The four methods for eliminating abnormal data are: 1. "isolation forest"; 2. DBSCAN; 3. OneClassSVM; 4. "Local Outlier Factor", which calculates a numerical score to reflect a sample Abnormal degree.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, Dell G3 computer.
outlier detection outlier identification method
1. isolation forest Isolated forest
1.1 Test sample example
File test.pkl
1.2 Isolated Forest demo
Isolated Forest Principle
By randomly dividing features, a random forest is established, which can be divided after a smaller number of divisions. The point is considered an abnormal point.
# 参考https://blog.csdn.net/ye1215172385/article/details/79762317
# 官方例子https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/ensemble/plot_isolation_forest.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-ensemble-plot-isolation-forest-py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
# 构造训练样本
n_samples = 200 #样本总数
outliers_fraction = 0.25 #异常样本比例
n_inliers = int((1. - outliers_fraction) * n_samples)
n_outliers = int(outliers_fraction * n_samples)
X = 0.3 * rng.randn(n_inliers // 2, 2)
X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2] #正常样本
X_train = np.r_[X_train, np.random.uniform(low=-6, high=6, size=(n_outliers, 2))] #正常样本加上异常样本
# 构造模型并拟合
clf = IsolationForest(max_samples=n_samples, random_state=rng, contamination=outliers_fraction)
clf.fit(X_train)
# 计算得分并设置阈值
scores_pred = clf.decision_function(X_train)
threshold = np.percentile(scores_pred, 100 * outliers_fraction) #根据训练样本中异常样本比例,得到阈值,用于绘图
# plot the line, the samples, and the nearest vectors to the plane
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-7, 7, 50), np.linspace(-7, 7, 50))
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.title("IsolationForest")
# plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(Z.min(), threshold, 7), cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r) #绘制异常点区域,值从最小的到阈值的那部分
a = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[threshold], linewidths=2, colors='red') #绘制异常点区域和正常点区域的边界
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[threshold, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred') #绘制正常点区域,值从阈值到最大的那部分
b = plt.scatter(X_train[:-n_outliers, 0], X_train[:-n_outliers, 1], c='white',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
c = plt.scatter(X_train[-n_outliers:, 0], X_train[-n_outliers:, 1], c='black',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlim((-7, 7))
plt.ylim((-7, 7))
plt.legend([a.collections[0], b, c],
['learned decision function', 'true inliers', 'true outliers'],
loc="upper left")
plt.show()
1.3 If you modify it yourself, X_train can be changed to the data you need
There is no standardization here. You can standardize it first and then remove outliers based on standardization. from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
from scipy import stats
rng = np.random.RandomState(42)
X_train = X_train_demo.values
outliers_fraction = 0.1
n_samples = 500
# 构造模型并拟合
clf = IsolationForest(max_samples=n_samples, random_state=rng, contamination=outliers_fraction)
clf.fit(X_train)
# 计算得分并设置阈值
scores_pred = clf.decision_function(X_train)
threshold = stats.scoreatpercentile(scores_pred, 100 * outliers_fraction) #根据训练样本中异常样本比例,得到阈值,用于绘图
# plot the line, the samples, and the nearest vectors to the plane
range_max_min0 = (X_train[:,0].max()-X_train[:,0].min())*0.2
range_max_min1 = (X_train[:,1].max()-X_train[:,1].min())*0.2
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(X_train[:,0].min()-range_max_min0, X_train[:,0].max()+range_max_min0, 500),
np.linspace(X_train[:,1].min()-range_max_min1, X_train[:,1].max()+range_max_min1, 500))
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.title("IsolationForest")
# plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(Z.min(), threshold, 7), cmap=plt.cm.Blues_r) #绘制异常点区域,值从最小的到阈值的那部分
a = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[threshold], linewidths=2, colors='red') #绘制异常点区域和正常点区域的边界
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[threshold, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred') #绘制正常点区域,值从阈值到最大的那部分
is_in = clf.predict(X_train)>0
b = plt.scatter(X_train[is_in, 0], X_train[is_in, 1], c='white',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
c = plt.scatter(X_train[~is_in, 0], X_train[~is_in, 1], c='black',
s=20, edgecolor='k')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlim((X_train[:,0].min()-range_max_min0, X_train[:,0].max()+range_max_min0,))
plt.ylim((X_train[:,1].min()-range_max_min1, X_train[:,1].max()+range_max_min1,))
plt.legend([a.collections[0], b, c],
['learned decision function', 'inliers', 'outliers'],
