This article brings you relevant knowledge about javascript, which mainly introduces knowledge points including a simple introduction to JavaScript, basic JavaScript syntax, etc. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Related recommendations: javascript tutorial
1. A simple introduction to JavaScript
1.1. Client-side scripting language
runs in the client browser. Every browser has a JavaScript parsing engine
Script language: No need to compile, it can be directly parsed and executed by the browser
Function: It can enhance the interaction process between users and html pages, and can control html elements , giving the page some dynamic effects and enhancing the user experience
1.2. History of JavaScript development
In 1992, Nombase developed the first client-side scripting language, specifically used for forms of verification. Named: C--, later renamed: ScriptEase
In 1995, Netscape developed a client-side scripting language: LiveScript. Later, experts from SUN were invited to modify LiveScript and name it JavaScript
In 1996, Microsoft copied JavaScript and developed the JScript language
In 1997, ECMA (European Computer Manufacturers Association) formulated the client-side script language Standard: ECMAScript unifies the encoding method of all client-side scripting languages.
JavaScript = ECMAScript + JavaScript自己特有的东西(BOM+DOM)
1.3.JavaScript advantages
a. Interpreted language
b. Object-based
c. Event driven
d. Weak type
e .High security
f.Cross-platform
1.4.JavaScript reference
If you need to insert JavaScript into the HTML page, please use<script></script> Label. <script> and </script> tell JavaScript where to start and end. <script> For personal use </script>console.log()
1.7.JavaScript comment
 // This is the code: a single sentence comment, usually the ctrl L key in the editor.
// This is the code: a single sentence comment, usually the ctrl L key in the editor.
1.8.What are the common identifiers in JavaScript
1.9.What are the common HTML events in JavaScript

1.10. Common JavaScript operators

1.11. Common JavaScript assignment operators

1.12. JavaScript Common Comparison Operators

1.13. JavaScript Common Logical Operators

2. Describe the basic JavaScript syntax in detail
2.1. Variable
<script></script>
window.alert()document.write()innerHTML
console.log()
// 声明一个变量名为test的变量。var test;
2.1.2. Variable naming rules and specifications
1. From letters , numbers, underscores, symbols, and cannot start with numbers
2. Keywords cannot be used, for example: while3. Case-sensitive
Specifications: Conventional writing1. Variable names must have Meaning.2.2.1.Number2. Comply with camel case nomenclature. Camel case nomenclature: the first letter is lowercase, and the first letter of the following words is capitalized, such as userName.
Number type, String type, Boolean type, Undefined type, Null type, Object type
2.2. Data type
where data Types include:
Number number type: Contains integers and decimals
For example:var age, name, sex;//声明age、name、sex三个变量
Value range://同时声明变量并赋值var age = 10, name = "小强", sex = "1";
Value Determine whether you can use decimals to verify decimals and do not use NaN to verify whether it is NaN (NaN----not a number), but you can use isNaN— is not a number and the result is NaN
Such as:
var num = 10; //十进制var num1 = 012; //八进制var num2 = ox123; //十六进制
2.2.2.StringString escape character:
| Escape sequence | Characters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backspace | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paper feed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line feed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enter | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Horizontal tab (Ctrl-I) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Single quotes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Double quotes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Double slash | ## |
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| String.match(Reg) | 返回RegExp匹配的包含全部字符串的数组或null |
| String.search(Reg) | 返回RegExp匹配字符串首次出现的位置 |
| String.replace(Reg, newStr) | 用newStr替换RegExp匹配结果,并返回新字符串 |
| String.split(Reg) | 返回字符串按指定RegExp拆分的数组 |
var str = 'a1b2c3a4a5',
reg = /a/g;console.log(str.match(reg)); //["a", "a", "a"]var str = 'a1b2c3a4a5',
reg = /a/;console.log(str.search(reg)); //0var str = 'a1b2c3a4a5',
reg = /a/g;console.log(str.replace(reg,function(){
console.log(arguments);
return 5555;}));var str = 'a,b,c,d',
reg = /,/g;//console.log(str.split(',')); //["a", "b", "c", "d"]console.log(str.split(reg)) //["a", "b", "c", "d"]
2.7.3.RegExp对象的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| RegExp.exec(String) | 在字符串中执行匹配搜索,返回首次匹配结果数组 |
| RegExp.test(String) | 在字符串中测试模式匹配,返回true或false |
2.7.4.修饰符
修饰符也称作标识符,可指定匹配的模式,修饰符用于执行区分大小写和全局匹配。
i忽略大小写匹配。
g全局匹配,没有g只匹配第一个元素,就不在进行匹配。
m执行多行匹配
var patt = /pattern/i; //忽略大小写匹配var patt = /pattern/g; //全局匹配var patt = /pattern/m; //执行多行匹配
2.7.5.元字符
在正则表达式中具有特殊意义的专用字符。
特殊的转译字符. \ /。
. 单个任意字符,除了换行符\n与制表符\r \ 转义字符,将具有特殊意义的符号转义成普通符号: \.\d 数字[0~9]\D 非数字 \s 空格 \S 非空格 \w 字符[字母|数字|下划线]\W 非字符 \b 单词边界( 除了 (字)字母 数字_ 都算单词边界) \B 非单词边界
var reg = /\./;//匹配.var reg = /\\/;//匹配\var reg = /\//;//匹配/var str = '\\';var reg = /\\/g;console.log(reg.test(str)); //true
2.8.JavaScript常用对象
2.8.1.Date对象
Date对象是一个有关日期和时间的对象。它具有动态性,必须试用new关键字创建一个实例,如:
var Mydata=new Date();
Date对象没有提供直接访问的属性,只有获取和设置日期的方法,如下表

