This article brings you relevant knowledge about Git, which mainly introduces issues related to creating, deleting, viewing and merging branches in version management. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended study: "Git Learning Tutorial"
1 Basic Concept of Branch
Single branch:
At the beginning, the master branch is a line. Git uses master to point to the latest submission, and then uses HEAD to point to master, you can determine the current branch and the submission point of the current branch:

Every time you submit, the master branch will move forward one step, so that as you continue to submit , the line of the master branch is getting longer and longer.
Multiple branches:
When we create a new branch, such as dev, Git creates a new pointer called dev, pointing to The same commit as master, and then point HEAD to dev, it means that the current branch is on dev
You see, Git creates A branch is very fast, because except for adding a dev pointer and changing the HEAD pointer, there are no changes to the files in the workspace!

However, from now on, modifications and submissions to the workspace will be for the dev branch. For example, after a new submission, dev The pointer moves forward one step, while the master pointer remains unchanged:

Multi-branch merge:
Point master to the current commit of dev , the merge is completed, and Git merges branches very quickly! Just change the pointer and the contents of the workspace will remain unchanged!

After merging branches, you can even delete the dev branch. Deleting the dev branch means deleting the dev pointer. After deletion, we are left with a master branch:

2 Branch Management
2.1 Create Branch
- uses
git checkout:
$ git checkout -b dev Switched to a new branch 'dev'
git checkout command plus the -b parameter to create and switch, which is equivalent to the following two commands:
$ git branch dev $ git checkout dev Switched to branch 'dev'
- Use
git switch:
to create and switch to a new dev branch, you can use:
$ git switch -c dev
Note:
git switchandgit checkoutare used exactly the same for branch operations. Then you can usegit branchandgit switchas much as possible for branch operations.
Becausegit checkoutIn addition to operating branches, it can also operate files (can rewrite the workspace).
2.2 View branch
$ git branch * dev master
2.3 Merge branch
git mergeCommand: used to merge the specified branch to the current branch.
# 切换回当前的分支:$ git checkout master Switched to branch 'master'# 合并到指定分支:$ git merge dev Updating 599dbdb..4aac6c7 Fast-forward readme.txt | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
The Fast forward mode ("fast forward mode") is used above, but in this mode, after deleting the branch, the branch information will be lost.
If you want to forcefully disable Fast forward mode, Git will generate a new commit during merge, so that branch information can be seen from the branch history.
$ git merge --no-ff -m "merge with no-ff" dev Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy. readme.txt | 1 + 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
The merged result is as follows: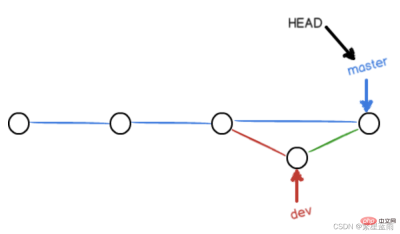
2.4 Delete branch
$ git branch -d dev Deleted branch dev (was 4aac6c7).
3 Resolve merge conflicts
