Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >MySQL summarizes the MVCC principle of InnoDB
MySQL summarizes the MVCC principle of InnoDB
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-04-18 18:25:042203browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces issues related to the MVCC principle of InnoDB. MVCC is multi-version concurrency control, mainly to improve the concurrency of the database. Performance, let’s take a look at it, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
MVCC full name is Multi-Version Concurrency Control, which is multi-version concurrency control, mainly for Improve the concurrency performance of the database. When a read or write request occurs for the same row of data, it will be locked and blocked. But MVCC uses a better way to handle read-write requests, so that no locking occurs when a read-write request conflict occurs. This read refers to the snapshot read, not the current read. The current read is a locking operation and is a pessimistic lock. So how does it achieve reading and writing without locking? What do snapshot reading and current reading mean? We will all learn this later.
MySQL can avoid phantom read problems to a large extent under the REPEATABLE READ isolation level. How does MySQL do this?
Version chain
We know that for tables using the InnoDB storage engine, its clustered index records contain two necessary hidden columns (row_id It is not necessary. The row_id column will not be included when the table we create has a primary key or a non-NULL UNIQUE key):
trx_id: Each time a transaction clusters a certain When the index record is modified, the transaction ID of the transaction will be assigned to the trx_id hidden column.
roll_pointer: Every time a clustered index record is changed, the old version will be written to the undo log, and then this hidden column is equivalent to a pointer, which can Use it to find the information before the record was modified.
In order to illustrate this problem, we create a demonstration table:
CREATE TABLE `teacher` ( `number` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `domain` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`number`)) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
Then insert a piece of data into this table:
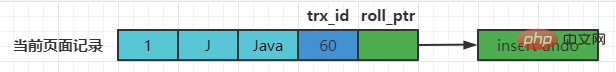
mysql> insert into teacher values(1, 'J', 'Java');Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
The current data This is it:
mysql> select * from teacher; +--------+------+--------+ | number | name | domain | +--------+------+--------+ | 1 | J | Java | +--------+------+--------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
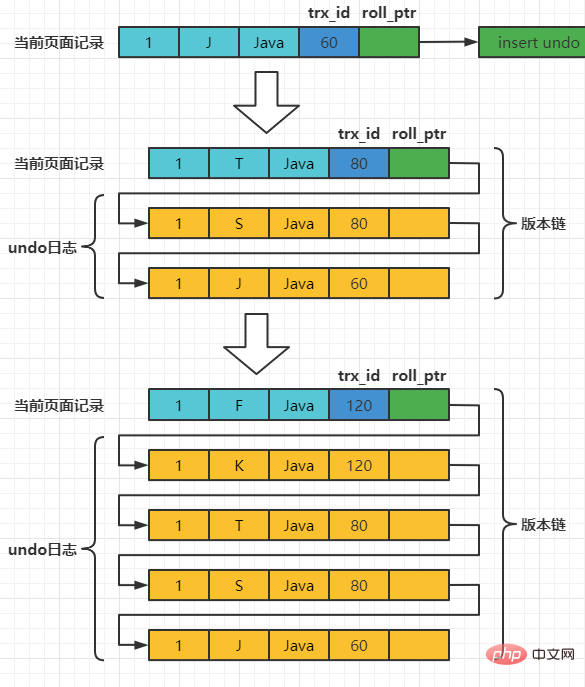
Assume that the transaction ID of inserting the record is 60, then the diagram of the record at this moment is as follows:
Assume that the next two A transaction with transaction IDs of 80 and 120 performs an UPDATE operation on this record. The operation process is as follows:
| Trx80 | Trx120 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| begin | ||||||||||||||
| ##commit | ||||||||||||||
|
每次对记录进行改动,都会记录一条undo日志,每条undo日志也都有一个roll_pointer属性(INSERT操作对应的undo日志没有该属性,因为该记录并没有更早的版本),可以将这些undo日志都连起来,串成一个链表,所以现在的情况就像下图一样:
对该记录每次更新后,都会将旧值放到一条undo日志中,就算是该记录的一个旧版本,随着更新次数的增多,所有的版本都会被roll_pointer属性连接成一个链表,我们把这个链表称之为版本链,版本链的头节点就是当前记录最新的值。另外,每个版本中还包含生成该版本时对应的事务id。于是可以利用这个记录的版本链来控制并发事务访问相同记录的行为,那么这种机制就被称之为多版本并发控制(Mulit-Version Concurrency Control MVCC)。 ReadView对于使用READ UNCOMMITTED隔离级别的事务来说,由于可以读到未提交事务修改过的记录,所以直接读取记录的最新版本就好了。 对于使用SERIALIZABLE隔离级别的事务来说,InnoDB使用加锁的方式来访问记录。 对于使用READ COMMITTED和REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的事务来说,都必须保证读到已经提交了的事务修改过的记录,也就是说假如另一个事务已经修改了记录但是尚未提交,是不能直接读取最新版本的记录的,核心问题就是:READ COMMITTED和REPEATABLE READ隔离级别在不可重复读和幻读上的区别,这两种隔离级别关键是需要判断一下版本链中的哪个版本是当前事务可见的。 为此,InnoDB提出了一个ReadView的概念,这个ReadView中主要包含4个比较重要的内容:
有了这个ReadView,这样在访问某条记录时,只需要按照下边的步骤判断记录的某个版本是否可见:
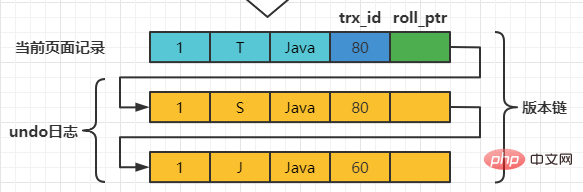
在MySQL中,READ COMMITTED和REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的的一个非常大的区别就是它们生成ReadView的时机不同。 我们还是以表teacher为例,假设现在表teacher中只有一条由事务id为60的事务插入的一条记录,接下来看一下READ COMMITTED和REPEATABLE READ所谓的生成ReadView的时机不同到底不同在哪里。 READ COMMITTED每次读取数据前都生成一个ReadView假设现在系统里有两个事务id分别为80、120的事务在执行: # Transaction 80 set session transaction isolation level read committed; begin update teacher set name='S' where number=1; update teacher set name='T' where number=1; 此刻,表teacher中number为1的记录得到的版本链表如下所示:
假设现在有一个使用READ COMMITTED隔离级别的事务开始执行: set session transaction isolation level read committed; # 使用READ COMMITTED隔离级别的事务 begin; # SELECE1:Transaction 80、120未提交 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE number = 1; # 得到的列name的值为'J' 这个SELECE1的执行过程如下:
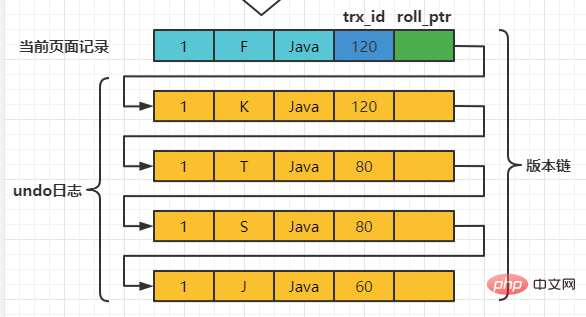
之后,我们把事务id为80的事务提交一下,然后再到事务id为120的事务中更新一下表teacher 中number为1的记录: set session transaction isolation level read committed; # Transaction 120 begin update teacher set name='K' where number=1; update teacher set name='F' where number=1; 此刻,表teacher 中number为1的记录的版本链就长这样:
然后再到刚才使用READ COMMITTED隔离级别的事务中继续查找这个number 为1的记录,如下: # 使用READ COMMITTED隔离级别的事务 begin; # SELECE1:Transaction 80、120未提交 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE number = 1; # 得到的列name的值为'J' # SELECE2:Transaction 80提交、120未提交 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE number = 1; # 得到的列name的值为'T' 这个SELECE2 的执行过程如下:
以此类推,如果之后事务id为120的记录也提交了,再次在使用READCOMMITTED隔离级别的事务中查询表teacher中number值为1的记录时,得到的结果就是’F’了,具体流程我们就不分析了。 总结一下就是:使用READCOMMITTED隔离级别的事务在每次查询开始时都会生成一个独立的ReadView。 REPEATABLE READ —— 在第一次读取数据时生成一个ReadView对于使用REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的事务来说,只会在第一次执行查询语句时生成一个ReadView,之后的查询就不会重复生成了。我们还是用例子看一下是什么效果。 假设现在系统里有两个事务id分别为80、120的事务在执行: # Transaction 80 begin update teacher set name='S' where number=1; update teacher set name='T' where number=1; 此刻,表teacher中number为1的记录得到的版本链表如下所示:
假设现在有一个使用REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的事务开始执行: # 使用REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的事务 begin; # SELECE1:Transaction 80、120未提交 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE number = 1; # 得到的列name的值为'J' 这个SELECE1的执行过程如下(与READ COMMITTED的过程一致):
之后,我们把事务id为80的事务提交一下,然后再到事务id为120的事务中更新一下表teacher 中number为1的记录: # Transaction 80 begin update teacher set name='K' where number=1; update teacher set name='F' where number=1; 此刻,表teacher 中number为1的记录的版本链就长这样:
然后再到刚才使用REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的事务中继续查找这个number为1的记录,如下: # 使用REPEATABLE READ隔离级别的事务 begin; # SELECE1:Transaction 80、120未提交 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE number = 1; # 得到的列name的值为'J' # SELECE2:Transaction 80提交、120未提交 SELECT * FROM teacher WHERE number = 1; # 得到的列name的值为'J' 这个SELECE2的执行过程如下:
That is to say, the results obtained by the two SELECT queries are repeated, and the recorded column values are all '''J''''. This is the meaning of repeatable reading. If we submit the record with transaction ID 120 later, and then continue to search for the record with number 1 in the transaction that just used REPEATABLE READ isolation level, the result will still be 'J', specifically You can analyze the execution process yourself. Phantom reading phenomenon and phantom reading solution under MVCCWe already know that MVCC can solve the non-repeatable reading problem under the REPEATABLE READ isolation level, so phantom reading Woolen cloth? How is MVCC solved? Phantom reading is when a transaction reads records multiple times according to the same conditions. The last read reads a record that has not been read before, and this record comes from a new record added by another transaction. We can think about it, transaction T1 under the REPEATABLE READ isolation level first reads multiple records based on a certain search condition, then transaction T2 inserts a record that meets the corresponding search condition and submits it, and then transaction T1 Then execute the query based on the same search criteria. What will be the result? According to the comparison rules in ReadView: Regardless of whether transaction T2 is opened before transaction T1, transaction T1 cannot see the submission of T2. Please analyze it yourself according to the version chain, ReadView and visibility judgment rules introduced above. However, MVCC in InnoDB under the REPEATABLE READ isolation level can avoid phantom reading to a large extent, rather than completely prohibiting phantom reading. What's going on? Let’s look at the following situation:
|
The above is the detailed content of MySQL summarizes the MVCC principle of InnoDB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!