Home >Database >Mysql Tutorial >Detailed analysis of MySQL transactions
Detailed analysis of MySQL transactions
- WBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBOYWBforward
- 2022-03-10 17:59:111786browse
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces the transaction ACID characteristics of MySQL and the syntax of the MySQL transaction control process, and introduces exceptions that may occur in concurrent transaction processing Situations, such as dirty reads, phantom reads, non-repeatable reads, etc., and finally introduce the transaction isolation level, I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended study: mysql learning tutorial
In actual business scenarios, how to ensure the integrity of operations is an important issue , execute a series of logically strongly related operations in sequence. If an error occurs midway, it is likely to cause data confusion.
Imagine the scene of withdrawing money from an ATM. When we withdraw a thousand yuan, the ATM will spit out a thousand yuan at once after the counting is completed, instead of spitting out a hundred yuan each time ten times. This In order to ensure the integrity of the operation, either a thousand yuan is completely withdrawn and the balance is deducted, or not a penny is withdrawn and the balance remains unchanged, without data inconsistency caused by machine failure in the middle. Such a complete operation is called transaction. All operations in a transaction are either executed successfully or not at all.
This article will introduce the MySQL transaction ACID features and the syntax of the MySQL transaction control process, and introduce possible exceptions in concurrent transaction processing, such as dirty reads, phantom reads, and non-repeatable Read and so on, and finally introduce the transaction isolation level.
About locks and MVCC to achieve transaction isolation, we will introduce them in subsequent articles.
ACID Features
Transaction processing is a management mechanism for MySQL operations that must be executed in a batch. During the transaction process, unless the entire batch of operations is executed correctly, any operation in the middle will If an error occurs, it will Rollback to the original safe state to ensure that no erroneous changes are caused to the system data.
We mentioned in the previous article that after MySQL 5.5, the default storage engine was replaced from MyISAM to InnoDB. One of the important reasons for this is because InnoDB supports transactions. We use SHOW ENGINES Let’s take a look at the descriptions of various storage engines in MySQL. 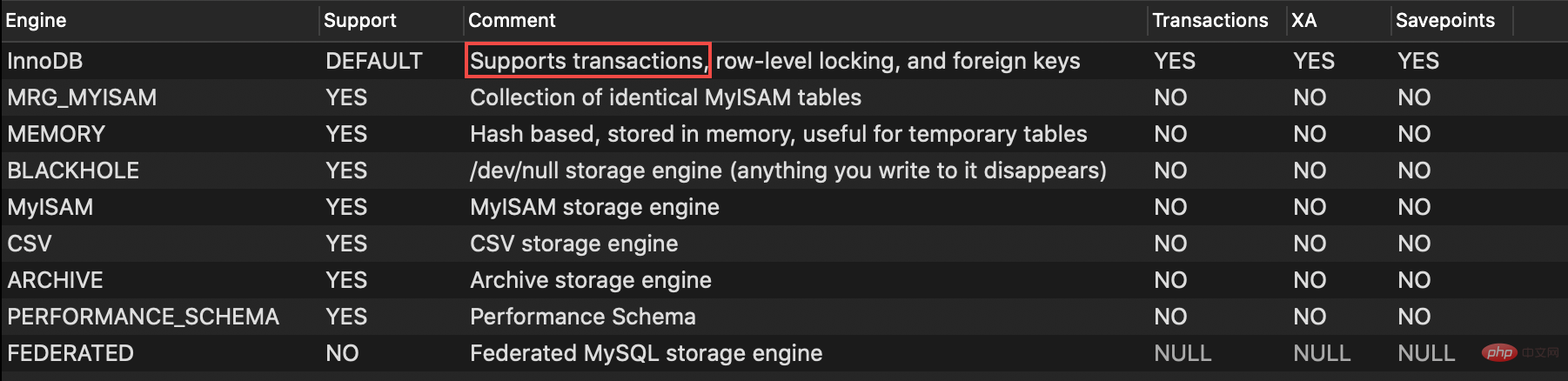
The four most important characteristics of transactions are often called ACID CharacteristicsA - Atomicity Atomicity: A transaction is an indivisible The smallest unit, all operations in a transaction either succeed or fail, with no intermediate state. Atomicity is mainly achieved through rollback log (undo log) in the transaction log. When a transaction modifies the database, InnoDB will generate an undo log of the opposite operation based on the operation, such as the insert operation. , a delete record will be generated. If the transaction execution fails or rollback is called, it will be restored to the state before execution based on the contents of the undo log.
C - Consistency Consistency: The data is in a legal consistency state before and after transaction execution. Even if an exception occurs, the integrity of the database will not be destroyed due to exceptions. Constraints, such as uniqueness constraints, etc.
I - Isolation Isolation: Each transaction is independent of each other and will not be affected by the execution of other transactions. The transaction is not visible to other transactions before committing. Isolation is defined by the isolation level of the transaction, and the lock mechanism is used to ensure the isolation of write operations, and MVCC is used to ensure the isolation of read operations, which will be introduced in detail below.
D - Durability Persistence: The modifications to the data after the transaction is committed are persistent and will not be lost even if the database is down. Through the redo log in the transaction log (redo log) to ensure. Before the transaction is modified, the change information will be pre-written into the redo log. If the database goes down, the records in the redo log will be read after recovery to restore the data.
Transaction control syntax
MySQL transaction control has several important nodes, namely transaction start, commit, rollback and save point.
Opening a transaction means that the transaction begins execution. The statement is START TRANSACTION or BEGIN. Submitting the transaction means writing all updates in the transaction to the physical database on the disk. The transaction When normal execution ends, the statement is COMMIT. If an exception occurs and rollback is required, the statement is ROLLBACK. It should be noted that once a transaction has been committed, it cannot be rolled back. Therefore, when an exception is caught during code execution, rollback needs to be executed directly instead of commit.
For example, A transfers 100 yuan to B:
// 正常执行,提交 BEGIN; # 开启事务 UPDATE account_balance SET balance = balance - 100.00 WHERE account_name = 'A'; UPDATE account_balance SET balance = balance + 100.00 WHERE account_name = 'B'; COMMIT; # 提交事务 // 发生异常,回滚 BEGIN; # 开启事务 UPDATE account_balance SET balance = balance - 100.00 WHERE account_name = 'A'; UPDATE account_balance SET balance = balance + 100.00 WHERE account_name = 'B'; ROLLBACK; # 事务回滚
In complex scenarios, sometimes we do not need to roll back the entire operation, but execute it in batches and roll back to a certain node Just fine, it is equivalent to nesting several sub-transactions under a large transaction. In MySQL, you can use the retention point SAVEPOINT to achieve this.
BEGIN; insert into user_tbl (id) values (1) ; insert into user_tbl (id) values (2) ; ROLLBACK; # 1,2 都没有写入 BEGIN; insert into user_tbl (id) values (1) ; SAVEPOINT s1; insert into user_tbl (id) values (2) ; ROLLBACK TO s1; # 回滚到保留点 s1, 因此 1 成功写入,2 被回滚, 最终结果为 1 RELEASE SAVEPOINT s1; # 释放保留点
顺便提一下,事务有隐式事务(自动提交)和显示事务(必须手动提交)两种,MySQL 默认为隐式事务,会进行自动提交,通过 autocommit 参数来控制。
# 查看变量 SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'autocommit'; +---------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------+-------+ | autocommit | ON | +---------------+-------+ # 开启自动提交(默认) SET autocommit = 1; # 关闭自动提交 SET autocommit = 0;
在自动提交状态下,如果没有显示的开启事务,那每一条语句都是一个事务,系统会自动对每一条 sql 执行 commit 操作。使用 BEGIN 或 START TRANSACTION 开启一个事务之后,自动提交将保持禁用状态,直到使用 COMMIT 或 ROLLBACK 结束事务之后,自动提交模式会恢复到之前的状态。
关于事务还有另一个参数 completion_type,默认取值为 0 (NO_CHAIN)
# 查看变量 SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'completion_type'; +-----------------+----------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-----------------+----------+ | completion_type | NO_CHAIN | +-----------------+----------+
completion_type = 0: 默认值,执行 commit 后不会自动开启新的事务。
completion_type = 1: 执行 commit 时,相当于执行 COMMIT AND CHAIN,自动开启一个相同隔离级别的事务。
completion_type = 2: 执行 commit 时,相当于执行 COMMIT AND RELEASE,提交事务后自动断开服务器连接。
事务并发异常
在实际产线环境下,可能会存在大规模并发请求的情况,如果没有妥善的设置事务的隔离级别,就可能导致一些异常情况的出现,最常见的几种异常为脏读(Dirty Read)、幻读(Phantom Read)和不可重复读(Unrepeatable Read)。
脏读
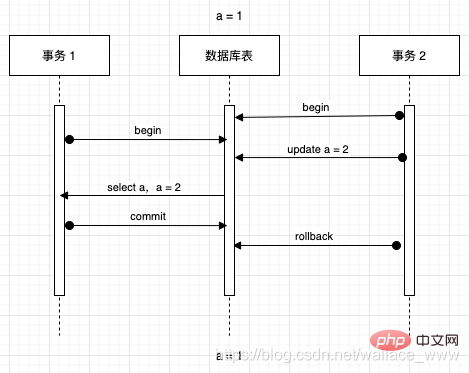
脏读指一个事务访问到了另一个事务未提交的数据,如下过程:
- 假设 a 的值为 1,事务 2 把 a 改为 2,此时事务还未提交
- 在这个时候,事务 1 读取 a,读得 a 的值为 2,事务 1 读取完成
- 结果事务 2 回滚了对 a 的修改(或者是未 commit),于是 a 的值变回 1
