Home >Common Problem >what is an encoder
what is an encoder
- 青灯夜游Original
- 2022-01-06 16:29:389228browse
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts signals (such as bit streams) or data into signal forms that can be used for communication, transmission, and storage. The encoder converts angular displacement or linear displacement into electrical signals. The former is called a code disc and the latter is called a code ruler.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
An encoder is a device that compiles and converts signals (such as bit streams) or data into signal forms that can be used for communication, transmission, and storage. The encoder converts angular displacement or linear displacement into electrical signals. The former is called a code disc and the latter is called a code ruler.
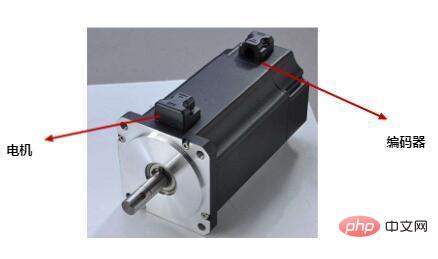
Encoders can be classified in the following ways.
1. Classification according to the different ways of engraving holes on the code disk
(1) Incremental type: It sends out a pulse signal every time the angle of the unit is rotated (there are also sine and cosine signals, and then Subdivide it and chop out pulses with higher frequency), usually A-phase, B-phase, Z-phase output. A-phase and B-phase are pulse outputs delayed by 1/4 period of each other. The positive and negative pulses can be distinguished according to the delay relationship. Inversion, and the frequency can be multiplied by 2 or 4 by taking the rising and falling edges of phase A and phase B; phase Z is a single-turn pulse, that is, one pulse is sent out per turn.
(2) Absolute value type: It corresponds to one circle. Each reference angle emits a unique binary value corresponding to the angle. Multiple positions can be recorded and measured through external lap recording devices.
2. According to the output type of the signal, it is divided into: voltage output, open collector output, push-pull complementary output and long-line drive output.
3. Classification based on the mechanical installation form of the encoder
(1) Shaft type: Shaft type can be divided into clamping flange type, synchronous flange type and servo installation type, etc. .
(2) Bushing type: Bushing type can be divided into semi-hollow type, fully hollow type and large-diameter type.
4. Based on the working principle of the encoder, it can be divided into: photoelectric type, magnetoelectric type and contact brush type.
For more related knowledge, please visit the FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of what is an encoder. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