2.8.2.String对象
String对象是JavaScript提供的字符串处理对象,创建对象实例后才能引用,它提供了对字符串进行处理的属性和方法(类似java一样)具体如下表:
属性 length —返回字符串中字符的个数。
注意:一个汉字也是一个字符!!

2.8.3.Math对象
属性:
Math对象方法:
三角函数(sin(), cos(), tan(),asin(), acos(), atan(), atan2())是以弧度返回值的。可以通过除法Math.PI / 180把弧度转换为角度,也可以通过其他方法来转换。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Math.abs(x) | 返回x的绝对值. |
| Math.acos(x) | 返回x的反余弦值. |
| Math.acosh(x) | 返回x的反双曲余弦值. |
| Math.asin(x) | 返回x的反正弦值. |
| Math.asinh(x) | 返回x的反双曲正弦值. |
| Math.atan(x) | 以介于 -PI/2 与 PI/2 弧度之间的数值来返回 x 的反正切值. |
| Math.atanh(x) | 返回 x 的反双曲正切值. |
| Math.atan2(x, y) | 返回 y/x 的反正切值. |
| Math.cbrt(x) | 返回x的立方根. |
| Math.ceil(x) | 返回x向上取整后的值. |
| Math.clz32(x) | Returns the number of leading zeroes of a 32-bit integer. |
| Math.cos(x) | 返回x的余弦值. |
| Math.cosh(x) | 返回x的双曲余弦值. |
| Math.exp(x) | 返回 Ex, 当x为参数, E 是欧拉常数 (2.718…), 自然对数的底. |
| Math.expm1(x) | 返回 exp(x)-1 的值. |
| Math.floor(x) | 返回小于x的最大整数。 |
| Math.fround(x) | Returns the nearest single precision float representation of a number. |
| Math.hypot([x[,y[,…]]]) | Returns the square root of the sum of squares of its arguments. |
| Math.imul(x) | Returns the result of a 32-bit integer multiplication. |
| Math.log(x) | Returns the natural logarithm (loge, also ln) of a number. |
| Math.log1p(x) | Returns the natural logarithm of 1 + x (loge, also ln) of a number. |
| Math.log10(x) | Returns the base 10 logarithm of x. |
| Math.log2(x) | Returns the base 2 logarithm of x. |
| Math.max([x[,y[,…]]]) | 返回0个到多个数值中最大值. |
| Math.min([x[,y[,…]]]) | 返回0个到多个数值中最小值. |
| Math.pow(x,y) | 返回x的y次幂. |
| Math.random() | 返回0到1之间的伪随机数. 可能等于0,但是一定小于1 |
| Math.round(x) | 返回四舍五入后的整数.但是Math.round(-4.40)值为-4 |
| Math.sign(x) | 返回x的符号函数, 判定x是正数,负数还是0. |
| Math.sin(x) | 返回正弦值. |
| Math.sinh(x) | 返回x的双曲正弦值. |
| Math.sqrt(x) | 返回x的平方根. |
| Math.tan(x) | 返回x的正切值. |
| Math.tanh(x) | 返回x的双曲正切值. |
| Math.toSource() | 返回字符串 “Math”. |
| Math.trunc(x) | 返回x的整数部分,去除小数. |
例子1:写一个函数,返回从min到max之间的随机整数,包括min不包括max
function getRandomArbitrary(min, max) {
return min + Math.random() * (max - min);}
例子2:写一个函数,生成一个长度为 n 的随机字符串,字符串字符的取值范围包括0到9,a到 z,A到Z
function getRandomInt(min, max) {
return min + Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1));}function randomStr(n){
var dict = '1234567890abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ';
var str = '';
for(i = 0; i <h3 id="数组对象">2.8.4.数组对象</h3><p>数组的分类**<br> 1、二维数组,二维数组的本质是数组中的元素又是数组。</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">var arr = [[1,2],[a,b]];alert(arr[1][0]); //a 第2列第1行所在的元素2、稀疏数组
稀疏数组是包含从0开始的不连续索引的数组。在稀疏数组中一般length属性值比实际元素个数大(不常见)
举例
var a=["a",,"b",,,,"c",,];
数组对象属性
| 属性 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| length 属性 | 表示数组的长度,即其中元素的个数 |
| prototype 属性 | 返回对象类型原型的引用 |
| constructor 属性 | 表示创建对象的函数 |
1.length属性:
alert(arr.length); //显示数组的长度10arr.length=15; //增大数组的长度,length属性是可变的alert(arr.length); //显示数组的长度已经变为15
2.prototype 属性
prototype 属性返回对象类型原型的引用。prototype 属性是object共有的。
objectName.prototype
objectName 参数是object对象的名称。
说明:用 prototype 属性提供对象的类的一组基本功能。 对象的新实例“继承”赋予该对象原型的操作。
对于数组对象,用以下例子说明prototype 属性的用途。
