Now that the database series has been updated, I think everyone has a general understanding of all the concepts. When I was reading the comments this week, I found a netizen's question that I found very interesting: How to design an index? How do you design indexes? How to design more efficiently?

Preface
We know that the index is a tree-like Tree structure based on a linked list, which can quickly retrieve data. Currently, almost all RDBMS databases implement it. Index features, such as MySQL's B Tree index, MongoDB's BTree index, etc.
In the process of business development, whether the index design is efficient or not determines the execution efficiency of the SQL corresponding to the interface. An efficient index can reduce the response time of the interface and also reduce the cost. Our realistic goal is: index Design -> Reduce interface response time -> Reduce server configuration -> Reduce cost, which must ultimately be implemented in cost, because the boss is most concerned about cost.
Today I will talk to you about indexes in MySQL and how to design indexes. Only by using indexes can we improve the RT of the lower interface and improve user health.
Index in MySQL
The InnoDB engine in MySQL uses the B Tree structure to store the index, which can minimize the number of disk IOs during data query. At the same time, the height of the tree directly affects the performance of the query. Generally, the height of the tree is maintained at 3 to 4 layers.
B Tree consists of three parts: root, branch and Leaf. The root and branch do not store data, only pointer addresses. All data is stored in Leaf Node, and a two-way linked list is used between Leaf Nodes. Link, the structure is as follows:
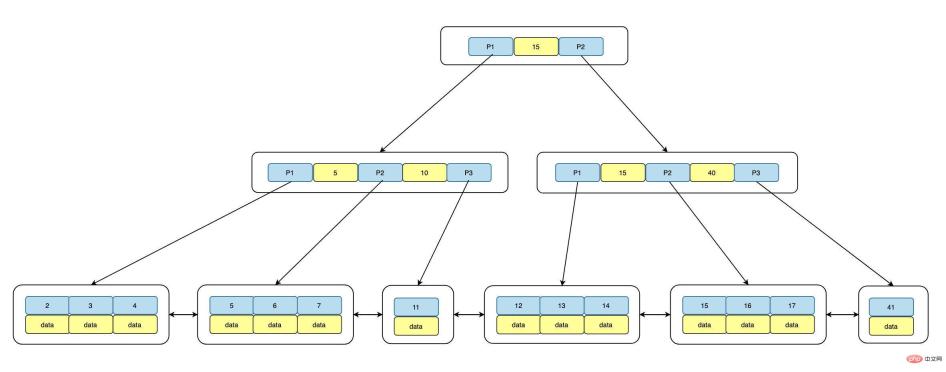
As you can see from the above, each Leaf Node is composed of three parts, namely the predecessor pointer p_prev, data data and successor pointer p_next, while data The data is in order. The default is ascending ASC. The key values distributed on the right side of the B tree are always greater than the left ones. At the same time, the distance from the root to each Leaf is equal, that is, the IO required to access any Leaf Node is the same. , that is, the height of the index tree is Level 1 IO operation.
We can think of the index in MySQL as a small table, occupying disk space. The process of creating an index is actually the process of sorting according to the index columns. Sort first in sort_buffer_size. If the amount of data to be sorted is large, the capacity of sort_buffer_size If not, you need to sort through temporary files. The most important thing is that sorting operations (distinct, group by, order by) can be avoided through indexing.
Clustered Index
The table in MySQL is IOT (Index Organization Table, index organization table). The data is stored in the order of the primary key id (logically continuous, physically discontinuous), and the primary key id is a clustered index that stores the entire row of data. If there is no explicit primary key specified, MySQL will combine all columns to construct a row_id as the primary key, such as the table users (id, user_id, user_name, phone, primary key(id)), id is a clustered index, which stores the entire row of data id, user_id, user_name, phone.
