An article to talk about the current limiting strategy in Redis
This article will take you to understand the current limiting in Redis, and introduce the simple current limiting strategy and funnel current limiting. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

1. Simple current limiting
Basic principles
How to organize plans when the system processing capacity is limited External requests put pressure on the system. First, let’s look at some simple current limiting strategies to prevent brute force attacks. For example, if you want to access an IP, you can only access it 10 times every 5 seconds, and if it exceeds the limit, it will be blocked. [Related recommendations: Redis Video Tutorial]
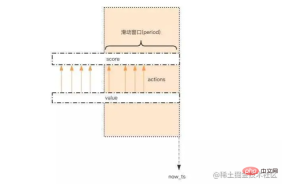
As shown above, a sliding window is generally used to count the number of visits within an interval.
Use zset to record the number of IP visits. Each IP is saved through key, and score saves the current timestamp. , value Only use timestamp or UUID to implement
Code implementation
public class RedisLimiterTest {
private Jedis jedis;
public RedisLimiterTest(Jedis jedis) {
this.jedis = jedis;
}
/**
* @param ipAddress Ip地址
* @param period 特定的时间内,单位秒
* @param maxCount 最大允许的次数
* @return
*/
public boolean isIpLimit(String ipAddress, int period, int maxCount) {
String key = String.format("ip:%s", ipAddress);
// 毫秒时间戳
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
Pipeline pipe = jedis.pipelined();
// redis事务,保证原子性
pipe.multi();
// 存放数据,value 和 score 都使用毫秒时间戳
pipe.zadd(key, currentTimeMillis, "" + UUID.randomUUID());
// 移除窗口区间所有的元素
pipe.zremrangeByScore(key, 0, currentTimeMillis - period * 1000);
// 获取时间窗口内的行为数量
Response<Long> count = pipe.zcard(key);
// 设置 zset 过期时间,避免冷用户持续占用内存,这里宽限1s
pipe.expire(key, period + 1);
// 提交事务
pipe.exec();
pipe.close();
// 比较数量是否超标
return count.get() > maxCount;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("localhost", 6379);
RedisLimiterTest limiter = new RedisLimiterTest(jedis);
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
// 验证IP 10秒钟之内只能访问5次
boolean isLimit = limiter.isIpLimit("222.73.55.22", 10, 5);
System.out.println("访问第" + i + "次, 结果:" + (isLimit ? "限制访问" : "允许访问"));
}
}
}Execution result
访问第1次, 结果:允许访问 访问第2次, 结果:允许访问 访问第3次, 结果:允许访问 访问第4次, 结果:允许访问 访问第5次, 结果:允许访问 访问第6次, 结果:限制访问 访问第7次, 结果:限制访问 ... ...
Disadvantages: It is necessary to record all the behavior records in the time window, which is very large. For example, the scenario of limiting the number of times to no more than 1 million times in 60 seconds is not suitable for such current limiting, because it will consume a lot of storage space.
2. Funnel current limit
Basic principle
- ##The capacity of the funnel is limited. If it is full, it will be filled. Not going in anymore.
- If you release the spout, the water will flow downward. After a part of it flows away, you can continue to fill it with water.
- If the flow rate of water from the spout is greater than the rate of water filling, then the funnel will never be full.
- If the flow rate of the funnel is less than the filling rate, then once the funnel is full, the filling needs to be paused and wait for the funnel to empty.
Sample codepublic class FunnelLimiterTest {
static class Funnel {
int capacity; // 漏斗容量
float leakingRate; // 漏嘴流水速率
int leftQuota; // 漏斗剩余空间
long leakingTs; // 上一次漏水时间
public Funnel(int capacity, float leakingRate) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.leakingRate = leakingRate;
this.leftQuota = capacity;
this.leakingTs = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
void makeSpace() {
long nowTs = System.currentTimeMillis();
long deltaTs = nowTs - leakingTs; // 距离上一次漏水过去了多久
int deltaQuota = (int) (deltaTs * leakingRate); // 腾出的空间 = 时间*漏水速率
if (deltaQuota < 0) { // 间隔时间太长,整数数字过大溢出
this.leftQuota = capacity;
this.leakingTs = nowTs;
return;
}
if (deltaQuota < 1) { // 腾出空间太小 就等下次,最小单位是1
return;
}
this.leftQuota += deltaQuota; // 漏斗剩余空间 = 漏斗剩余空间 + 腾出的空间
this.leakingTs = nowTs;
if (this.leftQuota > this.capacity) { // 剩余空间不得高于容量
this.leftQuota = this.capacity;
}
}
boolean watering(int quota) {
makeSpace();
if (this.leftQuota >= quota) { // 判断剩余空间是否足够
this.leftQuota -= quota;
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
// 所有的漏斗
private Map<String, Funnel> funnels = new HashMap<>();
/**
* @param capacity 漏斗容量
* @param leakingRate 漏嘴流水速率 quota/s
*/
public boolean isIpLimit(String ipAddress, int capacity, float leakingRate) {
String key = String.format("ip:%s", ipAddress);
Funnel funnel = funnels.get(key);
if (funnel == null) {
funnel = new Funnel(capacity, leakingRate);
funnels.put(key, funnel);
}
return !funnel.watering(1); // 需要1个quota
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
FunnelLimiterTest limiter = new FunnelLimiterTest();
for (int i = 1; i <= 50; i++) {
// 每1s执行一次
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 漏斗容量是2 ,漏嘴流水速率是0.5每秒,
boolean isLimit = limiter.isIpLimit("222.73.55.22", 2, (float)0.5/1000);
System.out.println("访问第" + i + "次, 结果:" + (isLimit ? "限制访问" : "允许访问"));
}
}
}
Execution results
访问第1次, 结果:允许访问 # 第1次,容量剩余2,执行后1 访问第2次, 结果:允许访问 # 第2次,容量剩余1,执行后0 访问第3次, 结果:允许访问 # 第3次,由于过了2s, 漏斗流水剩余1个空间,所以容量剩余1,执行后0 访问第4次, 结果:限制访问 # 第4次,过了1s, 剩余空间小于1, 容量剩余0 访问第5次, 结果:允许访问 # 第5次,由于过了2s, 漏斗流水剩余1个空间,所以容量剩余1,执行后0 访问第6次, 结果:限制访问 # 以此类推... 访问第7次, 结果:允许访问 访问第8次, 结果:限制访问 访问第9次, 结果:允许访问 访问第10次, 结果:限制访问
- We observe
- Funnel
Several fields of the object, we found that the contents of theFunnelobject can be stored in ahashstructure by field, and the fields of thehashstructure will be added when filling. After taking it out and performing logical operations, the new value is backfilled into thehashstructure to complete a behavior frequency detection.But there is a problem, we cannot guarantee the atomicity of the entire process. Get the value from the - hash
structure, then operate it in the memory, and then backfill it into thehashstructure. These three processes cannot be atomic, which means that appropriate locking control is required. Once the lock is locked, it means there will be a lock failure. If the lock fails, you need to choose to retry or give up.If you try again, it will cause performance degradation. If you give up, it will affect the user experience. At the same time, the complexity of the code has also increased a lot. This is a really hard choice, how do we solve this problem? - Redis-Cell
The savior is here!
Redis-Cell
Redis 4.0 provides a current-limiting Redis module calledredis-cell. This module also uses the funnel algorithm and provides atomic current limiting instructions.
This module has only one instruction cl.throttle, and its parameters and return values are slightly complicated. Next, let us take a look at how to use this instruction.
> cl.throttle key:xxx 15 30 60 1
- 15
: 15 capacity This is the funnel capacity - 30 60
: 30 operations / 60 seconds This is the water leakage rate - 1
: need 1 quota (optional parameter, default value is also 1)
> cl.throttle laoqian:reply 15 30 60 1) (integer) 0 # 0 表示允许,1表示拒绝 2) (integer) 15 # 漏斗容量capacity 3) (integer) 14 # 漏斗剩余空间left_quota 4) (integer) -1 # 如果拒绝了,需要多长时间后再试(漏斗有空间了,单位秒) 5) (integer) 2 # 多长时间后,漏斗完全空出来(left_quota==capacity,单位秒)When executing the current limiting instruction, if it is rejected, it needs to be discarded Or try again.
cl.throttle The instruction is very thoughtful, and even the retry time is calculated for you. Just take the fourth value of the returned result array and perform sleep. If you don’t want to block Threads can also be retried with asynchronous scheduled tasks.
Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of An article to talk about the current limiting strategy in Redis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Understanding NoSQL: Key Features of RedisApr 13, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Understanding NoSQL: Key Features of RedisApr 13, 2025 am 12:17 AMKey features of Redis include speed, flexibility and rich data structure support. 1) Speed: Redis is an in-memory database, and read and write operations are almost instantaneous, suitable for cache and session management. 2) Flexibility: Supports multiple data structures, such as strings, lists, collections, etc., which are suitable for complex data processing. 3) Data structure support: provides strings, lists, collections, hash tables, etc., which are suitable for different business needs.
 Redis: Identifying Its Primary FunctionApr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Redis: Identifying Its Primary FunctionApr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AMThe core function of Redis is a high-performance in-memory data storage and processing system. 1) High-speed data access: Redis stores data in memory and provides microsecond-level read and write speed. 2) Rich data structure: supports strings, lists, collections, etc., and adapts to a variety of application scenarios. 3) Persistence: Persist data to disk through RDB and AOF. 4) Publish subscription: Can be used in message queues or real-time communication systems.
 Redis: A Guide to Popular Data StructuresApr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Redis: A Guide to Popular Data StructuresApr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AMRedis supports a variety of data structures, including: 1. String, suitable for storing single-value data; 2. List, suitable for queues and stacks; 3. Set, used for storing non-duplicate data; 4. Ordered Set, suitable for ranking lists and priority queues; 5. Hash table, suitable for storing object or structured data.
 How to implement redis counterApr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counterApr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PMRedis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to use the redis command lineApr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command lineApr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PMUse the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to build the redis cluster modeApr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster modeApr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PMRedis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to read redis queueApr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queueApr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PMTo read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to use redis cluster zsetApr 10, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
How to use redis cluster zsetApr 10, 2025 pm 10:09 PMUse of zset in Redis cluster: zset is an ordered collection that associates elements with scores. Sharding strategy: a. Hash sharding: Distribute the hash value according to the zset key. b. Range sharding: divide into ranges according to element scores, and assign each range to different nodes. Read and write operations: a. Read operations: If the zset key belongs to the shard of the current node, it will be processed locally; otherwise, it will be routed to the corresponding shard. b. Write operation: Always routed to shards holding the zset key.


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software

VSCode Windows 64-bit Download
A free and powerful IDE editor launched by Microsoft

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

ZendStudio 13.5.1 Mac
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools






