Summarize Oracle view knowledge points
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-05-24 13:51:392356browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about Oracle, which mainly introduces related issues about views. A view is a database object, which is obtained from one or more data tables or views. Let’s take a look at the virtual table exported from . I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Oracle Video Tutorial"
- View is a database object that is a virtual table derived from one or more data tables or views.
The- data corresponding to the view is not actually stored in the view, but is stored in the referenced data table.
The structure and data of the view are the results of querying the data table.
#According to the conditions given when creating the view, the view can be part of a data table or a union of multiple base tables.
- It stores the definition of the
- query statement to be retrieved for use when referencing the view.
Advantages of using views:
- Simplified data operations: Views can Simplify how users work with data.
- Focus on specific data: Unnecessary data or sensitive data may not appear in the view.
View provides a simple and effective security mechanism that can customize different users' access rights to data.- Provide backward compatibility: Views enable users to create backward-compatible interfaces for tables when their schema changes.
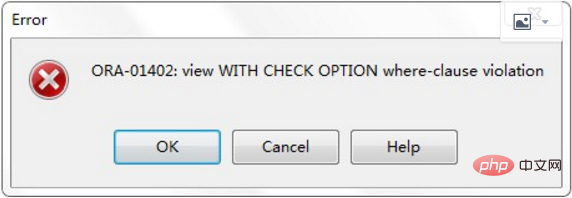
1. Create a modified viewCREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE] VIEW 'view_name'AS 'sub_query'[WITH CHECK OPTION]-- 只读[WITH READ ONLY]
| Description | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| If the created view already exists, | Oracle will automatically rebuild the view |
||||||||||
| This view will be automatically created regardless of whether the base table exists | Oracle |
||||||||||
| A complete | SELECT statement, in which an alias can be defined | ##WITH CHECK OPTION||||||||||
| WITH READ ONLY | |||||||||||
| DML | operations can be performed on this view |
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SNAPTIME$$ | 用于表示刷新时间。 |
| DMLTYPE$$ | 用于表示 DML 操作类型(I 表示 INSERT,D 表示 DELETE,U 表示 UPDATE)。 |
| OLD_NEW$$ | 用于表示这个值是新值还是旧值(N(EW)表示新值,O(LD)表示旧值,U 表示 UPDATE 操作)。 |
| CHANGE_VECTOR$$ | 表示修改矢量,用来表示被修改的是哪个或哪几个字段(此列是 RAW 类型)。其实 Oracle 采用的方式就是用每个 BIT 位去映射一个列。插入操作显示为: FE,删除显示为:OO,更新操作则根据更新字段的位置而显示不同的值。 |
- 当手动刷新物化视图后,物化视图日志被清空,物化视图更新。
begin
DBMS_MVIEW.refresh('MV_ADDRESS4', 'C');end;
推荐教程:《Oracle视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Summarize Oracle view knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
Statement:
This article is reproduced at:csdn.net. If there is any infringement, please contact admin@php.cn delete
Previous article:How to delete constraints in oracleNext article:How to delete constraints in oracle