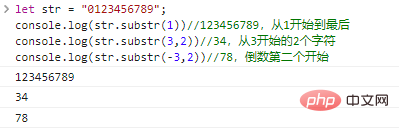
.substr(start,len) |
从start开始长为len的子串 |
可负 |
方法多了自然就选择困难了,这里建议记住
.A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings就可以了,相比于其他两种更灵活。
.A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings、A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings
我们在前文中已经提及过字符串的比较,字符串按照字典序进行排序,每个字符背后都是一个编码,ASCII编码就是一个重要的参考。
例如:
console.log('a'>'Z');//true
字符之间的比较,本质上是代表字符的编码之间的比较。JavaScript使用UTF-16编码字符串,每个字符都是一个16为的代码,想要知道比较的本质,就需要使用.codePointAt(idx)获得字符的编码:
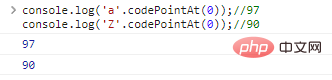
console.log('a'.codePointAt(0));//97console.log('Z'.codePointAt(0));//90
代码执行结果:
使用String.fromCodePoint(code)可以把编码转为字符:
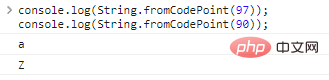
console.log(String.fromCodePoint(97));console.log(String.fromCodePoint(90));
代码执行结果如下:
这个过程可以用转义符\u实现,如下:
console.log('\u005a');//Z,005a是90的16进制写法console.log('\u0061');//a,0061是97的16进制写法
下面我们探索一下编码为[65,220]区间的字符:
let str = '';for(let i = 65; i<p>代码执行部分结果如下:</p><p><img src="/static/imghwm/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/067/0f4e2a78ef52090d845bd32f6b72d01c-17.png" class="lazy" alt="A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings"></p><p>上图并没有展示所有的结果,快去试试吧。</p><h2>.localeCompare()</h2><p>基于国际化标准<code>ECMA-402</code>,<code>JavaScript</code>已经实现了一个特殊的方法(<code>.localeCompare()</code>)比较各种字符串,采用<code>str1.localeCompare(str2)</code>的方式:</p><ol>
<li>如果<code>str1 ,返回负数;</code>
</li>
<li>如果<code>str1 > str2</code>,返回正数;</li>
<li>如果<code>str1 == str2</code>,返回0;</li>
</ol><p>举个例子:</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">console.log("abc".localeCompare('def'));//-1为什么不直接使用比较运算符呢?
这是因为英文字符有一些特殊的写法,例如,á是a的变体:
console.log('á' <p>虽然也是<code>a</code>,但是比<code>z</code>还要大!!</p><p>此时就需要使用<code>.localeCompare()</code>方法:</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">console.log('á'.localeCompare('z'));//-1常用方法
-
str.trim()去除字符串前后空白字符,str.trimStart()、str.trimEnd()删除开头、结尾的空格;let str = " 999 ";console.log(str.trim());//999
-
str.repeat(n)重复n次字符串;let str = '6';console.log(str.repeat(3));//666
-
str.replace(substr,newstr)替换第一个子串,str.replaceAll()用于替换所有子串;let str = '9+9';console.log(str.replace('9','6'));//6+9console.log(str.replaceAll('9','6'));//6+6
还有很多其他方法,我们可以访问手册获取更多知识。
进阶内容
生僻字、A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings、特殊符号
JavaScript使用UTF-16编码字符串,也就是使用两个字节(16位)表示一个字符,但是16位数据只能表示65536个字符,对于常见字符自然不在话下,但是对于生僻字(中文的)、A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings、罕见数学符号等就力不从心了。
这种时候就需要扩展,使用更长的位数(32位)表示特殊字符,例如:
console.log(''.length);//2console.log('?'.length);//2代码执行结果:
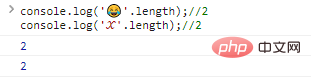
这么做的结果是,我们无法使用常规的方法处理它们,如果我们单个输出其中的每个字节,会发生什么呢?
console.log(''[0]);console.log(''[1]);代码执行结果:
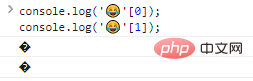
可以看到,单个输出字节是不能识别的。
好在A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings和.A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings两个方法是可以处理这种情况的,这是因为二者是最近才加入的。在旧版本的JavaScript中,只能使用String.fromCharCode()和.charCodeAt()两个方法转换编码和字符,但是他们不适用于特殊字符的情况。
我们可以通过判断一个字符的编码范围,判断它是否是一个特殊字符,从而处理特殊字符。如果一个字符的代码在0xd800~0xdbff之间,那么他是32位字符的第一部分,它的第二部分应该在0xdc00~0xdfff。
举个例子:
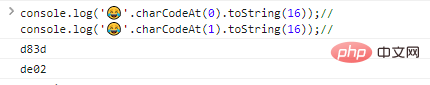
console.log(''.charCodeAt(0).toString(16));//d83
dconsole.log('?'.charCodeAt(1).toString(16));//de02代码执行结果:
规范化
在英文中,存在很多基于字母的变体,例如:字母 a 可以是 àáâäãåā 的基本字符。这些变体符号并没有全部存储在UTF-16编码中,因为变化组合太多了。
为了支持所有的变体组合,同样使用多个Unicode字符表示单个变体字符,在编程过程中,我们可以使用基本字符加上“装饰符号”的方式表达特殊字符:
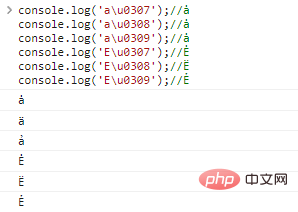
console.log('a\u0307');//ȧ
console.log('a\u0308');//ȧ
console.log('a\u0309');//ȧ
console.log('E\u0307');//Ė
console.log('E\u0308');//Ë
console.log('E\u0309');//Ẻ代码执行结果:
一个基础字母还可以有多个装饰,例如:
console.log('E\u0307\u0323');//Ẹ̇
console.log('E\u0323\u0307');//Ẹ̇代码执行结果:
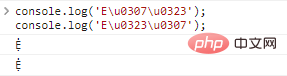
这里存在一个问题,在多个装饰的情况下,装饰的排序不同,实际上展示的字符是一样的。
如果我们直接比较这两种表示形式,却会得到错误的结果:
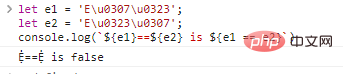
let e1 = 'E\u0307\u0323';
let e2 = 'E\u0323\u0307';
console.log(`${e1}==${e2} is ${e1 == e2}`)代码执行结果:
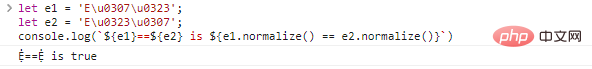
为了解决这种情况,有一个**Unicode规范化算法,可以将字符串转为通用**格式,由str.normalize()实现:
<span style="max-width:90%" microsoft yahei sans gb helvetica neue tahoma arial sans-serif>let e1 = 'E\u0307\u0323';<br>let e2 = 'E\u0323\u0307';<br>console.log(`${e1}==${e2} is ${e1.normalize() == e2.normalize()}`)</span><br>代码执行结果:
【相关推荐:javascript视频教程、web前端】
The above is the detailed content of A detailed introduction to common basic methods of JavaScript strings. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!