- 这就导致事实上 a 的值为 1,但是事务 1 取得的结果为 2,所以事务 1 读到了脏数据,发生脏读

不可重复读
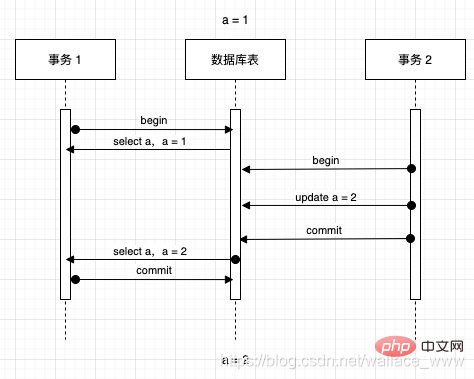
不可重复读指一个事务多次读取同一数据的过程中,数据值 内容 发生了改变,导致没有办法读到相同的值,描述的是针对同一条数据 update/delete 的现象,如下过程:
- 事务 1 读取 a,此时 a = 1
- 此时事务 2 将 a 修改为 2,并成功提交,改动生效
- 事务 1 又一次读取 a,此时 a = 2
- 事务 1 在同一个事务里面两次读取同一个值,数据值内容却发生了改变,发生不可重复读

幻读
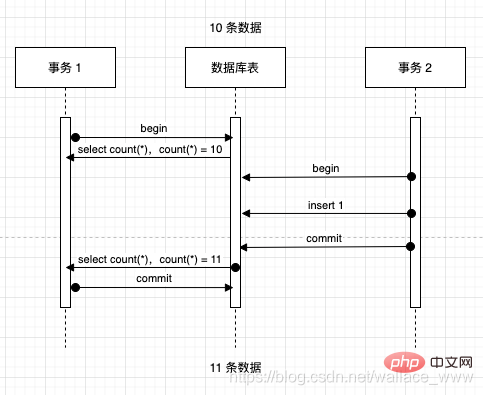
幻读指一个事务多次读取同一数据的过程中,全局数据(如数据行数)发生了改变,仿佛产生了幻觉,描述的是针对全表 insert/delete 的现象,如下过程:
- 事务 1 第一次读取数量,得到 10 条数据
- 此时事务 2 插入了一条数据并成功提交,改动生效,数据变成 11 条
- 事务 1 再次读取数量,得到 11 条数据,对事务 1 而言莫名其妙的多了一条,好像产生幻觉了一样,发生幻读

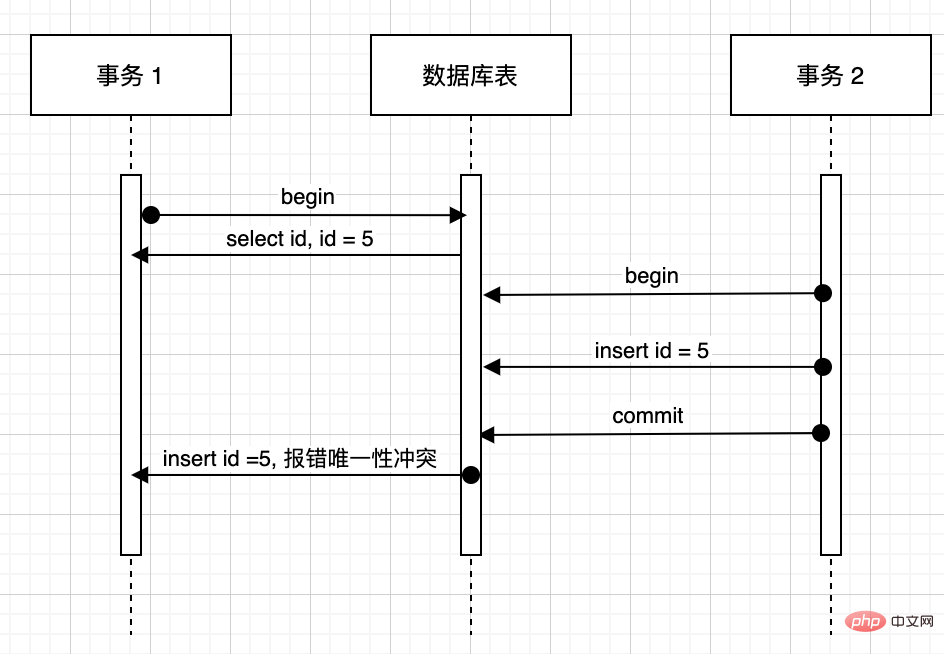
或者是另一种场景,比如对于有唯一性约束的字段(如 id),发生如下过程:
- 事务 1 要插入 id = 5 的记录,先查询数据库,发现不存在 id = 5 的数据,可以正常插入。
- 这时候事务 2 插入了一条数据 id = 5。
- 事务 1 插入 id = 5 时,发现报错唯一性冲突,对事务 1 来讲就好像见了鬼了,我刚刚明明检查过没有,怎么这时候又有了。

事务隔离级别
串行化的事务处理方式当然是最安全的,但是串行无法满足数据库高并发访问的需求,作为妥协,有时不得不降低数据库的隔离标准来换取事务的并发能力,通过在可控的范围内牺牲正确性来换取效率的提升,这种权衡通过事务的隔离级别来实现。
数据库有 4 种事务隔离级别,由低到高依次为 读未提交 Read Uncommitted 、读已提交 Read Committed 、可重复读 Repeatable Read 、串行化 Serializable 。
读未提交 Read Uncommitted
允许读取未提交的内容,这种级别下的查询不会加锁,因此脏读、不可重复读、幻读都有可能发生。读已提交 Read Committed
只允许读取已提交的内容,这种级别下的查询不会发生脏读,因为脏数据属于未提交的数据,所以不会被读取,但是依然有可能发生不可重复读和幻读。-
可重复读 Repeatable Read (MySQL 的默认隔离级别)
使用行级锁来保证一个事务在相同查询条件下两次查询得到的数据结果一致,可以避免脏读和不可重复读,但是没有办法避免幻读。需要特殊注意的是,Innodb 在 Repeatable Read 下通过 MVCC 提供了稳定的视图,因此 Innodb 的 RR 隔离级别下是不会出现上述幻读异常中的第一个场景的,但第二个场景还是会出现。
串行化 Serializable
使用表级锁来保证所有事务的串行化,可以防止所有的异常情况,但是牺牲了系统的并发性。
查看隔离级别的命令为
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'transaction_isolation'; # 或者 SELECT @@global.tx_isolation, @@tx_isolation;
第二种方式可以查看全局和当前会话的隔离级别。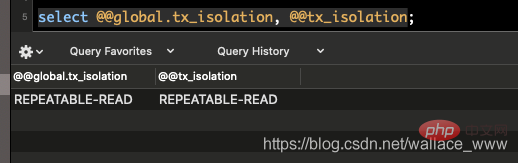
设置隔离级别的命令为
# 将当前会话的隔离级别设为读未提交 SET SESSION TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED; # 将全局的隔离级别设为读未提交 SET GLOBAL TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL READ UNCOMMITTED;
结语
本文简单介绍了 MySQL 事务的语法和 ACID 特性,以及事务并发处理中可能出现的异常情况和为了防止这些异常而设计的事务隔离级别。有兴趣的朋友可以尝试在两个不同的 MySQL 客户端来模拟四种隔离级别下三种异常的发生情况,在之后的文章中,会继续深入探讨 MySQL 是如何实现隔离级别的。
推荐学习:mysql学习视频教程
The above is the detailed content of Detailed analysis of MySQL transactions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!