Conflict situations occur As shown in the figure below, Git cannot perform "quick merge" and must manually resolve conflicts before committing. 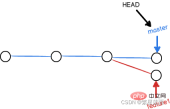
Result after merge conflict:
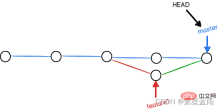
3.1 Solve it on the git official website
ClickMerge request, select the branch content we need, and then select merge. 
3.2 Local solution
- Step 1. Pull and check the branch used for merging
git fetch origingit checkout -b "feature1" "origin/feature1"
- Steps 2. View and make changes locally
Git using>> ;>>>> Mark the content of different branches, such as the following:
Git is a distributed version control system. Git is free software distributed under the GPL. Git has a mutable index called stage. Git tracks changes of files.>>>>>> feature1
- 步骤三. 合并分支并解决冲突
git fetch origingit checkout "master"git merge --no-ff "feature1"
- 步骤四. 推送代码并合并
git push origin "master"
其他方法为:
- 法1:
保留本地最新修改,并拉取仓库中 的代码到本地
git stash git pull origin master git stash pop
- 法2:
放弃本地代码,新修改的都不要了,退回上一版本,再拉取代码到本地
git reset --hard git pull origin master # 或git fetch --allgit reset --hard origin/master git pull
4 分支转移
git cherry-pick命令的作用,就是将指定的提交commit应用于其他分支。
$ git cherry-pick \<commithash></commithash>
上面命令就会将指定的提交commitHash,应用于当前分支。这会在当前分支产生一个新的提交,当然它们的哈希值会不一样。
举例来说,代码仓库有master和feature两个分支。
a - b - c - d Master \\ e - f - g Feature
现在将提交f应用到master分支。
\# 切换到 master 分支 $ git checkout master\# Cherry pick 操作 $ git cherry-pick f
上面的操作完成以后,代码库就变成了下面的样子。
a - b - c - d - f Master \\ e - f - g Feature
从上面可以看到,master分支的末尾增加了一个提交f。
git cherry-pick命令的参数,不一定是提交的哈希值,分支名也是可以的,表示转移该分支的最新提交。
$ git cherry-pick feature
上面代码表示将feature分支的最近一次提交,转移到当前分支。
Cherry pick 支持一次转移多个提交。
$ git cherry-pick \<hasha> \<hashb></hashb></hasha>
上面的命令将 A 和 B 两个提交应用到当前分支。这会在当前分支生成两个对应的新提交。
如果想要转移一系列的连续提交,可以使用下面的简便语法。
$ git cherry-pick A..B
上面的命令可以转移从 A 到 B 的所有提交。它们必须按照正确的顺序放置:提交 A 必须早于提交 B,否则命令将失败,但不会报错。
注意,使用上面的命令,提交 A 将不会包含在 Cherry pick 中。如果要包含提交 A,可以使用下面的语法。
$ git cherry-pick A^..B
`git cherry-pick`命令的常用配置项如下。 #### -e,--edit 打开外部编辑器,编辑提交信息。 #### -n,--no-commit 只更新工作区和暂存区,不产生新的提交。 #### -x 在提交信息的末尾追加一行`cherry picked from commit ...`,方便以后查到这个提交是如何产生的。 #### -s,--signoff 在提交信息的末尾追加一行操作者的签名,表示是谁进行了这个操作。 #### -m parent-number,--mainline parent-number 如果原始提交是一个合并节点,来自于两个分支的合并,那么 `Cherry pick` 默认将失败,因为它不知道应该采用哪个分支的代码变动。 `-m`配置项告诉 Git,应该采用哪个分支的变动。它的参数`parent-number`是一个从1开始的整数,代表原始提交的父分支编号。 ```bash $ git cherry-pick -m 1 \<commithash></commithash>
上面命令表示,Cherry pick 采用提交commitHash来自编号1的父分支的变动。
一般来说,1号父分支是接受变动的分支,2号父分支是作为变动来源的分支。
如果操作过程中发生代码冲突,Cherry pick会停下来,让用户决定如何继续操作。
(1)–continue
用户解决代码冲突后,第一步将修改的文件重新加入暂存区(git add .),第二步使用下面的命令,让 Cherry pick 过程继续执行。
$ git cherry-pick --continue
(2)–abort
发生代码冲突后,放弃合并,回到操作前的样子。
(3)–quit
发生代码冲突后,退出 Cherry pick,但是不回到操作前的样子。
Cherry pick 也支持转移另一个代码库的提交,方法是先将该库加为远程仓库。
转移另一个代码库的提交
$ git remote add target git://gitUrl
上面命令添加了一个远程仓库target。
然后,将远程代码抓取到本地。
$ git fetch target
上面命令将远程代码仓库抓取到本地。
接着,检查一下要从远程仓库转移的提交,获取它的哈希值。
$ git log target/master
最后,使用git cherry-pick命令转移提交。
$ git cherry-pick \<commithash></commithash>
5 常用的分支
在实际开发中,我们应该按照几个基本原则进行分支管理:
首先,master分支应该是非常稳定的,也就是仅用来发布新版本,平时不能在上面干活;
其次,干活都在dev分支上,也就是说,dev分支是不稳定的,到某个时候,比如1.0版本发布时,再把dev分支合并到master上,并在master分支发布1.0版本;
小伙伴们每个人都在dev分支上干活,每个人都有自己的分支,时不时地往dev分支上合并就可以了。

