 Web Front-end
Web Front-end JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial Angular learning using Tooltip as an example to understand custom instructions
Angular learning using Tooltip as an example to understand custom instructionsAngular learning using Tooltip as an example to understand custom instructions
This article will help you continue learning angular, taking Tooltip as an example to learn about custom instructions, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

In the previous article, we have given an overview of Angular related content. In the part of custom instructions, we have been able to write them, but in actual scenarios, we still need standardized management.
Angular is an upgraded version of Angular.js. [Related tutorial recommendations: "angular tutorial"]
So, in this article, we will use Tooltip to explain the content of custom instructions.
Online renderings, as follows:
Directory structure
is above Based on the code project implemented in an article, execute the command line:
# 进入 directives 文件夹 $ cd directives # 创建 tooltip 文件夹 $ mkdir tooltip # 进入 tooltip 文件夹 $ cd tooltip # 创建 tooltip 组件 $ ng generate component tooltip # 创建 tooltip 指令 $ ng generate directive tooltip
After executing the above command line, you will get the file directory structure of app/directive/tooltip as follows:
tooltip ├── tooltip // tooltip 组件 │ ├── user-list.component.html // 页面骨架 │ ├── user-list.component.scss // 页面独有样式 │ ├── user-list.component.spec.ts // 测试文件 │ └── user-list.component.ts // javascript 文件 ├── tooltip.directive.spec.ts // 测试文件 └── tooltip.directive.ts // 指令文件
Well, here I put the components at the same level as tooltip, mainly to facilitate management. Of course, this varies from person to person, you can put it in the public components components folder.
Write tooltip component
In the html file, there are:
<div class="caret"></div>
<div class="tooltip-content">{{data.content}}</div>In the style file .scss, there are:
$black: #000000;
$white: #ffffff;
$caret-size: 6px;
$tooltip-bg: transparentize($black, 0.25); // transparentize 是 sass 的语法
$grid-gutter-width: 30px;
$body-bg-color: $white;
$app-anim-time: 200ms;
$app-anim-curve: ease-out;
$std-border-radius: 5px;
$zindex-max: 100;
// :host 伪类选择器,给组件元素本身设置样式
:host {
position: fixed;
padding: $grid-gutter-width/3 $grid-gutter-width/2;
background-color: $tooltip-bg;
color: $body-bg-color;
opacity: 0;
transition: all $app-anim-time $app-anim-curve;
text-align: center;
border-radius: $std-border-radius;
z-index: $zindex-max;
}
.caret { // 脱字符
width: 0;
height: 0;
border-left: 6px solid transparent;
border-right: 6px solid transparent;
border-bottom: 6px solid $tooltip-bg;
position: absolute;
top: -$caret-size;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -$caret-size/2;
border-bottom-color: $tooltip-bg;
}Well~,
cssis a magical thing, I will arrange an article to explain it latersassRelated content...