给数组对象添加返回数组中最大元素值的方法。要完成这一点,声明一个函数,将它加入 Array.prototype, 并使用它。
function array_max( ){
var i, max = this[0];
for (i = 1; i <p>3.constructor 属性</p><blockquote><p>constructor 属性表示创建对象的函数。<br> object.constructor //object是对象或函数的名称。<br> 说明:constructor 属性是所有具有prototype 的对象的成员。它们包括除 Global 和 Math对象以外的所有JScript固有对象。constructor属性保存了对构造特定对象实例的函数的引用。</p></blockquote><p>例如:</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">x = new String("Hi");if (x.constructor == String) // 进行处理(条件为真)。//或function MyFunc {// 函数体。}y = new MyFunc;if (y.constructor == MyFunc) // 进行处理(条件为真)。Array的对象方法
说明:部分是ECMAScript5的新特性(IE678不支持)
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| concat() | 连接两个或者更多的数组,并返回结果 |
| join() | 将数组的元素组起一个字符串 |
| pop() | 删除并返回数组的最后一个元素 |
| push() | 数组末尾添加一个或者多个元素,返回新的长度 |
| reverse | 颠倒数组中元素的顺序 |
| shift() | 删除并返回数组的第一个元素 |
| slice() | 从某个已有的数组返回选定的元素 |
| sort() | 对数组元素排序 |
| splice() | 删除元素,并向数组添加新元素 |
| toSource() | 返回该对象的源代码 |
| toString() | 把数组转化为字符串并返回结果 |
| toLocalString() | 把数组转化为本地元素并返回结果 |
| unshift | 向数组开头添加一个或者更多的元素,并返回新的长度 |
| valueof() | 返回数组对象的原始值 |
| forEach() | 遍历数组对象 |
| map() | 对数组做一些映射 |
| filter() | 过滤 |
| every() | 检查判断 |
| some() | 检查判断 |
| reduce() | 两两执行一定的操作 |
| reduceRight() | 从右到左执行操作 |
| indexOf() | 数组检索查找某个元素 |
| Array.isArray([]) | 判断是否是数组 |
主要对一些新特性进行讲解
concat
concat作用是拼接数组,需要注意的是也可以把一个数组元素作为拼接的元素,如果这样的话,数组会被拉平,再和其它的元素拼接起来成为新的数组,但是不会被拉平两次,concat不会修改原数组。
例如:
var arr=[1,2,3,4,5];arr.concat([10,11],13);//[1,2,3,4,5,10,11,13]arr.concat([1,[2,3]]);//[1,2,3,4,5,1,[1,3]]
slice
slice(a,b)a和b可以取负数,表示从a位置开始截取到b位置的一段数组,是一个左闭右开的区间,a和b可以取负数,如果是负数代表倒数第a/b个元素
var arr=[1,2,3,4,5];arr.slice(1,3);//[2,3]arr.slice(1);//[2,3,4,5]arr.slice(1,-1);//[2,3,4]arr.slice(-4,-3);//[2]
splice
splice删除元素并向数组添加新元素
object.splice(a)从左边开始删除a个元素
object.splice(a,b)从a位置开始截取其中的b个元素
object.splice(a,b,c,d)从a位置开始截取b个元素,并将c和d或者更多的元素插入原数组
需要注意的是splice会修改原数组
var arr=[1,2,3,4,5];arr.splice(2);//[3,4,5]arr;//[1,2];原数组被修改了var arr=[1,2,3,4,5];arr.splice(2,2);//[3,4]arr;//[1,2,5];var arr=[1,2,3,4,5];arr.splice(1,1,‘a’,‘b’);//[2]arr;//[1,"a","b",3,4,5];
foreach
foreach()函数从头到尾把数组遍历一遍。有三个参数分别是:数组元素,元素的索引,数组本身
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];arr.forEach(function(x, index, a){//分别对应:数组元素,元素的索引,数组本身
console.log(x + '|' + index + '|' + (a === arr));});// 1|0|true// 2|1|true// 3|2|true// 4|3|true// 5|4|true
reduce()
Array的reduce()把一个函数作用在这个Array的[x1, x2, x3…]上,这个函数必须接收两个参数,reduce()把结果继续和序列的下一个元素做累积计算,其效果就是:
[x1, x2, x3, x4].reduce(f) = f(f(f(x1, x2), x3), x4)
var arr = [1, 2, 3];var sum = arr.reduce(function(x, y) {
return x + y}, 0); //参数 0是可选的,如果写了参数0那第一次传递的两个值就是0和1如果不写第一次传递的就是数组的前两个值,计算结果是6arr; //[1, 2, 3]arr = [3, 9, 6];var max = arr.reduce(function(x, y) {
console.log(x + "|" + y);
return x > y ? x : y;});// 3|9// 9|6max; // 9
数组和一般对象的比较
| 数组/一般对象 | |
|---|---|
| 相同点 | 都可以继承,对象不一定是数组,都可以当做对象添加属性 |
| 不同点 | 数组自动更新length按索引访问数组比访问一般对象属性明显迅速。数组对象继承Array.prototype上的大量数组操作方法 |
数组和字符串的比较
| 数组 /字符串 | |
|---|---|
| 相同点 | 字符串是数组的一种 |
| 不同点 | 字符串是不可变的数组,字符串没有数组的方法 |
2.9.JSON
2.9.1.stringify()
用于把js对象序列化为JSON字符串