5.1 bug分支
在开发过程中,bug 就像家常便饭一样。有了 bug 就需要修复,在 Git 中,由于分支是如此的强大,所以,每个 bug 都可以通过一个新的临时分支来修复,修复后,合并分支,然后将临时分支删除。
当你接到一个修复一个代号101的 bug 的任务时,很自然地,你想创建一个分支 issue-101 来修复它,但是,等等,当前正在dev上进行的工作还没有提交:
$ git status On branch dev Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD \<file>..." to unstage) new file: hello.py Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add \<file>..." to update what will be committed) (use "git checkout -- \<file>..." to discard changes in working directory) modified: readme.txt</file></file></file>
并不是你不想提交,而是工作只进行到一半,还没法提交,预计完成还需1天时间。但是,必须在两个小时内修复该 bug,怎么办?
幸好,Git还提供了一个stash功能,可以把当前工作现场“储藏”起来,等以后恢复现场后继续工作:
$ git stash Saved working directory and index state WIP on dev: f52c633 add merge
现在,用git status查看工作区,就是干净的(除非有没有被Git管理的文件),因此可以放心地创建分支来修复 bug。
首先确定要在哪个分支上修复 bug,假定需要在master分支上修复,就从master创建临时分支:
$ git checkout master Switched to branch 'master'Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 6 commits. (use "git push" to publish your local commits)$ git checkout -b issue-101 Switched to a new branch 'issue-101'
现在修复bug,需要把“Git is free software …”改为“Git is a free software …”,然后提交:
$ git add readme.txt $ git commit -m "fix bug 101"[issue-101 8842ff5] fix bug 101 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
修复完成后,切换到master分支,并完成合并,最后删除issue-101分支:
$ git switch master Switched to branch 'master'Your branch is ahead of 'origin/master' by 6 commits. (use "git push" to publish your local commits)$ git merge --no-ff -m "merged bug fix 101" issue-101 Merge made by the 'recursive' strategy. readme.txt | 2 +- 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
太棒了,原计划两个小时的 bug 修复只花了5分钟!现在,是时候接着回到dev分支干活了!
$ git switch dev Switched to branch 'dev'$ git status On branch dev nothing to commit, working tree clean
工作区是干净的,刚才的工作现场存到哪去了?用git stash list命令看看:
$ git stash list
stash@{0}: WIP on dev: f52c633 add merge
工作现场还在,Git 把stash内容存在某个地方了,但是需要恢复一下,有两个办法:
一是用git stash apply恢复,但是恢复后,stash内容并不删除,你需要用git stash drop来删除;
另一种方式是用git stash pop,恢复的同时把stash内容也删了:
$ git stash pop
On branch dev
Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD \<file>..." to unstage)
new file: hello.py
Changes not staged for commit: (use "git add \<file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- \<file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: readme.txt
Dropped refs/stash@{0} (5d677e2ee266f39ea296182fb2354265b91b3b2a)</file></file></file>
再用git stash list查看,就看不到任何stash内容了:
$ git stash list
你可以多次stash,恢复的时候,先用git stash list查看,然后恢复指定的stash,用命令:
$ git stash apply stash@{0}
在master分支上修复了bug后,我们要想一想,dev分支是早期从master分支分出来的,所以,这个bug其实在当前dev分支上也存在。
那怎么在dev分支上修复同样的bug?重复操作一次,提交不就行了?在 Git 中还有比这更简单的方法可以实现。
同样的 bug,要在dev上修复,我们只需要把8842ff5 fix bug 101这个提交所做的修改“复制”到dev分支。注意:我们只想复制8842ff5 fix bug 101这个提交所做的修改,并不是把整个master分支merge过来。
为了方便操作,Git 专门提供了一个cherry-pick命令,让我们能复制一个特定的提交到当前分支:
$ git branch\* dev master $ git cherry-pick 8842ff5[dev 0944c8c] fix bug 101 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
Git 自动给dev分支做了一次提交,注意这次提交的commit是0944c8c,它并不同于master的8842ff5,因为这两个commit只是改动相同,但确实是两个不同的commit。用git cherry-pick,我们就不需要在dev分支上手动再把修 bug 的过程重复一遍。
有些聪明的童鞋会想了,既然可以在master分支上修复bug后,在dev分支上可以“重放”这个修复过程,那么直接在dev分支上修复 bug,然后在master分支上“重放”行不行?当然可以,不过你仍然需要git stash命令保存现场,才能从dev分支切换到master分支。
5.2 feature分支
在开发过程中,除了 bug 外,也还会有无穷无尽的新的功能要不断添加进来。
添加一个新功能时,你肯定不希望因为一些实验性质的代码,把主分支搞乱了,所以,每添加一个新功能,最好新建一个feature分支,在上面开发,完成后,合并,最后,删除该feature分支。
现在,你终于接到了一个新任务:开发代号为Vulcan的新功能,该功能计划用于下一代星际飞船。
于是准备开发:
$ git switch -c feature-vulcan Switched to a new branch 'feature-vulcan'
5分钟后,开发完毕:
$ git add vulcan.md $ git status On branch feature-vulcan Changes to be committed: (use "git reset HEAD \<file>..." to unstage) new file: vulcan.md $ git commit -m "add feature vulcan"[feature-vulcan d12cf23] add feature vulcan 1 file changed, 3 insertions(+) create mode 100644 vulcan.md</file>
切回dev,准备合并:
$ git switch dev
一切顺利的话,feature分支和bug分支是类似的,合并,然后删除。
但是!就在此时,接到上级命令,因经费不足,新功能必须取消!虽然白干了,但是这个包含机密资料的分支还是必须就地销毁:
$ git branch -d feature-vulcan error: The branch 'feature-vulcan' is not fully merged. If you are sure you want to delete it, run 'git branch -D feature-vulcan'.
销毁失败。Git 友情提醒,feature-vulcan分支还没有被合并,如果删除,将丢失掉修改,如果要强行删除,需要使用大写的-D参数。。
现在我们强行删除:
$ git branch -D feature-vulcan Deleted branch feature-vulcan (was d12cf23).