loc="upper left")
plt.show()1.4 Core code
1.4.1 Sample sample
import numpy as np # 构造训练样本 n_samples = 200 #样本总数 outliers_fraction = 0.25 #异常样本比例 n_inliers = int((1. - outliers_fraction) * n_samples) n_outliers = int(outliers_fraction * n_samples) X = 0.3 * rng.randn(n_inliers // 2, 2) X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2] #正常样本 X_train = np.r_[X_train, np.random.uniform(low=-6, high=6, size=(n_outliers, 2))] #正常样本加上异常样本
1.4.2 Core code implementation
clf = IsolationForest(max_samples=0.8, contamination=0.25)
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
# fit the model
# max_samples 构造一棵树使用的样本数,输入大于1的整数则使用该数字作为构造的最大样本数目,
# 如果数字属于(0,1]则使用该比例的数字作为构造iforest
# outliers_fraction 多少比例的样本可以作为异常值
clf = IsolationForest(max_samples=0.8, contamination=0.25)
clf.fit(X_train)
# y_pred_train = clf.predict(X_train)
scores_pred = clf.decision_function(X_train)
threshold = np.percentile(scores_pred, 100 * outliers_fraction) #根据训练样本中异常样本比例,得到阈值,用于绘图
## 以下两种方法的筛选结果,完全相同
X_train_predict1 = X_train[clf.predict(X_train)==1]
X_train_predict2 = X_train[scores_pred>=threshold,:]
# 其中,1的表示非异常点,-1的表示为异常点
clf.predict(X_train)
array([ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, -1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1,
-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1])2. DBSCAN
DBSCAN(Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise) Principle
With each point as the center, set the neighborhood And how many points are needed in the neighborhood. If the sample point is greater than the specified requirement, the point is considered to be in the same category as the points in the neighborhood. If it is less than the specified value, if the point is located in the neighborhood of other points, it is a boundary point.
2.1 DBSCAN demo
# 参考https://blog.csdn.net/hb707934728/article/details/71515160
#
# 官方示例 https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/cluster/plot_dbscan.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-cluster-plot-dbscan-py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors
import sklearn.datasets as ds
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def expand(a, b):
d = (b - a) * 0.1
return a-d, b+d
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 1000
centers = [[1, 2], [-1, -1], [1, -1], [-1, 1]]
#scikit中的make_blobs方法常被用来生成聚类算法的测试数据,直观地说,make_blobs会根据用户指定的特征数量、
# 中心点数量、范围等来生成几类数据,这些数据可用于测试聚类算法的效果。
#函数原型:sklearn.datasets.make_blobs(n_samples=100, n_features=2,
# centers=3, cluster_std=1.0, center_box=(-10.0, 10.0), shuffle=True, random_state=None)[source]
#参数解析:
# n_samples是待生成的样本的总数。
#
# n_features是每个样本的特征数。
#
# centers表示类别数。
#
# cluster_std表示每个类别的方差,例如我们希望生成2类数据,其中一类比另一类具有更大的方差,可以将cluster_std设置为[1.0, 3.0]。
data, y = ds.make_blobs(N, n_features=2, centers=centers, cluster_std=[0.5, 0.25, 0.7, 0.5], random_state=0)
data = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data)
# 数据1的参数:(epsilon, min_sample)
params = ((0.2, 5), (0.2, 10), (0.2, 15), (0.3, 5), (0.3, 10), (0.3, 15))
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), facecolor='w')
plt.suptitle(u'DBSCAN clustering', fontsize=20)
for i in range(6):
eps, min_samples = params[i]
#参数含义:
#eps:半径,表示以给定点P为中心的圆形邻域的范围
#min_samples:以点P为中心的邻域内最少点的数量
#如果满足,以点P为中心,半径为EPS的邻域内点的个数不少于MinPts,则称点P为核心点
model = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
model.fit(data)
y_hat = model.labels_
core_indices = np.zeros_like(y_hat, dtype=bool) # 生成数据类型和数据shape和指定array一致的变量
core_indices[model.core_sample_indices_] = True # model.core_sample_indices_ border point位于y_hat中的下标
# 统计总共有积累,其中为-1的为未分类样本
y_unique = np.unique(y_hat)
n_clusters = y_unique.size - (1 if -1 in y_hat else 0)
print (y_unique, '聚类簇的个数为:', n_clusters)
plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1) # 对第几个图绘制,2行3列,绘制第i+1个图
# plt.cm.spectral https://blog.csdn.net/robin_Xu_shuai/article/details/79178857
clrs = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 0.8, y_unique.size)) #用于给画图灰色
for k, clr in zip(y_unique, clrs):
cur = (y_hat == k)
if k == -1:
# 用于绘制未分类样本
plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=20, c='k')
continue
# 绘制正常节点
plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=30, c=clr, edgecolors='k')
# 绘制边缘点
plt.scatter(data[cur & core_indices][:, 0], data[cur & core_indices][:, 1], s=60, c=clr, marker='o', edgecolors='k')
x1_min, x2_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
x1_max, x2_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
x1_min, x1_max = expand(x1_min, x1_max)
x2_min, x2_max = expand(x2_min, x2_max)
plt.xlim((x1_min, x1_max))
plt.ylim((x2_min, x2_max))
plt.grid(True)