var person={name:"xiaoming",age:12}var json=JSON.stringify(person); //{"name":"xiaoming","age":12}
stringify() 除了可以接受对象外,还可以接受2个参数,第一个参数是过滤器,可以是对象属性的数组集合,也可以是函数;第二个参数是一个选项,表示是否在JSON字符串中保留缩进
数组过滤器:
json=JSON.stringify(person,['name']); //{"name":"xiaoming"}
函数过滤器:
json=JSON.stringify(person,function(key,value){
switch(key){
case "name":
return value+",wang";
case "age":
return undefined;
default:
return value;
}});//{"name":"xiaoming,wang"}
注意,如果函数返回undefined,则该属性就会被忽略;
字符串缩进:
json=JSON.stringify(person,null,4);{
"name": "xiaoming",
"age": 12}
2.9.2.toJSON()
向对象添加toJSON()方法:
var person={
name:"xiaoming",
age:12,
toJSON:function(){
return this.name+" is "+this.age;
}}json=JSON.stringify(person);console.log(json); //"xiaoming is 12"
2.9.3.parse()
parse()除了接受json字符串外,也可以接受一个函数参数。该函数接受2个值,一个键和一个值;
var person=JSON.parse('{"name":"xiaoming","age":12}');var person=JSON.parse('{"name":"xiaoming","age":12}',function(key,value){
if(key=="age"){
return value+10;
}
else{
return value;
}});
2.10.Ajax
2.10.1.创建步骤:
1.创建一个XMLHttpRequest异步对象
2.设置请求方式和请求地址
3.接着,用send发送请求
4.监听状态变化
5.最后,接收返回的数据
例:
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()xhr.open('GET', './data/test.json', true)xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
console.log(JSON.parse(xhr.responseText))
} else {
console.log('其它情况...')
}
}}xhr.send()
2.10.2.ajax在jQuery中的应用
$.ajax({
type:"post", //请求方式
url:"a.php", //服务器的链接地址
dataType:"json", //传送和接受数据的格式
data:{
username:"james",
password:"123456"
},
success:function(data){//接受数据成功时调用的函数
console.log(data);//data为服务器返回的数据
},
error:function(request){//请求数据失败时调用的函数
alert("发生错误:"+request.status);
}});
2.10.3.GET方法
结构
$.get( url,[ data ],[ callback ],[ type ])
参数解释: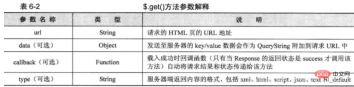
//步骤一:创建异步对象var ajax = new XMLHttpRequest();//步骤二:设置请求的url参数,参数一是请求的类型,参数二是请求的urlajax.open("get", "users.json");//步骤三:发送请求ajax.send();//步骤四:注册事件 onreadystatechange 状态改变就会调用ajax.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (ajax.readyState == 4 && ajax.status == 200) {
//步骤五:如果能够进到这个判断,说明数据完美的回来了,并且请求的页面是存在的
console.log(ajax.responseText);//输入响应的内容
}};
2.10.4.POST方法
它与$.get( )方法的结构和使用方式都相同,不过之间仍然有一下区别
2.10.5.get与post区别
1.post的安全性高于get;如果以get方式请求,请求参数会拼接到url后面,安全性性低,以post方式请求,请求参数会包裹在请求体中,安全性更高
2.数量区别:get方式传输的数据量小,规定不能超过2kb,post方式请求数据量大,没有限制。
3.传输速度:get的传输速度高于post
因为使用方法相同,因此只要改变jQuery函数,就可以将程序在GET请求和POST请求之间切换
2.11.Cookie
2.11.1.js中cookie的读取操作
function getCookie(c_name){ if (document.cookie.length>0){ //先查询cookie是否为空,为空就return "" c_start=document.cookie.indexOf(c_name + "=") //通过String对象的indexOf()来检查这个cookie是否存在,不存在就为 -1 if (c_start!=-1){ c_start=c_start + c_name.length+1 //最后这个+1其实就是表示"="号啦,这样就获取到了cookie值的开始位置 c_end=document.cookie.indexOf(";",c_start) //其实我刚看见indexOf()第二个参数的时候猛然有点晕,后来想起来表示指定的开始索引的位置...这句是为了得到值的结束位置。因为需要考虑是否是最后一项,所以通过";"号是否存在来判断 if (c_end==-1) c_end=document.cookie.length
return unescape(document.cookie.substring(c_start,c_end)) //通过substring()得到了值。想了解unescape()得先知道escape()是做什么的,都是很重要的基础,想了解的可以搜索下,在文章结尾处也会进行讲解cookie编码细节 } } return "" }
2.11.2.cookie简单存储操作
$.cookie("groupCode",222)
2.11.3.cookie设置过期时间