终于删除成功!
推荐学习:《Git教程》
The above is the detailed content of Summarize and organize branch operations of git version management. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Git and GitHub: Exploring Their Roles and FunctionsMay 09, 2025 am 12:25 AM
Git and GitHub: Exploring Their Roles and FunctionsMay 09, 2025 am 12:25 AMThe role and function of Git and GitHub in software development is to manage code and collaborative development. Git efficiently manages code versions through commit, branch and merge functions, while GitHub provides code hosting and collaboration tools such as PullRequest and Issues to improve team collaboration efficiency.
 GitHub: Discovering, Sharing, and Contributing to CodeMay 08, 2025 am 12:26 AM
GitHub: Discovering, Sharing, and Contributing to CodeMay 08, 2025 am 12:26 AMGitHub is the preferred platform for developers to discover, share and contribute code. 1) Find specific code bases through search functions, such as Python projects. 2) Create a repository and push code to share with developers around the world. 3) Participate in open source projects and contribute code through Fork and PullRequest.
 Using Git with GitHub: A Practical GuideMay 07, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Using Git with GitHub: A Practical GuideMay 07, 2025 am 12:11 AMGit is a version control system, and GitHub is an online platform based on Git. The steps to using Git and GitHub for code management and team collaboration include: 1. Initialize the Git repository: gitinit. 2. Add files to the temporary storage area: gitadd. 3. Submit changes: gitcommit-m"Initialcommit". 4. Related to the GitHub repository: gitremoteaddoriginhttps://github.com/username/repository.git. 5. Push code to GitHub: gitpush-uoriginmaste
 GitHub's Impact: Software Development and CollaborationMay 06, 2025 am 12:09 AM
GitHub's Impact: Software Development and CollaborationMay 06, 2025 am 12:09 AMGitHub has a far-reaching impact on software development and collaboration: 1. It is based on Git's distributed version control system, which improves code security and development flexibility; 2. Through functions such as PullRequest, it improves team collaboration efficiency and knowledge sharing; 3. Tools such as GitHubActions help optimize the development process and improve code quality.
 Using GitHub: Sharing, Managing, and Contributing to CodeMay 05, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Using GitHub: Sharing, Managing, and Contributing to CodeMay 05, 2025 am 12:12 AMThe methods of sharing, managing and contributing code on GitHub include: 1. Create a repository and push code, and write README and LICENSE files; 2. Use branches, tags and merge requests to manage code; 3. Fork the repository, modify and submit PullRequest contribution code. Through these steps, developers can effectively use GitHub to improve development efficiency and collaboration capabilities.
 Git vs. GitHub: A Comparative AnalysisMay 04, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Git vs. GitHub: A Comparative AnalysisMay 04, 2025 am 12:07 AMGit is a distributed version control system, and GitHub is a Git-based collaboration platform. Git is used for version control and code management, while GitHub provides additional collaboration features such as code review and project management.
 Git vs. GitHub: Understanding the DifferenceMay 03, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Git vs. GitHub: Understanding the DifferenceMay 03, 2025 am 12:08 AMGit is a distributed version control system, and GitHub is an online platform based on Git. Git is used for version control, branch management and merger, and GitHub provides code hosting, collaboration tools and social networking capabilities.
 GitHub: The Frontend, Git: The BackendMay 02, 2025 am 12:16 AM
GitHub: The Frontend, Git: The BackendMay 02, 2025 am 12:16 AMGit is a back-end version control system, and GitHub is a front-end collaboration platform based on Git. Git manages code version, GitHub provides user interface and collaboration tools, and the two work together to improve development efficiency.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

PhpStorm Mac version
The latest (2018.2.1) professional PHP integrated development tool