Then, in the javascript file tooltip.component.ts the content is as follows:
import {
Component,
ElementRef, // 元素指向
HostBinding,
OnDestroy,
OnInit
} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-tooltip', // 标识符,表明我这个组件叫做啥,这里是 app-tooltip
templateUrl: './tooltip.component.html', // 本组件的骨架
styleUrls: ['./tooltip.component.scss'] // 本组件的私有样式
})
export class TooltipComponent implements OnInit {
public data: any; // 在 directive 上赋值
private displayTimeOut:any;
// 组件本身 host 绑定相关的装饰器
@HostBinding('style.top') hostStyleTop!: string;
@HostBinding('style.left') hostStyleLeft!: string;
@HostBinding('style.opacity') hostStyleOpacity!: string;
constructor(
private elementRef: ElementRef
) { }
ngOnInit(): void {
this.hostStyleTop = this.data.elementPosition.bottom + 'px';
if(this.displayTimeOut) {
clearTimeout(this.displayTimeOut)
}
this.displayTimeOut = setTimeout((_: any) => {
// 这里计算 tooltip 距离左侧的距离,这里计算公式是:tooltip.left + 目标元素的.width - (tooltip.width/2)
this.hostStyleLeft = this.data.elementPosition.left + this.data.element.clientWidth / 2 - this.elementRef.nativeElement.clientWidth / 2 + 'px'
this.hostStyleOpacity = '1';
this.hostStyleTop = this.data.elementPosition.bottom + 10 + 'px'
}, 500)
}
// 组件销毁
ngOnDestroy() {
// 组件销毁后,清除定时器,防止内存泄露
if(this.displayTimeOut) {
clearTimeout(this.displayTimeOut)
}
}
}Writing tooltip instructions
This is the focus of this article. I will mark the specific instructions on the code~
Related filestooltip.directive.ts The content is as follows:
import {
ApplicationRef, // 全局性调用检测
ComponentFactoryResolver, // 创建组件对象
ComponentRef, // 组件实例的关联和指引,指向 ComponentFactory 创建的元素
Directive, ElementRef,
EmbeddedViewRef, // EmbeddedViewRef 继承于 ViewRef,用于表示模板元素中定义的 UI 元素。
HostListener, // DOM 事件监听
Injector, // 依赖注入
Input
} from '@angular/core';
import { TooltipComponent } from './tooltip/tooltip.component';
@Directive({
selector: '[appTooltip]'
})
export class TooltipDirective {
@Input("appTooltip") appTooltip!: string;
private componentRef!: ComponentRef<TooltipComponent>;
// 获取目标元素的相关位置,比如 left, right, top, bottom
get elementPosition() {
return this.elementRef.nativeElement.getBoundingClientRect();
}
constructor(
protected elementRef: ElementRef,
protected appRef: ApplicationRef,
protected componentFactoryResolver: ComponentFactoryResolver,
protected injector: Injector
) { }
// 创建 tooltip
protected createTooltip() {
this.componentRef = this.componentFactoryResolver
.resolveComponentFactory(TooltipComponent) // 绑定 tooltip 组件
.create(this.injector);
this.componentRef.instance.data = { // 绑定 data 数据
content: this.appTooltip,
element: this.elementRef.nativeElement,
elementPosition: this.elementPosition
}
this.appRef.attachView(this.componentRef.hostView); // 添加视图
const domElem = (this.componentRef.hostView as EmbeddedViewRef<any>).rootNodes[0] as HTMLElement;
document.body.appendChild(domElem);
}
// 删除 tooltip
protected destroyTooltip() {
if(this.componentRef) {
this.appRef.detachView(this.componentRef.hostView); // 移除视图
this.componentRef.destroy();
}
}
// 监听鼠标移入
@HostListener('mouseover')
OnEnter() {
this.createTooltip();
}
// 监听鼠标移出
@HostListener('mouseout')
OnOut() {
this.destroyTooltip();
}
}At this point, 99% functions have been completed. Now we can call it on the page. Call
on the page
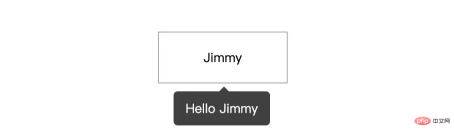
We add the following content on user-list.component.html:
<p style="margin-top: 100px;">
<!-- [appTooltip]="'Hello Jimmy'" 是重点 -->
<span
[appTooltip]="'Hello Jimmy'"
style="margin-left: 200px; width: 160px; text-align: center; padding: 20px 0; display: inline-block; border: 1px solid #999;"
>Jimmy</span>
</p>TooltipDirective We have declared this directive on app.module.ts, we can call it directly. The current effect is as follows:

The tooltip we implemented is a bottom-centered display, which is what we usually use the framework, such as angular ant design# The bottom attribute of tooltip in ##. For other attributes, if readers are interested, they can be expanded.
Introduction to Programming! !