Auxiliary index
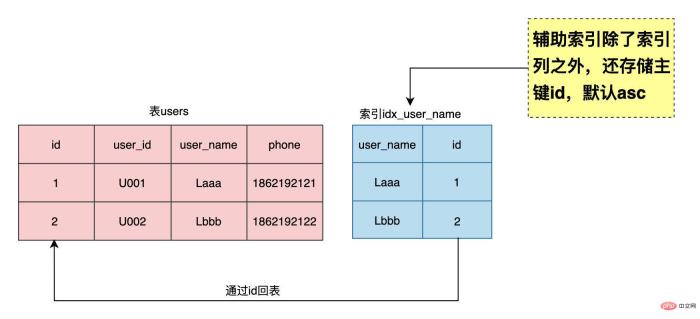
Auxiliary index is also called a secondary index. In addition to storing the index column, the index also stores the primary key id. For the index of user_name In terms of idx_user_name(user_name), it is actually equivalent to idx_user_name(user_name, id). MySQL will automatically add the primary key id at the end of the auxiliary index. Anyone familiar with Oracle database knows that in addition to the index column, the index also stores row_id (representing data The physical location consists of four parts: object number, data file number, data block number, data line number). We can also display the primary key id when creating an auxiliary index.
-- 创建user_name列上的索引 mysql> create index idx_user_name on users(user_name); -- 显示添加主键id创建索引 mysql> create index idx_user_name_id on users(user_name,id); -- 对比两个索引的统计数据 mysql> select a.space as tbl_spaceid, a.table_id, a.name as table_name, row_format, space_type, b.index_id , b.name as index_name, n_fields, page_no, b.type as index_type from information_schema.INNODB_TABLES a left join information_schema.INNODB_INDEXES b on a.table_id =b.table_id where a.name = 'test/users'; +-------------+----------+------------+------------+------------+----------+------------------+----------+------ | tbl_spaceid | table_id | table_name | row_format | space_type | index_id | index_name | n_fields | page_no | index_type | +-------------+----------+------------+------------+------------+----------+------------------+----------+------ | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 1254 | PRIMARY | 9 | 4 | 3 | | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 4003 | idx_user_name | 2 | 5 | 0 | | 518 | 1586 | test/users | Dynamic | Single | 4004 | idx_user_name_id | 2 | 45 | 0 | mysql> select index_name, last_update, stat_name, stat_value, stat_description from mysql.innodb_index_stats where index_name in ('idx_user_name','idx_user_name_id'); +------------------+---------------------+--------------+------------+-----------------------------------+ | index_name | last_update | stat_name | stat_value | stat_description | +------------------+---------------------+--------------+------------+-----------------------------------+ | idx_user_name | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | n_leaf_pages | 1358 | Number of leaf pages in the index | | idx_user_name | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | size | 1572 | Number of pages in the index | | idx_user_name_id | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | n_leaf_pages | 1358 | Number of leaf pages in the index | | idx_user_name_id | 2021-01-02 17:14:48 | size | 1572 | Number of pages in the index |
Compare the results of the two indexes. n_fields represents the number of columns in the index, n_leaf_pages represents the number of leaf pages in the index, and size represents the total number of pages in the index. You can see this through data comparison. The auxiliary index does contain the primary key id, which also shows that the two indexes are completely consistent.
| Index_name | n_fields | n_leaf_pages | size |
|---|---|---|---|
| idx_user_name | 2 | 1358 | 1572 |
| idx_user_name_id | 2 | 1358 | 1572 |
索引回表
上面证明了辅助索引包含主键id,如果通过辅助索引列去过滤数据有可能需要回表,举个例子:业务需要通过用户名user_name去查询用户表users的信息,业务接口对应的SQL:
select user_id, user_name, phone from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
我们知道,对于索引idx_user_name而言,其实就是一个小表idx_user_name(user_name, id),如果只查询索引中的列,只需要扫描索引就能获取到所需数据,是不需要回表的,如下SQL语句:
SQL 1: select id, user_name from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
SQL 2: select id from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
mysql> explain select id, name from users where name = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_user_name | idx_user_name | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index | mysql> explain select id from users where name = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------------+---------+-------+------+------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_user_name | idx_user_name | 82 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using index |
SQL 1和SQL 2的执行计划中的Extra=Using index 表示使用覆盖索引扫描,不需要回表,再来看上面的业务SQL:
select user_id, user_name, phone from users where user_name = 'Laaa';
可以看到select后面的user_id,phone列不在索引idx_user_name中,就需要通过主键id进行回表查找,MySQL内部分如下两个阶段处理:
Section 1: select **id** from users where user_name = 'Laaa' //id = 100101
Section 2: select user_id, user_name, phone from users where id = 100101;
将Section 2的操作称为回表,即通过辅助索引中的主键id去原表中查找数据。
索引高度
MySQL的索引时B+tree结构,即使表里有上亿条数据,索引的高度都不会很高,通常维持在3-4层左右,我来计算下索引idx_name的高度,从上面知道索引信息:index_id = 4003, page_no = 5,它的偏移量offset就是page_no x innodo_page_size + 64 = 81984,通过hexdump进行查看
$hexdump -s 81984 -n 10 /usr/local/var/mysql/test/users.ibd 0014040 00 02 00 00 00 00 00 00 0f a3 001404a
其中索引的PAGE_LEVEL为00,即idx_user_name索引高度为1,0f a3 代表索引编号,转换为十进制是4003,正是index_id。
数据扫描方式
全表扫描
从左到右依次扫描整个B+Tree获取数据,扫描整个表数据,IO开销大,速度慢,锁等严重,影响MySQL的并发。
对于OLAP的业务场景,需要扫描返回大量数据,这时候全表扫描的顺序IO效率更高。
索引扫描
通常来讲索引比表小,扫描的数据量小,消耗的IO少,执行速度块,几乎没有锁等,能够提高MySQL的并发。
对于OLTP系统,希望所有的SQL都能命中合适的索引总是美好的。
主要区别就是扫描数据量大小以及IO的操作,全表扫描是顺序IO,索引扫描是随机IO,MySQL对此做了优化,增加了change buffer特性来提高IO性能。
索引优化案例
分页查询优化
业务要根据时间范围查询交易记录,接口原始的SQL如下:
select * from trade_info where status = 0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59' order by id desc limit 102120, 20;
表trade_info上有索引idx_status_create_time(status,create_time),通过上面分析知道,等价于索引**(status,create_time,id)**,对于典型的分页limit m, n来说,越往后翻页越慢,也就是m越大会越慢,因为要定位m位置需要扫描的数据越来越多,导致IO开销比较大,这里可以利用辅助索引的覆盖扫描来进行优化,先获取id,这一步就是索引覆盖扫描,不需要回表,然后通过id跟原表trade_info进行关联,改写后的SQL如下:
select * from trade_info a , (select id from trade_info where status = 0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59' order by id desc limit 102120, 20) as b //这一步走的是索引覆盖扫描,不需要回表 where a.id = b.id;
很多同学只知道这样写效率高,但是未必知道为什么要这样改写,理解索引特性对编写高质量的SQL尤为重要。
分而治之总是不错的
营销系统有一批过期的优惠卷要失效,核心SQL如下:
-- 需要更新的数据量500w update coupons set status = 1 where status =0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59';
在Oracle里更新500w数据是很快,因为可以利用多个cpu core去执行,但是MySQL就需要注意了,一个SQL只能使用一个cpu core去处理,如果SQL很复杂或执行很慢,就会阻塞后面的SQL请求,造成活动连接数暴增,MySQL CPU 100%,相应的接口Timeout,同时对于主从复制架构,而且做了业务读写分离,更新500w数据需要5分钟,Master上执行了5分钟,binlog传到了slave也需要执行5分钟,那就是Slave延迟5分钟,在这期间会造成业务脏数据,比如重复下单等。