plt.title(u'$epsilon$ = %.1f m = %d clustering num %d'%(eps, min_samples, n_clusters), fontsize=16)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.9)
plt.show()
[-1 0 1 2 3] 聚类簇的个数为: 4
[-1 0 1 2 3] 聚类簇的个数为: 4
[-1 0 1 2 3 4] 聚类簇的个数为: 5
[-1 0] 聚类簇的个数为: 1
[-1 0 1] 聚类簇的个数为: 2
[-1 0 1 2 3] 聚类簇的个数为: 4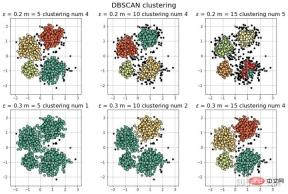
2.2 Using custom test examples
#
# 参考https://blog.csdn.net/hb707934728/article/details/71515160
#
# 官方示例 https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/cluster/plot_dbscan.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-cluster-plot-dbscan-py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors
import sklearn.datasets as ds
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
def expand(a, b):
d = (b - a) * 0.1
return a-d, b+d
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 1000
data = X_train_demo.values
# 数据1的参数:(epsilon, min_sample)
params = ((0.2, 5), (0.2, 10), (0.2, 15), (0.2, 20), (0.2, 25), (0.2, 30))
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), facecolor='w')
plt.suptitle(u'DBSCAN clustering', fontsize=20)
for i in range(6):
eps, min_samples = params[i]
#参数含义:
#eps:半径,表示以给定点P为中心的圆形邻域的范围
#min_samples:以点P为中心的邻域内最少点的数量
#如果满足,以点P为中心,半径为EPS的邻域内点的个数不少于MinPts,则称点P为核心点
model = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples)
model.fit(data)
y_hat = model.labels_
core_indices = np.zeros_like(y_hat, dtype=bool) # 生成数据类型和数据shape和指定array一致的变量
core_indices[model.core_sample_indices_] = True # model.core_sample_indices_ border point位于y_hat中的下标
# 统计总共有积累,其中为-1的为未分类样本
y_unique = np.unique(y_hat)
n_clusters = y_unique.size - (1 if -1 in y_hat else 0)
print (y_unique, '聚类簇的个数为:', n_clusters)
plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1) # 对第几个图绘制,2行3列,绘制第i+1个图
# plt.cm.spectral https://blog.csdn.net/robin_Xu_shuai/article/details/79178857
clrs = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 0.8, y_unique.size)) #用于给画图灰色
for k, clr in zip(y_unique, clrs):
cur = (y_hat == k)
if k == -1:
# 用于绘制未分类样本
plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=20, c='k')
continue
# 绘制正常节点
plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=30, c=clr, edgecolors='k')
# 绘制边缘点
plt.scatter(data[cur & core_indices][:, 0], data[cur & core_indices][:, 1], s=60, c=clr, marker='o', edgecolors='k')
x1_min, x2_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
x1_max, x2_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
x1_min, x1_max = expand(x1_min, x1_max)
x2_min, x2_max = expand(x2_min, x2_max)
plt.xlim((x1_min, x1_max))
plt.ylim((x2_min, x2_max))
plt.grid(True)
plt.title(u'$epsilon$ = %.1f m = %d clustering num %d'%(eps, min_samples, n_clusters), fontsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.9)
plt.show()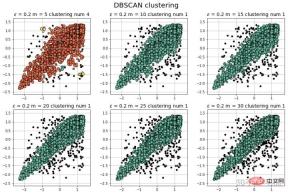
Note: It can be seen that at both ends of the test sample, DBSCAN can classify the samples at the "tip" better than the isolation forest.
2.3 Core code
model = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples) #Construct classifier
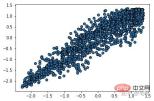
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN from sklearn import metrics data = X_train_demo.values eps, min_samples = 0.2, 10 # eps为领域的大小,min_samples为领域内最小点的个数 model = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples) # 构造分类器 model.fit(data) # 拟合 labels = model.labels_ # 获取类别标签,-1表示未分类 # 获取其中的core points core_indices = np.zeros_like(labels, dtype=bool) # 生成数据类型和数据shape和指定array一致的变量 core_indices[model.core_sample_indices_] = True # model.core_sample_indices_ border point位于labels中的下标 core_point = data[core_indices] # 获取非异常点 normal_point = data[labels>=0] # 绘制剔除了异常值后的图 plt.scatter(normal_point[:,0],normal_point[:,1],edgecolors='k') plt.show()
2.4 Construct filtering Function
This function is standardized first to facilitate analysis using fixed parameters
2.4.1 Filter function
def filter_data(data0, params):
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn import metrics
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(data0)
data = scaler.transform(data0)
eps, min_samples = params
# eps为领域的大小,min_samples为领域内最小点的个数
model = DBSCAN(eps=eps, min_samples=min_samples) # 构造分类器
model.fit(data) # 拟合
labels = model.labels_ # 获取类别标签,-1表示未分类
# 获取其中的core points
core_indices = np.zeros_like(labels, dtype=bool) # 生成数据类型和数据shape和指定array一致的变量
core_indices[model.core_sample_indices_] = True # model.core_sample_indices_ border point位于labels中的下标
core_point = data[core_indices]
# 获取非异常点
normal_point = data0[labels>=0]
return normal_point2.4.2 Measure classification results
(I’m too lazy to convert the markdown format, so I just took a screenshot::>_<::>

# 轮廓系数 metrics.silhouette_score(data, labels, metric='euclidean') [out]0.13250260550638607 # Calinski-Harabaz Index 系数 metrics.calinski_harabaz_score(data, labels,) [out]16.414158842632794
3. OneClassSVM
# reference:https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/svm/plot_oneclass.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-svm-plot-oneclass-py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.font_manager
from sklearn import svm
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-5, 5, 500), np.linspace(-5, 5, 500))
# Generate train data
X = 0.3 * np.random.randn(100, 2)
X_train = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# Generate some regular novel observations
X = 0.3 * np.random.randn(20, 2)
X_test = np.r_[X + 2, X - 2]
# Generate some abnormal novel observations
X_outliers = np.random.uniform(low=-4, high=4, size=(20, 2))
# fit the model
clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.1, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.1)
clf.fit(X_train)
y_pred_train = clf.predict(X_train)
y_pred_test = clf.predict(X_test)
y_pred_outliers = clf.predict(X_outliers)
n_error_train = y_pred_train[y_pred_train == -1].size
n_error_test = y_pred_test[y_pred_test == -1].size
n_error_outliers = y_pred_outliers[y_pred_outliers == 1].size
# plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the plane
Z = clf.decision_function(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.title("Novelty Detection")
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=np.linspace(Z.min(), 0, 7), cmap=plt.cm.PuBu)
a = plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0], linewidths=2, colors='darkred')
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0, Z.max()], colors='palevioletred')
s = 40
b1 = plt.scatter(X_train[:, 0], X_train[:, 1], c='white', s=s, edgecolors='k')
b2 = plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c='blueviolet', s=s,
edgecolors='k')
c = plt.scatter(X_outliers[:, 0], X_outliers[:, 1], c='gold', s=s,
edgecolors='k')
plt.axis('tight')
plt.xlim((-5, 5))
plt.ylim((-5, 5))
plt.legend([a.collections[0], b1, b2, c],
["learned frontier", "training observations",
"new regular observations", "new abnormal observations"],
loc="upper left",
prop=matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties(size=11))
plt.xlabel(
"error train: %d/200 ; errors novel regular: %d/40 ; "
"errors novel abnormal: %d/40"
% (n_error_train, n_error_test, n_error_outliers))
plt.show()
3.2 Core code
from sklearn import svm X_train = X_train_demo.values # 构造分类器 clf = svm.OneClassSVM(nu=0.2, kernel="rbf", gamma=0.2) clf.fit(X_train) # 预测,结果为-1或者1 labels = clf.predict(X_train) # 分类分数 score = clf.decision_function(X_train) # 获取置信度 # 获取正常点 X_train_normal = X_train[labels>0]
Before removing abnormal points
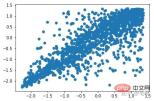
plt.scatter(X_train_normal[:,0],X_train_normal[:,1])
plt.show()

#
# 参考https://blog.csdn.net/hb707934728/article/details/71515160
#
# 官方示例 https://scikit-learn.org/stable/auto_examples/cluster/plot_dbscan.html#sphx-glr-auto-examples-cluster-plot-dbscan-py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.colors
from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor
def expand(a, b):
d = (b - a) * 0.1
return a-d, b+d
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 1000
data = X_train_demo.values
# 数据1的参数:(epsilon, min_sample)
params = ((0.01, 5), (0.05, 10), (0.1, 15), (0.15, 20), (0.2, 25), (0.25, 30))
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8), facecolor='w')
plt.suptitle(u'DBSCAN clustering', fontsize=20)
for i in range(6):
outliers_fraction, min_samples = params[i]
#参数含义:
#eps:半径,表示以给定点P为中心的圆形邻域的范围
#min_samples:以点P为中心的邻域内最少点的数量
#如果满足,以点P为中心,半径为EPS的邻域内点的个数不少于MinPts,则称点P为核心点
model = LocalOutlierFactor(n_neighbors=min_samples, contamination=outliers_fraction)
y_hat = model.fit_predict(X_train)
# 统计总共有积累,其中为-1的为未分类样本
y_unique = np.unique(y_hat)
# clrs = []
# for c in np.linspace(16711680, 255, y_unique.size):
# clrs.append('#%06x' % c)
plt.subplot(2, 3, i+1) # 对第几个图绘制,2行3列,绘制第i+1个图
# plt.cm.spectral https://blog.csdn.net/robin_Xu_shuai/article/details/79178857
clrs = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 0.8, y_unique.size)) #用于给画图灰色
for k, clr in zip(y_unique, clrs):
cur = (y_hat == k)
if k == -1:
# 用于绘制未分类样本
plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=20, c='k')
continue
# 绘制正常节点
plt.scatter(data[cur, 0], data[cur, 1], s=30, c=clr, edgecolors='k')
x1_max, x2_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
x1_min, x2_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
x1_min, x1_max = expand(x1_min, x1_max)
x2_min, x2_max = expand(x2_min, x2_max)
plt.xlim((x1_min, x1_max))
plt.ylim((x2_min, x2_max))
plt.grid(True)
plt.title(u'outliers_fraction = %.1f min_samples = %d'%(outliers_fraction, min_samples), fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.9)
plt.show()

from sklearn.neighbors import LocalOutlierFactor
X_train = X_train_demo.values
# 构造分类器
## 25个样本点为一组,异常值点比例为0.2
clf = LocalOutlierFactor(n_neighbors=25, contamination=0.2)
# 预测,结果为-1或者1
labels = clf.fit_predict(X_train)
# 获取正常点
X_train_normal = X_train[labels>0]
Before eliminating abnormal pointsplt.scatter(X_train[:,0],X_train[:,1])
plt.show()

plt.scatter(X_train_normal[:,0],X_train_normal[:,1])
plt.show()

FAQ column!
The above is the detailed content of What are the four methods for eliminating abnormal data?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

Safe Exam Browser
Safe Exam Browser is a secure browser environment for taking online exams securely. This software turns any computer into a secure workstation. It controls access to any utility and prevents students from using unauthorized resources.

EditPlus Chinese cracked version
Small size, syntax highlighting, does not support code prompt function

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

WebStorm Mac version
Useful JavaScript development tools