The above is the detailed content of Angular learning using Tooltip as an example to understand custom instructions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AM
The Relationship Between JavaScript, C , and BrowsersMay 01, 2025 am 12:06 AMIntroduction I know you may find it strange, what exactly does JavaScript, C and browser have to do? They seem to be unrelated, but in fact, they play a very important role in modern web development. Today we will discuss the close connection between these three. Through this article, you will learn how JavaScript runs in the browser, the role of C in the browser engine, and how they work together to drive rendering and interaction of web pages. We all know the relationship between JavaScript and browser. JavaScript is the core language of front-end development. It runs directly in the browser, making web pages vivid and interesting. Have you ever wondered why JavaScr
 Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AM
Node.js Streams with TypeScriptApr 30, 2025 am 08:22 AMNode.js excels at efficient I/O, largely thanks to streams. Streams process data incrementally, avoiding memory overload—ideal for large files, network tasks, and real-time applications. Combining streams with TypeScript's type safety creates a powe
 Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Performance and Efficiency ConsiderationsApr 30, 2025 am 12:08 AMThe differences in performance and efficiency between Python and JavaScript are mainly reflected in: 1) As an interpreted language, Python runs slowly but has high development efficiency and is suitable for rapid prototype development; 2) JavaScript is limited to single thread in the browser, but multi-threading and asynchronous I/O can be used to improve performance in Node.js, and both have advantages in actual projects.
 The Origins of JavaScript: Exploring Its Implementation LanguageApr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AM
The Origins of JavaScript: Exploring Its Implementation LanguageApr 29, 2025 am 12:51 AMJavaScript originated in 1995 and was created by Brandon Ike, and realized the language into C. 1.C language provides high performance and system-level programming capabilities for JavaScript. 2. JavaScript's memory management and performance optimization rely on C language. 3. The cross-platform feature of C language helps JavaScript run efficiently on different operating systems.
 Behind the Scenes: What Language Powers JavaScript?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Behind the Scenes: What Language Powers JavaScript?Apr 28, 2025 am 12:01 AMJavaScript runs in browsers and Node.js environments and relies on the JavaScript engine to parse and execute code. 1) Generate abstract syntax tree (AST) in the parsing stage; 2) convert AST into bytecode or machine code in the compilation stage; 3) execute the compiled code in the execution stage.
 The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and PredictionsApr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AM
The Future of Python and JavaScript: Trends and PredictionsApr 27, 2025 am 12:21 AMThe future trends of Python and JavaScript include: 1. Python will consolidate its position in the fields of scientific computing and AI, 2. JavaScript will promote the development of web technology, 3. Cross-platform development will become a hot topic, and 4. Performance optimization will be the focus. Both will continue to expand application scenarios in their respective fields and make more breakthroughs in performance.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and ToolsApr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Development Environments and ToolsApr 26, 2025 am 12:09 AMBoth Python and JavaScript's choices in development environments are important. 1) Python's development environment includes PyCharm, JupyterNotebook and Anaconda, which are suitable for data science and rapid prototyping. 2) The development environment of JavaScript includes Node.js, VSCode and Webpack, which are suitable for front-end and back-end development. Choosing the right tools according to project needs can improve development efficiency and project success rate.
 Is JavaScript Written in C? Examining the EvidenceApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Is JavaScript Written in C? Examining the EvidenceApr 25, 2025 am 12:15 AMYes, the engine core of JavaScript is written in C. 1) The C language provides efficient performance and underlying control, which is suitable for the development of JavaScript engine. 2) Taking the V8 engine as an example, its core is written in C, combining the efficiency and object-oriented characteristics of C. 3) The working principle of the JavaScript engine includes parsing, compiling and execution, and the C language plays a key role in these processes.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools

MantisBT
Mantis is an easy-to-deploy web-based defect tracking tool designed to aid in product defect tracking. It requires PHP, MySQL and a web server. Check out our demo and hosting services.

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment





