Home >Web Front-end >JS Tutorial >Detailed explanation of HTML element operations with JavaScript examples
Detailed explanation of HTML element operations with JavaScript examples
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-03-30 18:25:122711browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces issues related to the operation of html elements, including how to obtain the operated elements, the content of the operated elements, and the Properties, styles, etc., I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Related recommendations: javascript tutorial
1. Get the elements of the operation
Methods and properties of the document object
The document object provides some methods for finding elements. These methods can be used to obtain the operated element based on the element's id, name, class attributes and tag name.
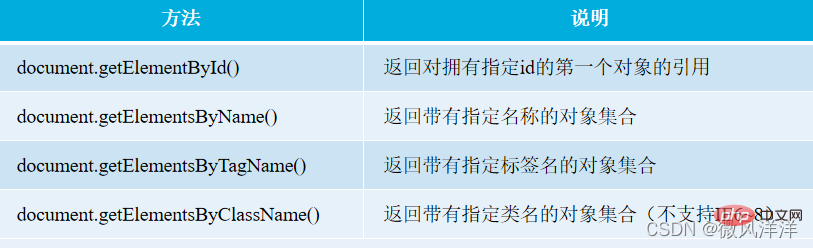
Summary
Except the document.getElementById() method returns the element with the specified id, all other methods return is a collection that meets the requirements. To get one of the objects, you can get it by subscript, which starts from 0 by default.
The document object provides some properties that can be used to obtain elements in the document. For example, get all form tags, image tags, etc.
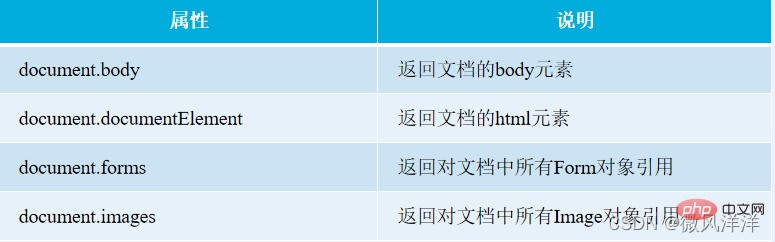
- The body attribute of the document object is used to return the body element.
- The documentElement property of the document object is used to return the root node html element of the HTML document.
Note
The operation elements obtained through the methods of the document object and the properties of the document object represent the same object. For example, document.getElementsByTagName(‘body’)[0] is identical to document.body.

HTML5’s new document object method
In HTML5, the element that is more convenient for obtaining operations is the document object. Two new methods have been added, namely querySelector() and querySelectorAll().
- querySelector() method is used to return a reference to the first object in the document that matches the specified element or CSS selector.
- querySelectorAll() method is used to return a collection of objects in the document that match the specified element or CSS selector.
Since these two methods are used in the same way, the following uses the document.querySelector() method as an example.
Methods and properties of the Element object
In DOM operations, the element object also provides methods for obtaining specified elements within an element. The two commonly used methods are getElementsByClassName( ) and getElementsByTagName(). They are used in the same way as the methods of the same name on the document object.

#In addition, the element object also provides the children attribute to obtain the child elements of the specified element. For example, get the child elements of ul in the above example.

- #The children attribute of the element object also returns a collection of objects. If you want to get one of the objects, you also need to get it by subscripting, starting from 0 by default.
- In addition, the document object also has the children attribute, and its first child element is usually an html element.
HTMLCollection object
- HTMLCollection object: return by calling the getElementsByClassName() method, getElementsByTagName() method, children attribute, etc. through the document object or Element object set of objects.
- NodeList object: When the document object calls the getElementsByName() method, the NodeList object is returned in Chrome and FireFox browsers, and the HTMLCollection object is returned in IE11.
The difference between HTMLCollection and NodeList objects:
- HTMLCollection object is used for element operations.
- NodeList object is used for node operations.
Tip: For the collection returned by the getElementsByClassName() method, getElementsByTagName() method and the children attribute, the id and name can be automatically converted into an attribute.

2. Element content
In JavaScript, if you want to operate on the obtained element content, you can use the DOM provided Property and method implementation.
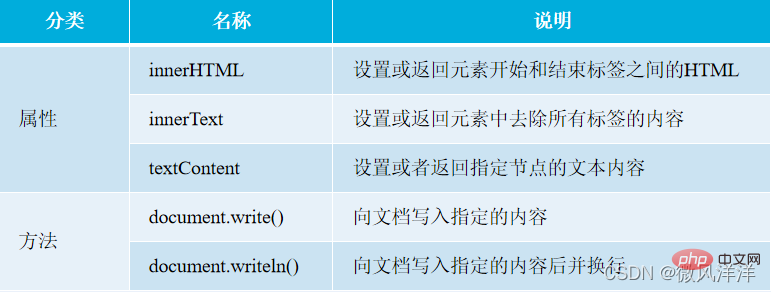
- The properties belong to the Element object and the methods belong to the document object.
- innerHTML will maintain the written format and tag style when used.
- innerText is plain text content with all formatting and tags removed.
- The textContent attribute will retain the text format after removing the tag.
For example

##Code implementation
nbsp;html> <meta> <title>元素内容操作</title> <p> The first paragraph... </p><p> The second paragraph... <a>third</a> </p> <script> var box = document.getElementById('box'); console.log(box.innerHTML); console.log(box.innerText); console.log(box.textContent); </script>
Note
The innerText attribute may cause browser compatibility issues when used. Therefore, it is recommended to use innerHTML to get or set the text content of elements as much as possible during development. At the same time, there are certain differences between the innerHTML attribute and the document.write() method in setting content. The former acts on the specified element, while the latter reconstructs the entire HTML document page. Therefore, readers should choose the appropriate implementation method according to actual needs during development[Case] Changing the box size
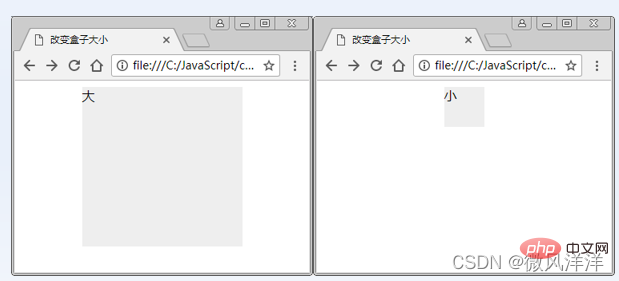 Code implementation ideas
Code implementation ideas
① Write HTML and set the size of p.
② Change the box size based on the number of user clicks. ③ When the number of clicks is an odd number, the boxes become larger, and when the number of clicks is an even number, the boxes become smaller.Code implementation
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<style>
.box{width:50px;height:50px;background:#eee;margin:0 auto;}
</style>
<p></p>
<script>
var box = document.getElementById('box');
var i = 0; // 保存用户单击盒子的次数
box.onclick = function() { // 处理盒子的单击事件
++i;
if (i % 2) { // 单击次数为奇数,变大
this.style.width = '200px';
this.style.height = '200px';
this.innerHTML = '大';
} else { // 单击次数为偶数,变小
this.style.width = '50px';
this.style.height = '50px';
this.innerHTML = '小';
}
};
</script>
3. Element attributesIn the DOM, in order to facilitate JavaScript to obtain, modify and traverse the specified The related attributes of HTML elements provide attributes and methods for operations.
Use the attributes attribute to get all the attributes of an HTML element, as well as the length of all attributes. 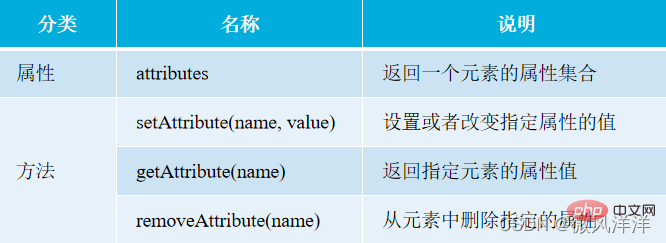
For example
##Code implementation
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>元素属性操作</title>
<style>
.gray{background: #CCC;}
#thick{font-weight: bolder;}
</style>
<p>test word.</p>
<script>
// 获取p元素
var ele = document.getElementsByTagName('p')[0];
// ① 输出当前ele的属性个数
console.log('未操作前属性个数:' + ele.attributes.length);
// ② 为ele添加属性,并查看属性个数
ele.setAttribute('align', 'center');
ele.setAttribute('title', '测试文字');
ele.setAttribute('class', 'gray');
ele.setAttribute('id', 'thick');
ele.setAttribute('style', 'font-size:24px;border:1px solid green;');
console.log('添加属性后的属性个数:' + ele.attributes.length);
// ③ 获取ele的style属性值
console.log('获取style属性值:' + ele.getAttribute('style'));
// ④ 删除ele的style属性,并查看剩余属性情况
ele.removeAttribute('style');
console.log('查看所有属性:');
for (var i = 0; i < ele.attributes.length; ++i) {
console.log(ele.attributes[i]);
}
</script>
4. Element style
Review: Modify the style through the operation of element attributes. Element style syntax: style.Attribute name.
Requirements: The horizontal dash "-" in the CSS style name needs to be removed, and the second English initial letter must be capitalized.
Example: The background-color that sets the background color needs to be changed to backgroundColor in the style attribute operation.
Note
The float style in CSS conflicts with the reserved words of JavaScript. Different browsers have different solutions. For example, IE9-11, Chrome, and FireFox can use "float" and "cssFloat", Safari browser uses "float", and IE6~8 use "styleFloat".
Question: An element can have multiple class selectors. How to operate the selector list during development?Original solution: Use the className attribute of the element object to obtain the result. The obtained result is a character type, and then process the string according to the actual situation. The method provided by HTML5: the class selector list of the new classList (read-only) element.
Example: If the class value of a p element is "box header navlist title", how to delete the header?HTML5 solution: p element object.classList.toggle("header");
For example
Code implementation
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>classList的使用</title>
<style>
.bg{background:#ccc;}
.strong{font-size:24px;color:red;}
.smooth{height:30px;width:120px;border-radius:10px;}
</style>
- PHP
- JavaScript
- C++
- Java
In addition, the classList attribute also provides many other related operation methods and properties.
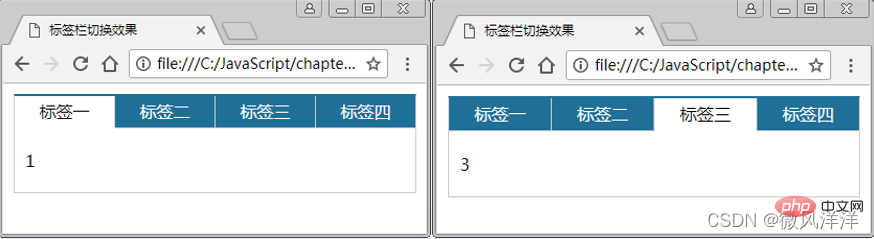
5. [Case] Tab bar switching effect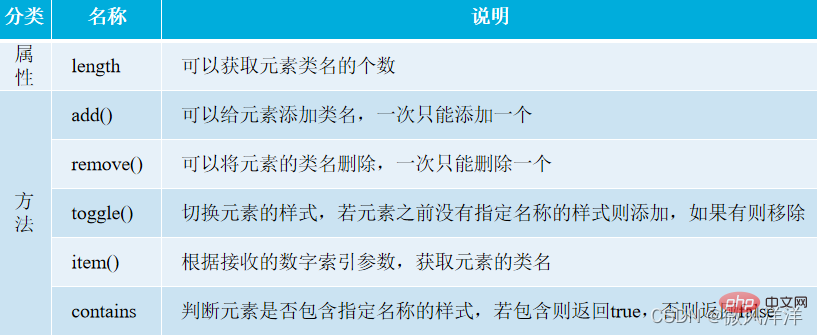
 ##Code implementation ideas
##Code implementation ideas
:
① Write HTML to realize the structure and style design of the tab bar, where class equals current to indicate the currently displayed tab, and the default is the a label.
- ② Get all tags and the display content corresponding to the tags.
- ③ Traverse and add a mouse-over event for each label. In the event handler, traverse all the display content corresponding to the label. When the mouse slides over the label, pass the classList The add() method adds current, otherwise it is removed through the remove() method.
Code
nbsp;html>
<meta>
<title>标签栏切换效果</title>
<style>
.tab-box{width:383px;margin:10px;border:1px solid #ccc;border-top:2px solid #206F96;}
.tab-head{height:31px;}
.tab-head-p{width:95px;height:30px;float:left;border-bottom:1px solid #ccc;border-right:1px solid #ccc;background:#206F96;line-height:30px;text-align:center;cursor:pointer;color:#fff;}
.tab-head .current{background:#fff;border-bottom:1px solid #fff;color:#000;}
.tab-head-r{border-right:0;}
.tab-body-p{display:none;margin:20px 10px;}
.tab-body .current{display:block;}
</style>
<p>
</p><p>
</p><p>标签一</p>
<p>标签二</p>
<p>标签三</p>
<p>标签四</p>
<!--jkdjfk?-->
<p>
</p><p> 1 </p>
<p> 2 </p>
<p> 3 </p>
<p> 4 </p>
<script>
// 获取标签栏的所有标签元素对象
var tabs = document.getElementsByClassName('tab-head-p');
// 获取标签栏的所有内容对象
var ps = document.getElementsByClassName('tab-body-p');
for (var i = 0; i < tabs.length; ++i) { // 遍历标签部分的元素对象
tabs[i].onmouseover = function() { // 为标签元素对象添加鼠标滑过事件
for (var i = 0; i < ps.length; ++i) { // 遍历标签栏的内容元素对象
if (tabs[i] == this) { // 显示当前鼠标滑过的li元素
ps[i].classList.add('current');
tabs[i].classList.add('current');
} else { // 隐藏其他li元素
ps[i].classList.remove('current');
tabs[i].classList.remove('current');
}
}
};
}
</script>
相关推荐:javascript教程
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of HTML element operations with JavaScript examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