document.cookie = "name=value;expires=date"
2.11.4.cookie修改
document.cookie = "username=zhangsan";document.cookie = "username=lisi";var cookies = document.cookie;console.log(cookies);
2.11.5.cookie删除
document.cookie = "username=zhangsan";document.cookie = "username=; expires=Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT";var cookies = document.cookie;console.log(cookies);
2.12.循环
2.12.1.for循环
for是最常用的循环,主要用来循环数组
let arr = [1,2,3];for (let i=0; i<arr.length><h3 id="Array-forEach">2.12.2.Array.forEach()</h3>
<p>语法:<code>arr.forEach(callback(currentValue [, index [, array]])[, thisArg]);</code></p>
<p>callback为数组中每个元素执行的函数,该函数接收三个参数,currentValue(数组中正在处理的当前元素),index(数组中正在处理的当前元素的索引),array(forEach() 方法正在操作的数组)</p>
<p>thisArg为当执行回调函数 callback 时,用作 this 的值。</p>
<pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">let arr = [1, 2, , 3]let arrCopy1 = []arr.map((item, index, arr) => {
arrCopy1.push(item * 2)})console.log(arrCopy1)// [2, 4, 6]
forEach() 为每个数组元素执行一次 callback 函数
那些已删除或者未初始化的项将被跳过(例如在稀疏数组上)
与map()和reduce()不同的是,它没有返回值,总是返回undefind。
forEach()除了抛出异常以外,没有办法中止或跳出 forEach() 循环。
2.12.3.while
while 语句可以在某个条件表达式为真的前提下,循环执行指定的一段代码,直到那个表达式不为真时结束循环
示例:
let n = 0;while (n <p><strong>注:使用break语句在condition计算结果为真之前停止循环</strong></p><h3 id="do-while">2.12.4.do…while</h3><p>do…while 语句创建一个执行指定语句的循环,直到condition值为 false。在执行statement 后检测condition,所以指定的statement至少执行一次</p><p>示例:</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">const list = ['a', 'b', 'c']let i = 0do {
console.log(list[i]) //value
console.log(i) //index
i = i + 1} while (i <h3 id="for-in">2.12.5.for…in</h3><p>for…in循环可以用来遍历对象的可枚举属性列表(包括[[Prototype]]链)</p><p>主要用于遍历对象,通过属性列表可以获取属性值</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">for (let property in object) {
console.log(property) //property name
console.log(object[property]) //property value}相关推荐:javascript学习教程
The above is the detailed content of A quick summary of JavaScript learning knowledge points. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Javascript Data Types : Is there any difference between Browser and NodeJs?May 14, 2025 am 12:15 AMJavaScript core data types are consistent in browsers and Node.js, but are handled differently from the extra types. 1) The global object is window in the browser and global in Node.js. 2) Node.js' unique Buffer object, used to process binary data. 3) There are also differences in performance and time processing, and the code needs to be adjusted according to the environment.
 JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PM
JavaScript Comments: A Guide to Using // and /* */May 13, 2025 pm 03:49 PMJavaScriptusestwotypesofcomments:single-line(//)andmulti-line(//).1)Use//forquicknotesorsingle-lineexplanations.2)Use//forlongerexplanationsorcommentingoutblocksofcode.Commentsshouldexplainthe'why',notthe'what',andbeplacedabovetherelevantcodeforclari
 Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: A Comparative Analysis for DevelopersMay 09, 2025 am 12:22 AMThe main difference between Python and JavaScript is the type system and application scenarios. 1. Python uses dynamic types, suitable for scientific computing and data analysis. 2. JavaScript adopts weak types and is widely used in front-end and full-stack development. The two have their own advantages in asynchronous programming and performance optimization, and should be decided according to project requirements when choosing.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Choosing the Right Tool for the JobMay 08, 2025 am 12:10 AMWhether to choose Python or JavaScript depends on the project type: 1) Choose Python for data science and automation tasks; 2) Choose JavaScript for front-end and full-stack development. Python is favored for its powerful library in data processing and automation, while JavaScript is indispensable for its advantages in web interaction and full-stack development.
 Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Python and JavaScript: Understanding the Strengths of EachMay 06, 2025 am 12:15 AMPython and JavaScript each have their own advantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1. Python is easy to learn, with concise syntax, suitable for data science and back-end development, but has a slow execution speed. 2. JavaScript is everywhere in front-end development and has strong asynchronous programming capabilities. Node.js makes it suitable for full-stack development, but the syntax may be complex and error-prone.
 JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript's Core: Is It Built on C or C ?May 05, 2025 am 12:07 AMJavaScriptisnotbuiltonCorC ;it'saninterpretedlanguagethatrunsonenginesoftenwritteninC .1)JavaScriptwasdesignedasalightweight,interpretedlanguageforwebbrowsers.2)EnginesevolvedfromsimpleinterpreterstoJITcompilers,typicallyinC ,improvingperformance.
 JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AM
JavaScript Applications: From Front-End to Back-EndMay 04, 2025 am 12:12 AMJavaScript can be used for front-end and back-end development. The front-end enhances the user experience through DOM operations, and the back-end handles server tasks through Node.js. 1. Front-end example: Change the content of the web page text. 2. Backend example: Create a Node.js server.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Which Language Should You Learn?May 03, 2025 am 12:10 AMChoosing Python or JavaScript should be based on career development, learning curve and ecosystem: 1) Career development: Python is suitable for data science and back-end development, while JavaScript is suitable for front-end and full-stack development. 2) Learning curve: Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners; JavaScript syntax is flexible. 3) Ecosystem: Python has rich scientific computing libraries, and JavaScript has a powerful front-end framework.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

SublimeText3 English version
Recommended: Win version, supports code prompts!

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

Dreamweaver Mac version
Visual web development tools

Atom editor mac version download
The most popular open source editor