优化思路:先获取where条件中的最小id和最大id,然后分批次去更新,每个批次1000条,这样既能快速完成更新,又能保证主从复制不会出现延迟。
优化如下:
- 先获取要更新的数据范围内的最小id和最大id(表没有物理delete,所以id是连续的)
mysql> explain select min(id) min_id, max(id) max_id from coupons where status =0 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+--- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+------------------------+------------------------+---------+--- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time | idx_status_create_time | 6 | NULL | 180300 | 100.00 | Using where; Using index |
Extra=Using where; Using index使用了索引idx_status_create_time,同时需要的数据都在索引中能找到,所以不需要回表查询数据。
- 以每次1000条commit一次进行循环update,主要代码如下:
current_id = min_id; for current_id < max_id do update coupons set status = 1 where id >=current_id and id <= current_id + 1000; //通过主键id更新1000条很快 commit; current_id += 1000; done
这两个案例告诉我们,要充分利用辅助索引包含主键id的特性,先通过索引获取主键id走覆盖索引扫描,不需要回表,然后再通过id去关联操作是高效的,同时根据MySQL的特性使用分而治之的思想既能高效完成操作,又能避免主从复制延迟产生的业务数据混乱。
MySQL索引设计
熟悉了索引的特性之后,就可以在业务开发过程中设计高质量的索引,降低接口的响应时间。
前缀索引
对于使用REDUNDANT或者COMPACT格式的InnoDB表,索引键前缀长度限制为767字节。如果TEXT或VARCHAR列的列前缀索引超过191个字符,则可能会达到此限制,假定为utf8mb4字符集,每个字符最多4个字节。
可以通过设置参数innodb_large_prefix来开启或禁用索引前缀长度的限制,即是设置为OFF,索引虽然可以创建成功,也会有一个警告,主要是因为index size会很大,效率大量的IO的操作,即使MySQL优化器命中了该索引,效率也不会很高。
-- 设置innodb_large_prefix=OFF禁用索引前缀限制,虽然可以创建成功,但是有警告。 mysql> create index idx_nickname on users(nickname); // `nickname` varchar(255) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 1 mysql> show warnings; +---------+------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Level | Code | Message | +---------+------+---------------------------------------------------------+ | Warning | 1071 | Specified key was too long; max key length is 767 bytes |
业务发展初期,为了快速实现功能,对一些数据表字段的长度定义都比较宽松,比如用户表users的昵称nickname定义为varchar(128),而且有业务接口需要通过nickname查询,系统运行了一段时间之后,查询users表最大的nickname长度为30,这个时候就可以创建前缀索引来减小索引的长度提升性能。
-- `nickname` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL定义的执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where nickname = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+-------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------------+---------+-------+------+-------- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_nickname | idx_nickname | 515 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
key_len=515,由于表和列都是utf8mb4字符集,每个字符占4个字节,变长数据类型+2Bytes,允许NULL额外+1Bytes,即128 x 4 + 2 + 1 = 515Bytes。创建前缀索引,前缀长度也可以不是当前表的数据列最大值,应该是区分度最高的那部分长度,一般能达到90%以上即可,例如email字段存储都是类似这样的值xxxx@yyy.com,前缀索引的最大长度可以是xxxx这部分的最大长度即可。
-- 创建前缀索引,前缀长度为30 mysql> create index idx_nickname_part on users(nickname(30)); -- 查看执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where nickname = 'Laaa'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+--------------------------------+-------------------+---------+- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+--------------------------------+-------------------+---------+- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | ref | idx_nickname_part,idx_nickname | idx_nickname_part | 123 | const | 1 | 100.00 | Using where |
可以看到优化器选择了前缀索引,索引长度为123,即30 x 4 + 2 + 1 = 123 Bytes,大小不到原来的四分之。
前缀索引虽然可以减小索引的大小,但是不能消除排序。
mysql> explain select gender,count(*) from users where nickname like 'User100%' group by nickname limit 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+--------------------------------+--------------+---------+----- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+--------------------------------+--------------+---------+----- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_nickname_part,idx_nickname | idx_nickname | 515 | NULL | 899 | 100.00 | Using index condition | --可以看到Extra= Using index condition表示使用了索引,但是需要回表查询数据,没有发生排序操作。 mysql> explain select gender,count(*) from users where nickname like 'User100%' group by nickname limit 10; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+---------+------+------ | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_nickname_part | idx_nickname_part | 123 | NULL | 899 | 100.00 | Using where; Using temporary | --可以看到Extra= Using where; Using temporaryn表示在使用了索引的情况下,需要回表去查询所需的数据,同时发生了排序操作。
复合索引
在单列索引不能很好的过滤数据的时候,可以结合where条件中其他字段来创建复合索引,更好的去过滤数据,减少IO的扫描次数,举个例子:业务需要按照时间段来查询交易记录,有如下的SQL:
select * from trade_info where status = 1 and create_time >= '2020-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2020-10-07 23:59:59';
开发同学根据以往复合索引的设计的经验:唯一值多选择性好的列作为复合索引的前导列,所以创建复合索idx_create_time_status是高效的,因为create_time是一秒一个值,唯一值很多,选择性很好,而status只有离散的6个值,所以认为这样创建是没问题的,但是这个经验只适合于等值条件过滤,不适合有范围条件过滤的情况,例如idx_user_id_status(user_id,status)这个是没问题的,但是对于包含有create_time范围的复合索引来说,就不适应了,我们来看下这两种不同索引顺序的差异,即idx_status_create_time和idx_create_time_status。
-- 分别创建两种不同的复合索引 mysql> create index idx_status_create_time on trade_info(status, create_time); mysql> create index idx_create_time_status on trade_info(create_time,status); -- 查看SQL的执行计划 mysql> explain select * from users where status = 1 and create_time >='2021-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2021-10-07 23:59:59'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------+--------------- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+-----------------------------------------------+--------------- | 1 | SIMPLE | trade_info | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time,idx_create_time_status | idx_status_create_time | 6 | NULL | 98518 | 100.00 | Using index condition |
从执行计划可以看到,两种不同顺序的复合索引都存在的情况,MySQL优化器选择的是idx_status_create_time索引,那为什么不选择idx_create_time_status,我们通过optimizer_trace来跟踪优化器的选择。
-- 开启optimizer_trace跟踪 mysql> set session optimizer_trace="enabled=on",end_markers_in_json=on; -- 执行SQL语句 mysql> select * from trade_info where status = 1 and create_time >='2021-10-01 00:00:00' and create_time <= '2021-10-07 23:59:59'; -- 查看跟踪结果 mysql>SELECT trace FROM information_schema.OPTIMIZER_TRACE\G;
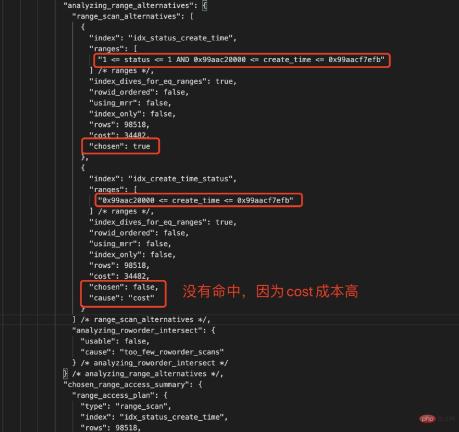
对比下两个索引的统计数据,如下所示:
| 复合索引 | Type | Rows | 参与过滤索引列 | Chosen | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| idx_status_create_time | Index Range Scan | 98518 | status AND create_time | True | Cost低 |
| idx_create_time_status | Index Range Scan | 98518 | create_time | False | Cost高 |
MySQL优化器是基于Cost的,COST主要包括IO_COST和CPU_COST,MySQL的CBO(Cost-Based Optimizer基于成本的优化器)总是选择Cost最小的作为最终的执行计划去执行,从上面的分析,CBO选择的是复合索引idx_status_create_time,因为该索引中的status和create_time都能参与了数据过滤,成本较低;而idx_create_time_status只有create_time参数数据过滤,status被忽略了,其实CBO将其简化为单列索引idx_create_time,选择性没有复合索引idx_status_create_time好。
复合索引设计原则
将范围查询的列放在复合索引的最后面,例如idx_status_create_time。
列过滤的频繁越高,选择性越好,应该作为复合索引的前导列,适用于等值查找,例如idx_user_id_status。
这两个原则不是矛盾的,而是相辅相成的。
跳跃索引
一般情况下,如果表users有复合索引idx_status_create_time,我们都知道,单独用create_time去查询,MySQL优化器是不走索引,所以还需要再创建一个单列索引idx_create_time。用过Oracle的同学都知道,是可以走索引跳跃扫描(Index Skip Scan),在MySQL 8.0也实现Oracle类似的索引跳跃扫描,在优化器选项也可以看到skip_scan=on。
| optimizer_switch |use_invisible_indexes=off,skip_scan=on,hash_join=on |
适合复合索引前导列唯一值少,后导列唯一值多的情况,如果前导列唯一值变多了,则MySQL CBO不会选择索引跳跃扫描,取决于索引列的数据分表情况。
mysql> explain select id, user_id,status, phone from users where create_time >='2021-01-02 23:01:00' and create_time <= '2021-01-03 23:01:00'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+---- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+---- | 1 | SIMPLE | users | NULL | range | idx_status_create_time | idx_status_create_time | NULL | NULL | 15636 | 11.11 | Using where; Using index for skip scan|
也可以通过optimizer_switch='skip_scan=off’来关闭索引跳跃扫描特性。
总结
本位为大家介绍了MySQL中的索引,包括聚集索引和辅助索引,辅助索引包含了主键id用于回表操作,同时利用覆盖索引扫描可以更好的优化SQL。
同时也介绍了如何更好做MySQL索引设计,包括前缀索引,复合索引的顺序问题以及MySQL 8.0推出的索引跳跃扫描,我们都知道,索引可以加快数据的检索,减少IO开销,会占用磁盘空间,是一种用空间换时间的优化手段,同时更新操作会导致索引频繁的合并分裂,影响索引性能,在实际的业务开发中,如何根据业务场景去设计合适的索引是非常重要的,今天就聊这么多,希望对大家有所帮助。
相关推荐:《mysql教程》
The above is the detailed content of How can MySQL make indexing more efficient?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 What Are the Limitations of Using Views in MySQL?May 14, 2025 am 12:10 AM
What Are the Limitations of Using Views in MySQL?May 14, 2025 am 12:10 AMMySQLviewshavelimitations:1)Theydon'tsupportallSQLoperations,restrictingdatamanipulationthroughviewswithjoinsorsubqueries.2)Theycanimpactperformance,especiallywithcomplexqueriesorlargedatasets.3)Viewsdon'tstoredata,potentiallyleadingtooutdatedinforma
 Securing Your MySQL Database: Adding Users and Granting PrivilegesMay 14, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Securing Your MySQL Database: Adding Users and Granting PrivilegesMay 14, 2025 am 12:09 AMProperusermanagementinMySQLiscrucialforenhancingsecurityandensuringefficientdatabaseoperation.1)UseCREATEUSERtoaddusers,specifyingconnectionsourcewith@'localhost'or@'%'.2)GrantspecificprivilegeswithGRANT,usingleastprivilegeprincipletominimizerisks.3)
 What Factors Influence the Number of Triggers I Can Use in MySQL?May 14, 2025 am 12:08 AM
What Factors Influence the Number of Triggers I Can Use in MySQL?May 14, 2025 am 12:08 AMMySQLdoesn'timposeahardlimitontriggers,butpracticalfactorsdeterminetheireffectiveuse:1)Serverconfigurationimpactstriggermanagement;2)Complextriggersincreasesystemload;3)Largertablesslowtriggerperformance;4)Highconcurrencycancausetriggercontention;5)M
 MySQL: Is it safe to store BLOB?May 14, 2025 am 12:07 AM
MySQL: Is it safe to store BLOB?May 14, 2025 am 12:07 AMYes,it'ssafetostoreBLOBdatainMySQL,butconsiderthesefactors:1)StorageSpace:BLOBscanconsumesignificantspace,potentiallyincreasingcostsandslowingperformance.2)Performance:LargerrowsizesduetoBLOBsmayslowdownqueries.3)BackupandRecovery:Theseprocessescanbe
 MySQL: Adding a user through a PHP web interfaceMay 14, 2025 am 12:04 AM
MySQL: Adding a user through a PHP web interfaceMay 14, 2025 am 12:04 AMAdding MySQL users through the PHP web interface can use MySQLi extensions. The steps are as follows: 1. Connect to the MySQL database and use the MySQLi extension. 2. Create a user, use the CREATEUSER statement, and use the PASSWORD() function to encrypt the password. 3. Prevent SQL injection and use the mysqli_real_escape_string() function to process user input. 4. Assign permissions to new users and use the GRANT statement.
 MySQL: BLOB and other no-sql storage, what are the differences?May 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
MySQL: BLOB and other no-sql storage, what are the differences?May 13, 2025 am 12:14 AMMySQL'sBLOBissuitableforstoringbinarydatawithinarelationaldatabase,whileNoSQLoptionslikeMongoDB,Redis,andCassandraofferflexible,scalablesolutionsforunstructureddata.BLOBissimplerbutcanslowdownperformancewithlargedata;NoSQLprovidesbetterscalabilityand
 MySQL Add User: Syntax, Options, and Security Best PracticesMay 13, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL Add User: Syntax, Options, and Security Best PracticesMay 13, 2025 am 12:12 AMToaddauserinMySQL,use:CREATEUSER'username'@'host'IDENTIFIEDBY'password';Here'showtodoitsecurely:1)Choosethehostcarefullytocontrolaccess.2)SetresourcelimitswithoptionslikeMAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR.3)Usestrong,uniquepasswords.4)EnforceSSL/TLSconnectionswith
 MySQL: How to avoid String Data Types common mistakes?May 13, 2025 am 12:09 AM
MySQL: How to avoid String Data Types common mistakes?May 13, 2025 am 12:09 AMToavoidcommonmistakeswithstringdatatypesinMySQL,understandstringtypenuances,choosetherighttype,andmanageencodingandcollationsettingseffectively.1)UseCHARforfixed-lengthstrings,VARCHARforvariable-length,andTEXT/BLOBforlargerdata.2)Setcorrectcharacters


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

SublimeText3 Linux new version
SublimeText3 Linux latest version

SAP NetWeaver Server Adapter for Eclipse
Integrate Eclipse with SAP NetWeaver application server.

MinGW - Minimalist GNU for Windows
This project is in the process of being migrated to osdn.net/projects/mingw, you can continue to follow us there. MinGW: A native Windows port of the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC), freely distributable import libraries and header files for building native Windows applications; includes extensions to the MSVC runtime to support C99 functionality. All MinGW software can run on 64-bit Windows platforms.

DVWA
Damn Vulnerable Web App (DVWA) is a PHP/MySQL web application that is very vulnerable. Its main goals are to be an aid for security professionals to test their skills and tools in a legal environment, to help web developers better understand the process of securing web applications, and to help teachers/students teach/learn in a classroom environment Web application security. The goal of DVWA is to practice some of the most common web vulnerabilities through a simple and straightforward interface, with varying degrees of difficulty. Please note that this software







